Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) issued the first set of guidelines for digital lending, to crack down on illegal activities by certain players. This follows the recommendation of a Working Group on Digital Lending that had submitted its report recently.
What is Digital Lending?
- Digital lending is a process of quick loan disbursal through electronic medium. It is considered as the most effective, convenient, and faster way to disburse loans as compared to the traditional method.
- With the maturing of the digital ecosystem and enhanced use of analytics, automation, and blockchain the lending financial institutions rely more on algorithms and automated processes for loan approvals and disbursals.
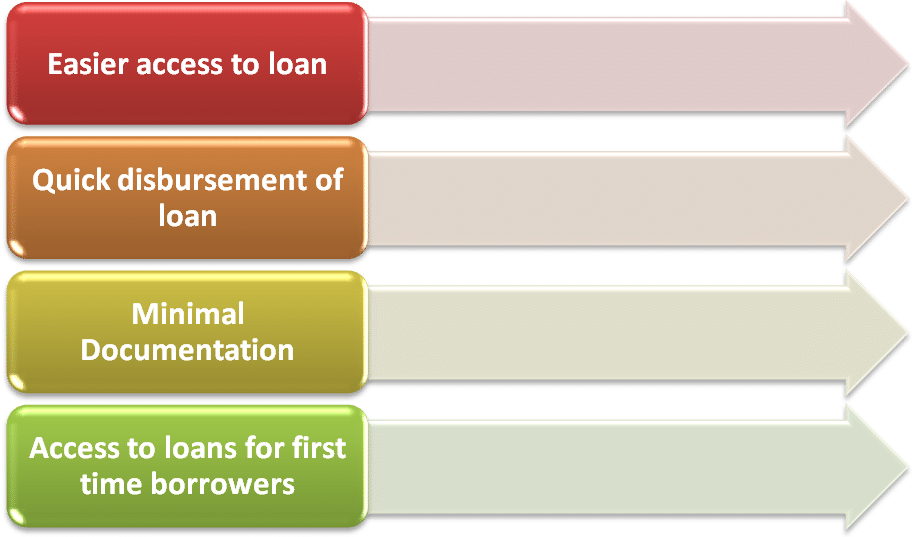
Benefits of Digital lending
- There has been a definite shift from the traditional mode of lending to digital lending in the recent past.
- It is attributable to the fact that the digital mode of lending offers many benefits that may not be found in traditional mode.
New norms
- As per the new norms, all loan disbursals and repayments will be required to be executed only between the bank accounts of the borrower and the Regulated Entities (RE) - such as a bank or a non-banking financial company - without any pass-through or pool account of the Lending Service Providers or any third party.
- Stating that digital lending channels had become prominent recently, the RBI said concerns had also emerged which, “if not mitigated, may erode the confidence of members of the public in the digital lending ecosystem.”
- The concerns relate to ‘unbridled engagement of third parties, mis-selling, breach of data privacy, unfair business conduct, charging of exorbitant interest rates, and unethical recovery practices.
- “A standardised Key Fact Statement must be provided to the borrower before executing the loan contract,” the RBI said in a circular. The norms prohibit any automatic increase in credit limit without borrowers’ consent.
- They also allow a cooling-off period in which borrowers can exit loans by paying the principal and the proportionate annual percentage rate (APR) sans penalty.
- The framework is based on the principle that the lending business can be carried out only by entities regulated either by the Reserve Bank or entities permitted to do so under any other law, RBI added.

Future of Lending Is Digital
- The industry has been alerted by Covid-19 to the tremendous potential of digital transformation. As customer demand for contactless transactions rises, more lenders will adopt technology to provide borrowers with maximum convenience.
- Even traditional banks and non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) are realizing the need to digitize processes such as customer onboarding, risk assessment, loan underwriting, disbursement, and repayment in order to reduce operational costs and enhance the customer experience.
- With services such as video-KYC, Aadhaar-based KYC, and websites and applications with cutting-edge functionalities, loan application procedures will become more efficient and less cumbersome.
- Additionally, the traditional credit underwriting procedure will undergo a radical transformation. Lenders will increasingly utilize cutting-edge technologies such as AI, ML, and big data analytics to collect and evaluate data from multiple sources in order to evaluate the creditworthiness of an applicant more quickly and efficiently.
- With the technology that enables alternative credit scoring, lenders can extend credit to a greater number of individuals, thereby advancing the cause of financial inclusion.
- In the coming years, technology will continue to disrupt the digital lending ecosystem, with a renewed emphasis on delivering an improved end-to-end customer experience.
https://epaper.thehindu.com/Home/ShareArticle?OrgId=GM4A4S5V5.1&imageview=0
















