





Disclaimer: Copyright infringement is not intended.
Context:
Diadromous Fish
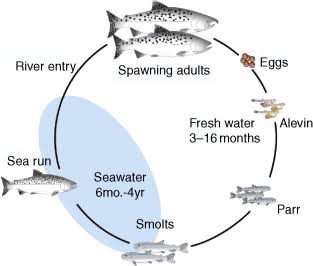
Differences among catadromous, anadromous, and diadromous fish:
|
Feature |
Diadromous Fish |
Anadromous Fish |
Catadromous Fish |
|
Definition |
Fish that migrate between freshwater and marine environments. |
Fish that live in the ocean and breed in freshwater. |
Fish that live in freshwater and breed in the ocean. |
|
Examples |
European eel, bull shark |
Salmon, striped bass, sea lamprey |
Europeaneel, American eel |
|
Migration Direction |
Both directions: freshwater to marine and marine to freshwater |
Marine to freshwater only |
Freshwater to marine only |
|
Purpose of Migration |
Feeding, breeding, and escaping harsh conditions |
Primarily for breeding |
Primarily for breeding |
|
Life Cycle Stages |
Utilize both freshwater and marine stages |
Marine juvenile stage, migrate to freshwater to spawn |
Freshwater juvenile stage, migrate to marine to spawn |
|
Adaptation |
Adapt to both saltwater and freshwater environments |
Adapt specifically for spawning in freshwater |
Adapt specifically for spawning in marine |
|
Habitat Usage |
Utilize different habitats throughout their life cycle |
Spend most of life in marine habitats, migrate to freshwater for spawning |
Spend most of life in freshwater habitats, migrate to marine for spawning |
Similarities:
Source:
|
PRACTICED QUESTION Match the Following: List I (Type of Fish):
List II (Characteristics): A. Fish that migrate between freshwater and marine environments. Options: A) 1-C, 2-A, 3-B B) 1-A, 2-B, 3-C C) 1-B, 2-C, 3-A D) 1-A, 2-C, 3-B Answer: C: 1-B, 2-C, 3-A Explanation:
|











© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved