Description
Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: www.cnbctv18.com
Context: The next delimitation of Lok Sabha constituencies in India is poised to bring about significant shifts in the country's political landscape.
Key Highlights
- Shift of Political Power: The delimitation process will result in a noticeable shift of political power from the southern states to the northern and eastern states. This shift was initially expected to be the central focus of the delimitation debate, with the southern states potentially losing seats.
- Delimitation was postponed until 2026 through a constitutional amendment in 2002, in the hope that population growth across the country would equalize. However, the population growth rates have not evened out, and northern states with higher growth rates, continue to grow faster.
- Gender Empowerment: The proposed reservation of one-third of seats in Parliament and Assemblies for women has introduced another dimension to the discussion. This change means that the next delimitation will involve not only a regional shift but also a shift from male to female representation across the entire country.
- There are concerns that the serious issues related to the diminishing influence of states that have stabilized their populations may be overshadowed by the nationwide consensus on women's empowerment.
Delimitation
About
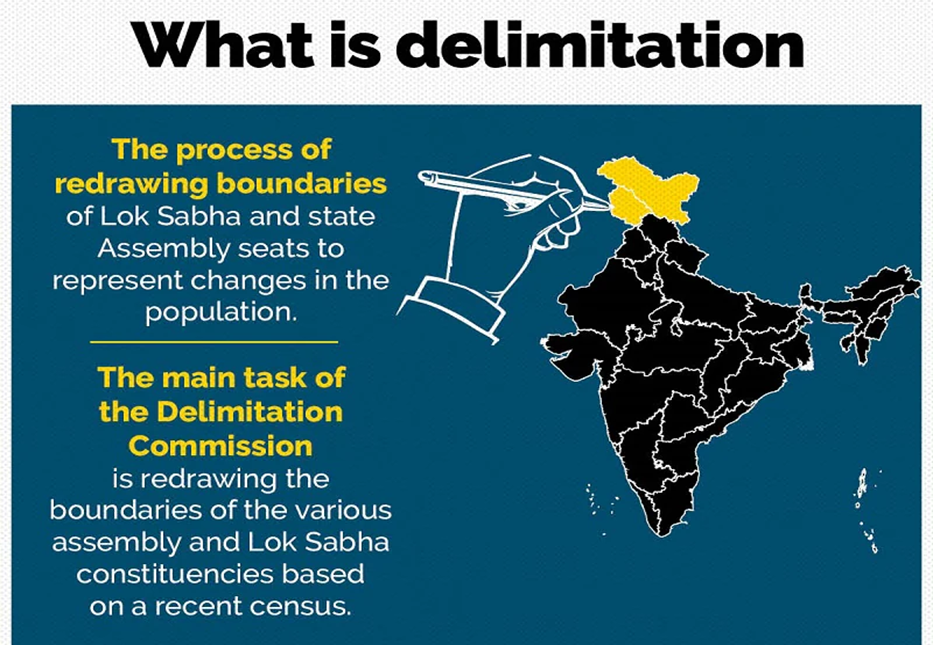
- Delimitation refers to the process of defining and adjusting the boundaries or territorial limits of electoral constituencies within a country. It is a critical aspect of the electoral system in many democracies and is carried out to ensure fair and equal representation of citizens in legislative bodies.
- It involves determining the number of seats allocated to different regions or states based on their population, with the aim of maintaining a balance and reflecting demographic changes.

Provision under the Indian Constitution
- The Constitution of India also contains provisions related to delimitation, particularly in Articles 81 (Lok Sabha) and 82 (Rajya Sabha). It mandates that delimitation must be conducted periodically to adjust the allocation of seats in accordance with population changes.
- The Delimitation Commission, also known as the Boundary Commission of India, is a significant body established under the provisions of the Delimitation Commission Act. Its primary responsibility is to redraw the boundaries of various assembly and Lok Sabha constituencies in India based on the most recent census data.
Role of the Delimitation Commission
- The primary task of the Delimitation Commission is to redefine the boundaries of electoral constituencies to ensure that each constituency has approximately the same number of voters. This process aims to achieve fair and equal representation in legislative bodies. It's important to note that the representation from each state remains unchanged during this exercise. However, the number of seats allocated for Scheduled Castes (SC) and Scheduled Tribes (ST) in a state may change in accordance with the census data.
