





Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
What is the digital economy?
The digital economy refers to economic activity that uses electronic communication and digital technologies to provide goods and services. The main building blocks of the digital economy are
Essential Elements of Digital Economy
Digital Economy facilitates and executes the buying and selling of products and services through electronic transactions undertaken by means of the internet. Its essential elements are:
Hyperconnectivity, i.e. emerging interconnectivity of people, firms, systems, etc. as a result of the internet, mobile technology and Internet of Things (IoT).
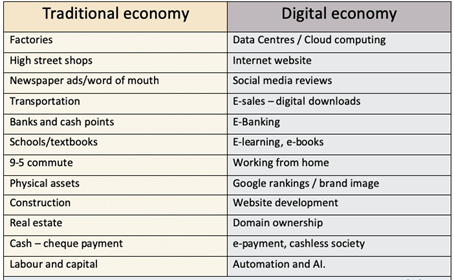
Examples of the digital economy
Airbnb – This enables tourists to book online. It has also made it possible for individual households to let our their house/room to tourists. Before the digital economy it was not practical.
E-commerce site: Amazon market place/Ebay.
Netflix – This enables consumers to purchase tv-series and films over the internet, without need for any physical good.
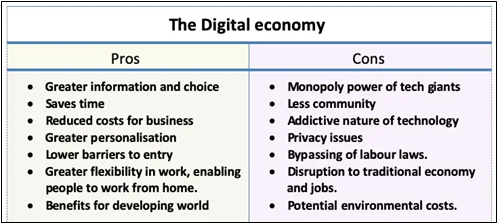
Advantages of the digital economy
Greater information
The internet has enabled consumers to have greater information and choice. For example, it makes it easier to compare prices between firms. It also brings information to a person’s fingertips.
Time saving
For the user, time is a determining factor when making purchases, managing their finances, traveling or even working.
Reduced costs
The digital economy considerably reduces the costs for the merchant and the maintenance of his business.
Increases flexibility
The flexibility that financial technology provides can be seen at all levels of exchange transactions - From the user and the numerous payment methods to the possibility of buying from anywhere in the world.
Provides more information and decision-making power
The power of decision for the user defines many things and the use of the digital economy is exactly that, more information for better decision making.
Process reinvention
The digital economy removes many of the barriers that previously defined the way certain processes are carried out. A clear example is work, which took a 180º turn with technological advances that allow, for example, working from home, making tele-working one of the most widely used alternatives today due to the multiple benefits it combines.
Lower barriers to entry
In some markets, aspects of the digital economy make it easier for new firms to enter. The digital economy has brought many new services which were inconceivable before, such as online home deliveries for grocery to dating apps.
Creates significant data which can give new insights
The mass production of data can help inform governments and charities about what is happening in the economy. For example, in tracking of COVID-19 spread, the use of an app on mobile phones may indicate where local hotspots emerge.
Contributes to Economic Growth:
The widespread digital economy has recorded tremendous growth and innovation as well as it can be broadly applied to other economic sectors.
Creates new jobs
Digital economy has given a boost to jobs too. In the last few years, the development of mobile apps has solely created millions of jobs worldwide.
Improves public services
A set of global access to broadband and a powerful information and communication technology services ecosystem provides a platform to improve service delivery in core sectors.
Rise in e-commerce
A recent growth in e-commerce transactions has been reported in the last few years. And all credit goes to the digitalization of commercial activities, due to which developing, buying, distributing, selling and tracking of products and services, has become much simpler, competitive, and profitable.
Digital delivery of goods and services
From aviation to banking, entertainment to education and insurance to hotel booking, one can easily get the goods and services of their need, online.
Transparency
In the digital economy, major commercial transactions take place online, which eliminates cash transactions, and ultimately increases transparency and reduces corruption.
Expands business opportunities
Digitalization enables small firms and businesses to actively participate in international buying and selling of goods and services.
Limitations of Digital Economy
Cybersecurity
An exponential increase in cyber threats has been reported in recent years due to increasing digitalization in the economy. Except if cybersecurity is countered successfully, it will not be easy to develop a safe and trusted environment, which is conducive to the growing business.
Disruptions in labour markets
Though it is assumed to create new job opportunities, there is also a risk related to the speed of labour market changes and destruction of basic jobs. As everything will be digitized and automated, processes that involve labour and manual work will be avoided and is replaced by technology-oriented work, which will result in loss of jobs and may also widen income inequality.
Strong infrastructure requirement
It requires strong infrastructure concerning internet, telecommunication and mobile industry. For the development of such industries, heavy investment is required, so as to link all the cities, towns and villages.
With the emergence of the digital economy, consumers can get easy and quick access to information, due to the digitization of the content. Moreover, sharing of information with their friends and acquaintances is now just a click away.
Monopoly power
Despite the potential for new start-ups, many aspects of the digital economy have become dominated by firms with monopoly power. For example, Amazon has cornered the market for online sales, meaning many firms have to go through the Amazon market place to reach consumers who go to Amazon out of habit. Similarly, Google and Facebook have all developed very strong brand loyalty and market share in their respective markets. This has made a few tech giants very profitable.
Addictive nature of technology
Whilst, in theory, the internet can save time, e.g. finding bus times is much easier with internet than paper copies, this time saved may be outweighed by the time we waste checking Facebook, twitter, internet searches. Also, the sheer volume of information can cause us to drown in information and lose sight of what we actually need. More choices do not necessarily lead to better outcomes.
Privacy issues
Harvesting and using data has become big business. Facebook collects a large range of data on its users and this has been bought by political interests who can give very targeted political ads to its users.
Bypassing of labour laws
The digital economy has created a trend towards using self-employed freelancers, who are not protected by the same labour laws. For example, delivery drivers for Uber drivers have often been employed on zero-hour contracts. This enables firms to cut labour costs, be more flexible, but it can leave workers without sick pay or employment protections.
Social media has led to more graphic content
The anonymous and distant nature of social media has exacerbated trends to personal attacks and the posting of conspiracy theories or posting of violent/sexual images. The digital economy has enabled the proliferation of content that is damaging to human well-being.
Disruption patterns.
The pace of digitalization can lead to structural unemployment, with some unskilled workers increasingly losing out to skilled workers. Combined with the monopoly power of big tech firms, it is causing an increased inequality in society, which may lead to feelings of alienation and unfairness.