History of Delimitation Commissions in India
- The first delimitation exercise post-independence took place in 1952 based on the 1951 census data. It resulted in the allocation of 494 Lok Sabha seats.
- In 1963, the delimitation exercise occurred after the reorganization of states in 1956. This time, only single-seat constituencies were created, based on the 1961 census data, resulting in 522 Lok Sabha seats and changes in assembly constituencies.
- The 1973 delimitation commission, chaired by Justice J. L. Kapur, increased the Lok Sabha seats from 522 to 543 (later increased to 543 with the inclusion of one more seat for the newly formed state of Sikkim). The total number of assembly seats across all states and Union Territories increased from 3,771 to 3,997.
- The most recent delimitation commission, established in 2002 after the 2001 census. It recommended no changes in Lok Sabha seats or their apportionment between the various states, resulting in 543 Lok Sabha seats and 4,123 assembly seats.
- Following the 84th amendment to the Indian Constitution in 2002, delimitation is scheduled to take place after 2026, based on the population data from the first census conducted after that year.
Key features of delimitation in India
- Periodic Review: Delimitation in India is conducted periodically to account for changes in population distribution. This means that after each decennial census, the boundaries of constituencies are reviewed and adjusted to ensure that they continue to reflect population changes accurately. This periodicity is crucial for maintaining equal representation and fairness in the electoral system.
- Independent Commission: Delimitation is carried out by an independent body known as the Delimitation Commission. This commission is typically composed of senior officials, including the Chief Election Commissioner and other Election Commissioners. Its independence is vital to ensure that the process is free from political interference and is conducted impartially.
- Equal Representation: The primary objective of delimitation is to achieve equal representation. This means that the Delimitation Commission aims to create constituencies with roughly the same number of voters. By doing so, it ensures that each citizen's vote carries equal weight in the electoral process, promoting the democratic principle of "one person, one vote."
- Data-Centric: Delimitation relies heavily on data, particularly census data and demographic statistics. These data sources provide the necessary information to determine the population of each constituency accurately. The commission uses this data to decide how to redraw constituency boundaries to achieve equal representation.
- Constitutional Mandate: The delimitation process in India is not merely a statutory requirement but is also governed by constitutional provisions. Articles 81 and 82 of the Constitution specify the need for delimitation and its basis in census data. This constitutional mandate underscores the significance of delimitation in upholding the principles of democracy and ensuring fair representation in legislative bodies.
Significance of Delimitation
- Equal Representation: Delimitation ensures that each citizen's vote carries equal weight. By periodically redistributing constituencies based on population changes, it helps create a more equitable distribution of seats. This prevents over-representation or under-representation of specific regions or communities, ensuring that every citizen has a fair opportunity to elect their representatives.
- Fairness in Elections: Delimitation promotes fairness in elections by striving to make constituencies as uniform in population size as possible. This mitigates the risk of certain constituencies having disproportionate influence in the political process. Fair elections are essential for a vibrant and responsive democracy.
- Demographic Changes: India is a dynamic country with significant demographic changes over time. Delimitation adapts the electoral boundaries to accommodate these demographic shifts. Without delimitation, older constituency boundaries might not accurately reflect the current population distribution.
- Preventing Gerrymandering: Delimitation helps prevent gerrymandering, which is the manipulation of constituency boundaries for political advantage. By entrusting the process to an independent commission, the potential for partisan manipulation is reduced, contributing to a more transparent and fair electoral system.
- Enhanced Political Equity: Delimitation encourages political equity by ensuring that various communities and regions have proportional representation based on their population. This prevents underrepresented areas from having their voices drowned out by more populous regions.
- Adapting to Population Growth: India's population continues to grow, but not uniformly across states and regions. Delimitation allows for adjustments to accommodate population growth, ensuring that representation remains in line with demographic changes.
- Transparency and Accountability: Delimitation commissions are expected to work transparently, allowing for public input and scrutiny of their decisions. This transparency enhances accountability and public trust in the electoral process.
Challenges in Delimitation
- Population Growth: One of the primary challenges in delimitation is dealing with uneven population growth across regions. Rapid population growth in some areas and slower growth in others can result in disparities in the number of eligible voters per constituency. This can make it difficult to achieve the goal of equal representation, as some constituencies may become significantly larger than others.
- Political Manipulation: Delimitation is vulnerable to political manipulation, especially when the ruling party has the authority to influence the process. There is a risk that ruling parties may redraw constituency boundaries in a way that favours their electoral prospects, a practice known as gerrymandering. This undermines the fairness and impartiality of the delimitation process.
- Complexity: Delimitation is a complex and data-intensive process that requires meticulous handling of demographic data. The accuracy of the process depends on the quality of the data and the ability to process and interpret it correctly. Errors in data handling can lead to inaccuracies in constituency boundaries, potentially resulting in legal challenges and disputes.
- Socioeconomic Disparities: India is characterized by significant socioeconomic disparities among regions. Delimitation should ideally consider not only population but also socioeconomic factors to ensure that historically marginalized communities have a fair opportunity for representation. Balancing these factors can be challenging.
- Geographic Factors: Geographic features, such as natural boundaries, can complicate the delimitation process. Some regions may be geographically isolated or have unique geographic challenges that must be taken into account when drawing constituency boundaries.
- Public Perception: Public perception of the delimitation process is important for its legitimacy. If there are suspicions of bias, political interference, or unfairness in the process, it can erode public trust in the electoral system.
- Legal and Constitutional Constraints: Delimitation must adhere to legal and constitutional constraints, which can be complex and subject to interpretation. These constraints may limit the flexibility of the Delimitation Commission in making adjustments based on population changes.
.jpg)
Way Forward
- Transparency: Ensuring transparency in the delimitation process is vital for public trust and confidence in the electoral system. Involving independent bodies and allowing for public scrutiny, consultation, and feedback can help demystify the process and make it more accountable. Transparent delimitation can also act as a check against potential political manipulation.
- Technology: Leveraging technology for data analysis and mapmaking is an excellent way to enhance the accuracy of the delimitation process. Advanced Geographic Information Systems (GIS) technology can help in precisely defining boundaries and ensuring that constituencies reflect demographic changes accurately. This reduces errors and the potential for disputes.
- Political Neutrality: Maintaining political neutrality in delimitation is crucial to upholding the integrity of the process. Ensuring that the Delimitation Commission operates independently and without political interference is essential. It's also important for political parties to respect the independence of the commission and refrain from attempting to influence its decisions for partisan gain.
- Regular Updates: Conducting delimitation exercises at regular intervals, as mandated by the Constitution, is essential to keeping constituencies in sync with changing demographics. This prevents the accumulation of significant disparities over time and ensures that representation remains equitable and responsive to population shifts.
Conclusion
- The process of delimitation is an important feature of India's electoral system, which aims to ensure democratic values and fair representation. However, it also faces some difficulties, such as population changes, regional disputes, and political interference. Therefore, it is vital to enhance transparency, use technology, and maintain impartiality for a successful and efficient delimitation process in the future.
Must Read Articles:
DELIMITATION COMMISSION: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/delimitation-commission-6
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Consider the following statements:
Statement 1: Delimitation is the process of defining and adjusting the boundaries of electoral constituencies within a country.
Statement 2: Delimitation aims to ensure fair and equal representation of citizens in legislative bodies.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
A) Both Statement-1 and Statement-2 are correct, and Statement-2 is the correct explanation for Statement-1
B) Both Statement-1 and Statement-2 are correct, and Statement-2 is not the correct explanation for Statement-1
C) Statement-1 is correct, but Statement-2 is incorrect
D) Statement-1 is incorrect, but Statement-2 is correct
Answer: A
Explanation: Both Statement-1 and Statement-2 are correct, and Statement-2 is the correct explanation for Statement-1. Delimitation is the process of defining and adjusting electoral constituency boundaries to ensure fair and equal representation.
|
https://epaper.thehindu.com/ccidist-ws/th/th_delhi/issues/52554/OPS/G5QBPC0DQ.1.png?cropFromPage=true