Environmental costs
Digital economy does not always imply a ‘green solution.’ Data centres use electricity and cause CO2 emissions. In the US, data centres account for around two per cent of U.S. electricity use in 2014.
A bigger potential cost is how the digital economy encourages a ‘throw-away’ culture. E.g. the planned obsolescence of mobile phones and computers, encouraging consumers to buy new models, leading to greater use of raw materials.

Some Initiatives taken to digitize India
Infrastructure
Under this initiative, the Government provides multiple programs that facilitate a reliable digital infrastructure. The following are some of the programs under this:
Services
Under this initiative, the Government has introduced multiple online services to facilitate greater reach and accessibility:
Empowerment

Under this initiative, the Government provides e-governance, skill development, and infrastructure development initiatives:
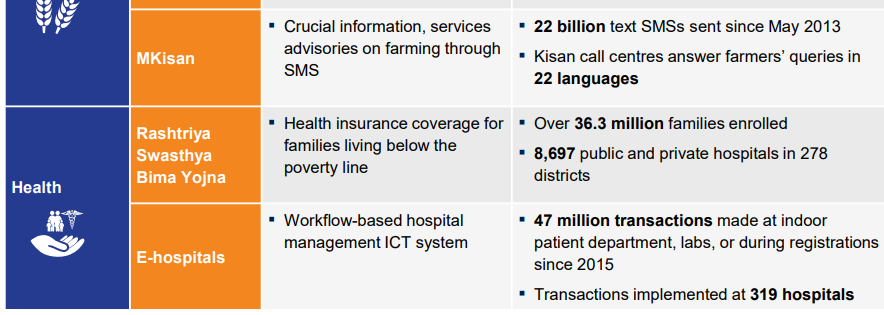
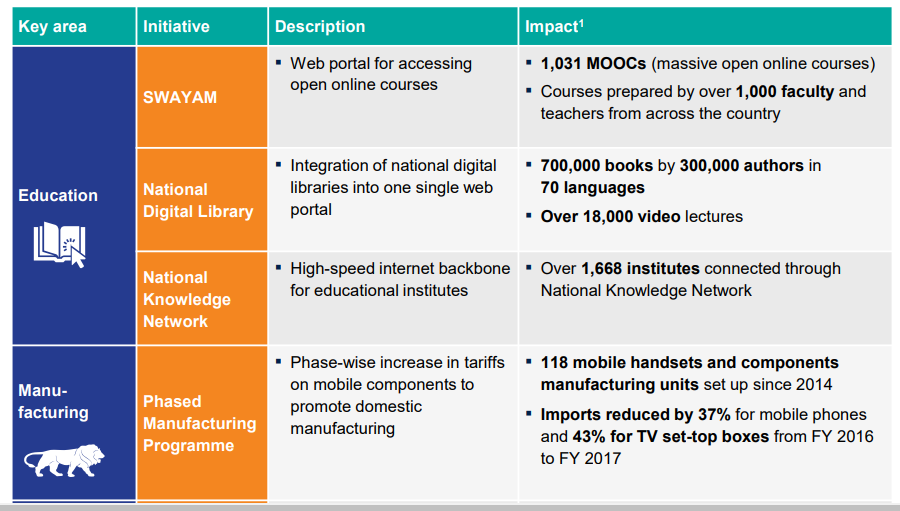
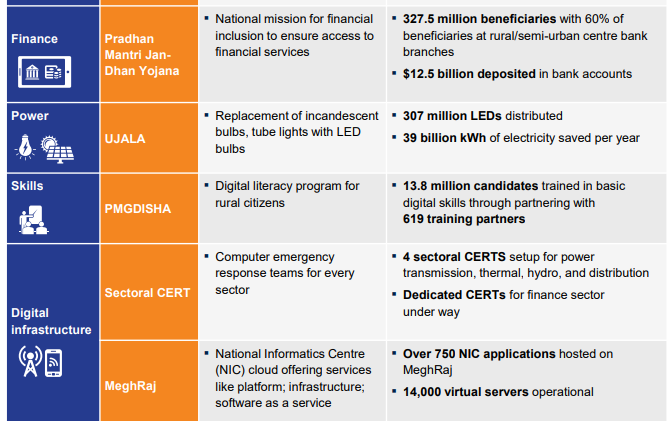
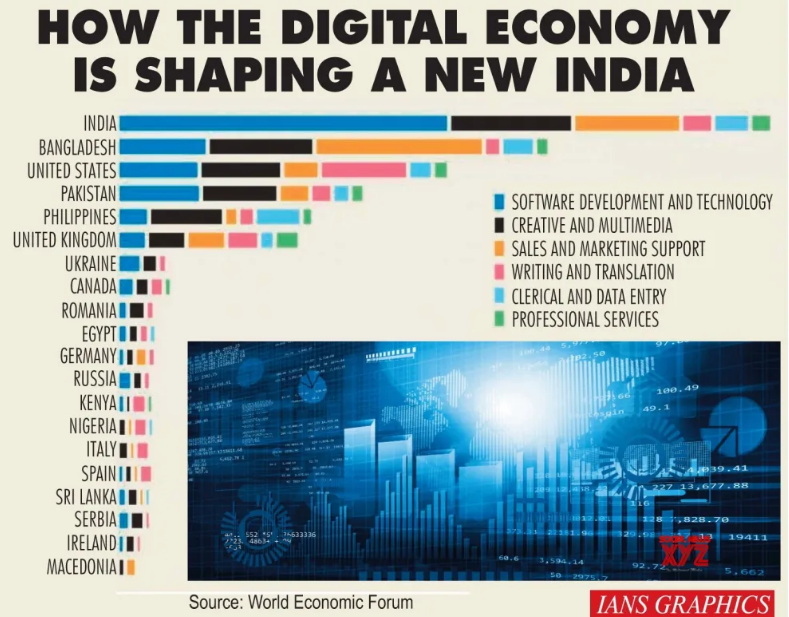
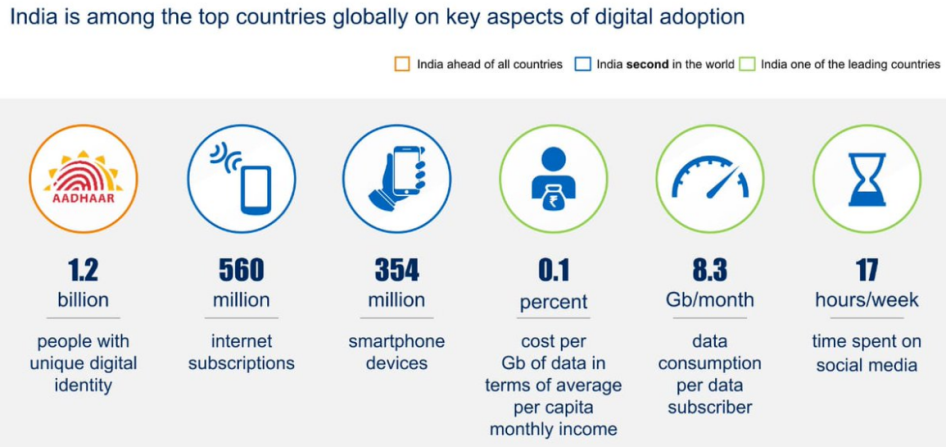
Significant achievements made by India in this field
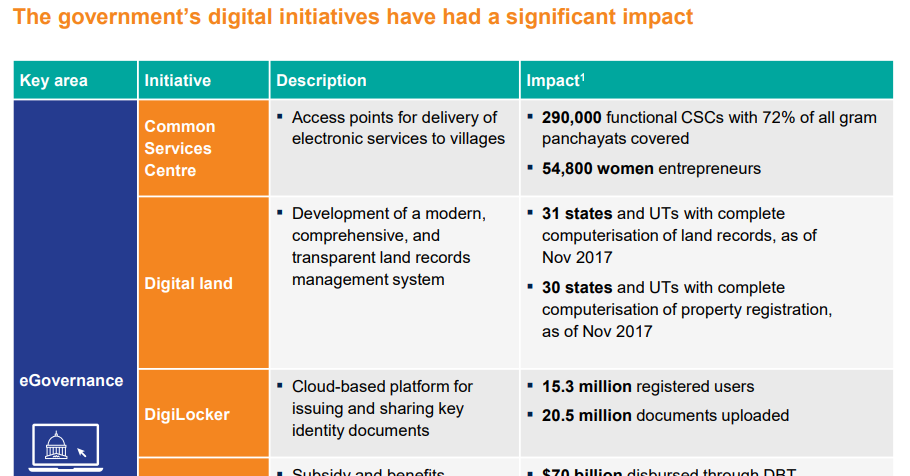
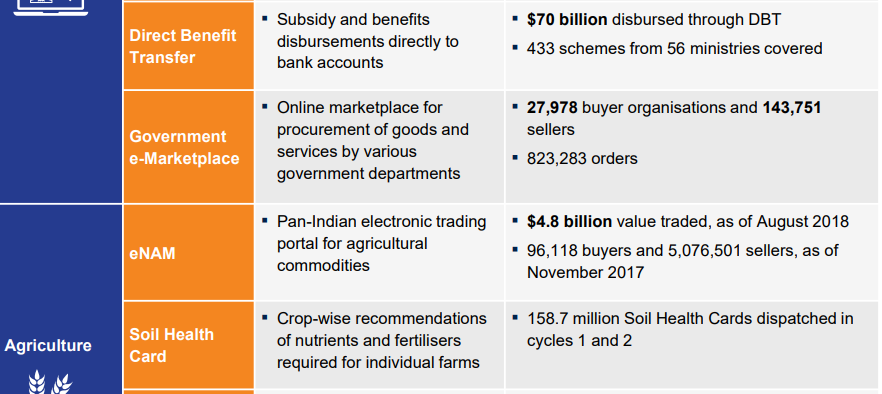

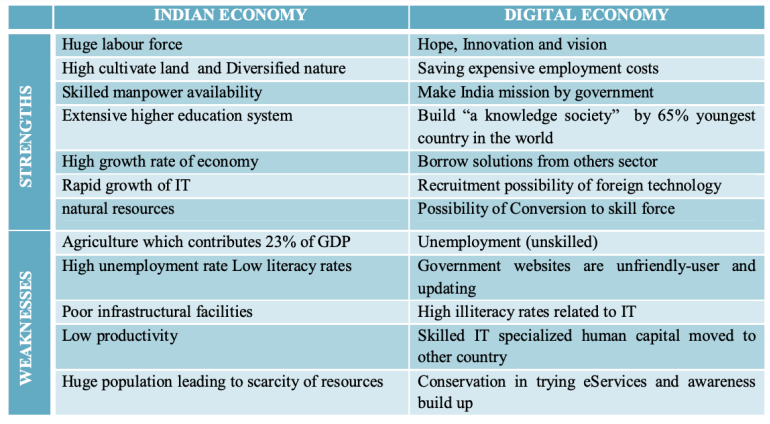
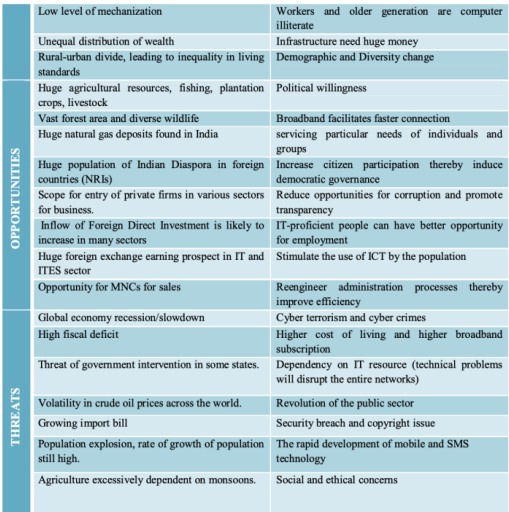
SWOT Analysis of India in this field
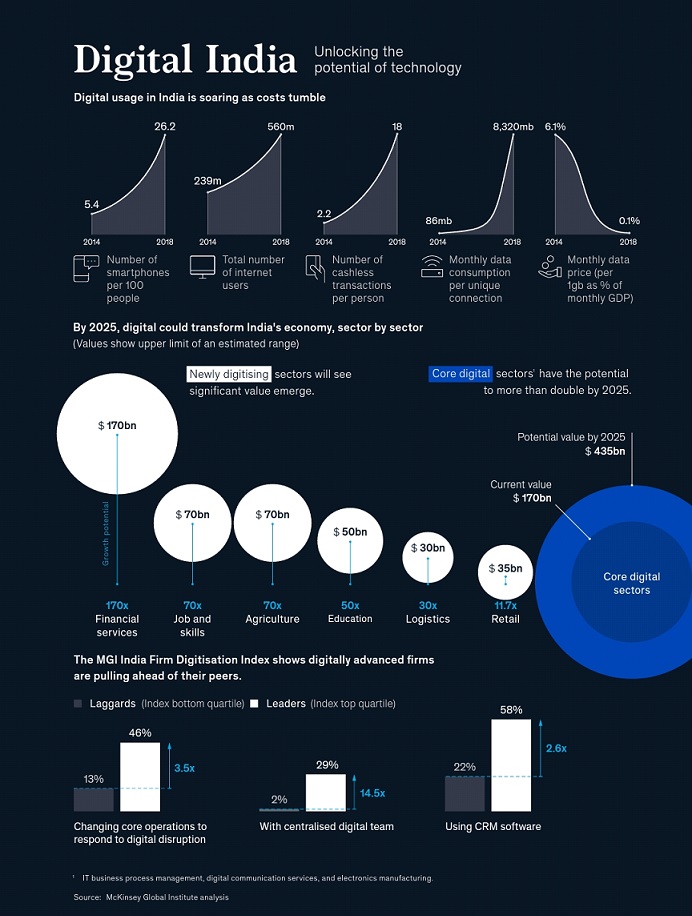
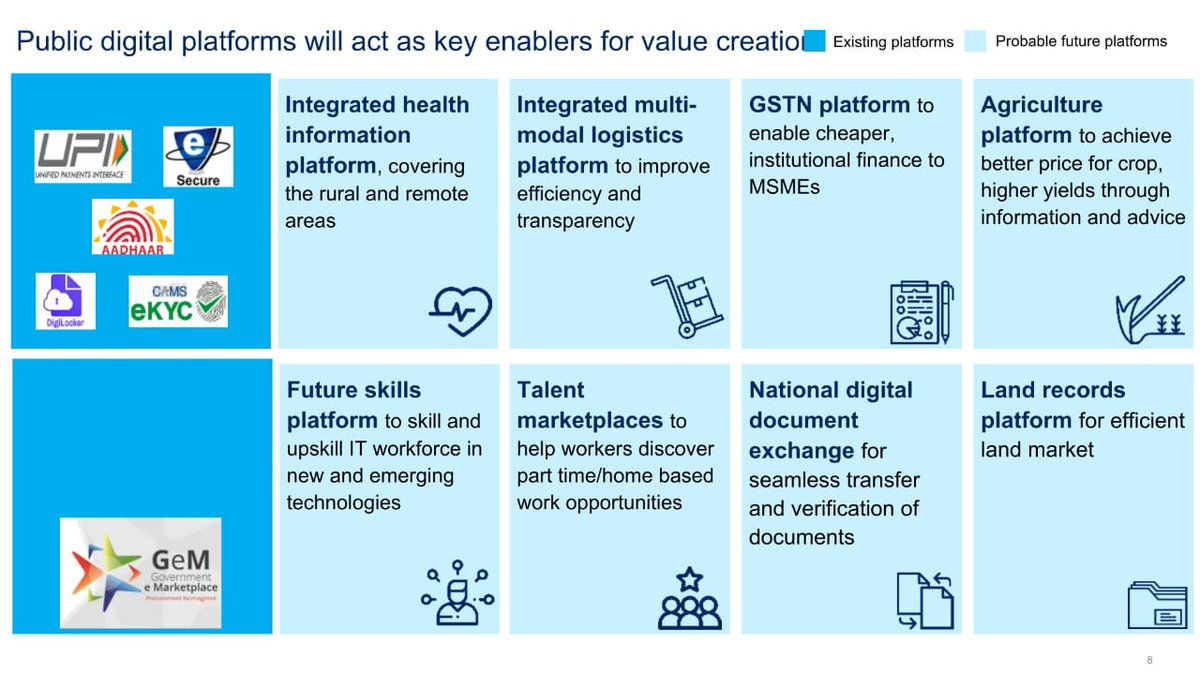
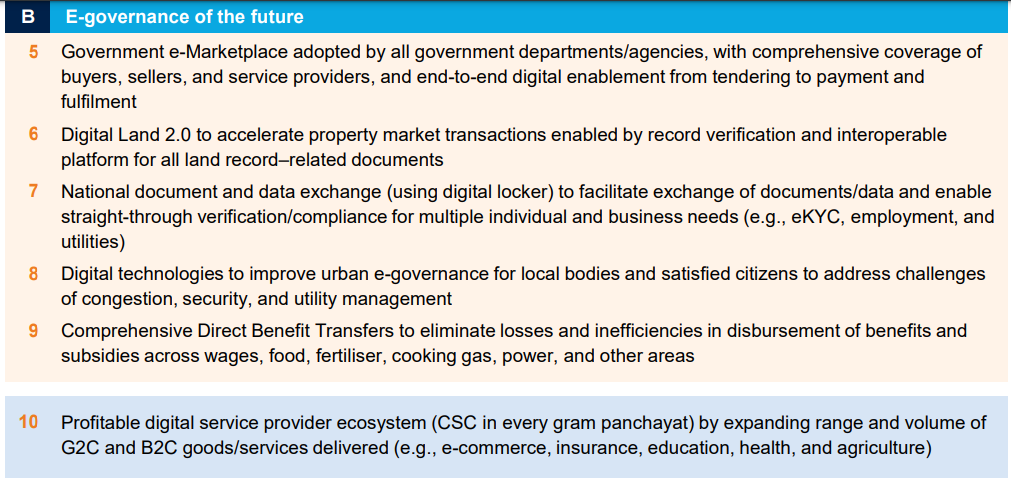
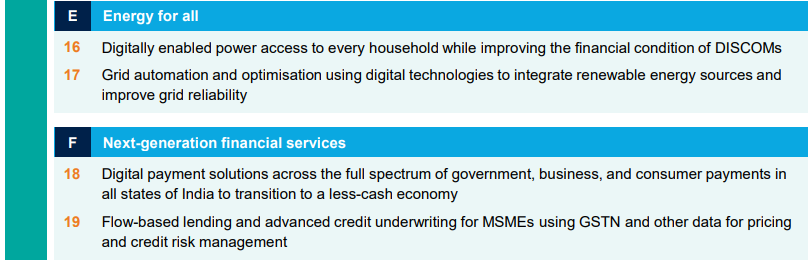
Future Potential





https://epaper.thehindu.com/Home/ShareArticle?OrgId=GP49V1KRL.1&imageview=0











© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved