Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- The National e-Governance Division (NeGD) of the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) in India is planning to integrate Personalised Adaptive Learning (PAL) into its existing Digital Infrastructure for Knowledge Sharing (DIKSHA) platform.
- PAL is a software-based approach that aims to provide each student with an individualized learning experience based on their unique needs and abilities.
Details
Background
- DIKSHA is an online platform and mobile application under the Education Ministry that offers e-content for schools.
- While it already includes assistive technologies for learners with visual or hearing challenges, it primarily serves as a static content repository.
Integration of PAL
- The integration of PAL into DIKSHA is expected to revolutionize the platform by leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) to cater to the specific learning needs of students.
- For example, if a student makes a mistake while learning a concept, the AI system will flag it and guide the student back to a basic video explaining the correct approach.

Challenges and Considerations
- PAL will require a significant effort to categorize and tag content across various subjects, and new content may need to be created.
- The initial focus is likely to be on subjects like chemistry, mathematics, and physics for Classes 9 to 12.
- Budget constraints have been a challenge, with significant costs associated with building the technology platform and streaming content from cloud-based servers.
Government's Motivation
- The Indian government's motivation for introducing PAL is to improve learning outcomes and school retention rates, especially for students in Classes 9 and 10, where a significant number drop out each year.
State Experiments
- Several states in India have already experimented with PAL through partnerships with private edtech companies. However, budget limitations have affected the implementation in some cases.
Timeline
- Despite the challenges, the government is committed to the development and implementation of PAL.
- It is expected to take several years to fully develop the technology and integrate it with DIKSHA.
- The NeGD plans to assess the market for edtech companies that can help with this initiative by floating an Expression of Interest.
Additional Features
- Additionally, the Ministry is also considering the introduction of voice commands in DIKSHA 2.0 as part of AI-enabled learning, allowing students to access chapter summaries and other content through voice commands, similar to the ChatGPT technology.
DIKSHA: DIGITAL INFRASTRUCTURE FOR KNOWLEDGE SHARING
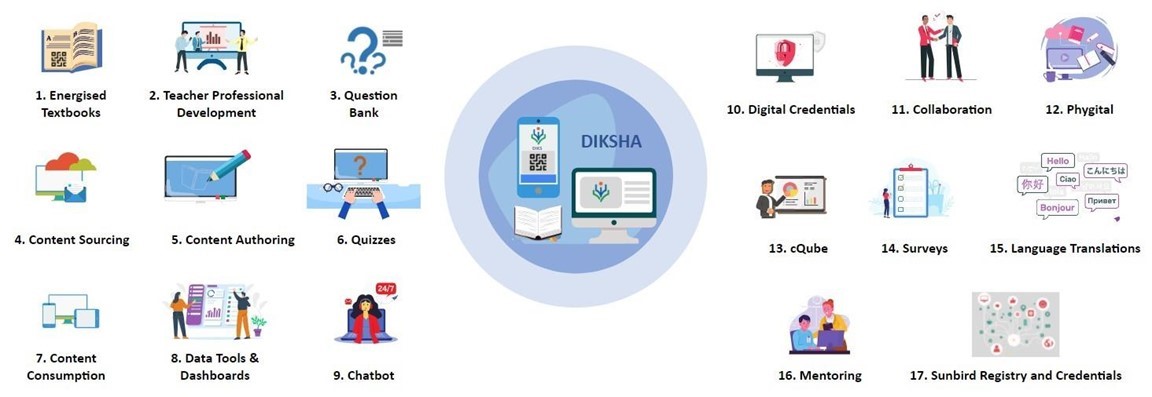
Overview
- DIKSHA, which stands for Digital Infrastructure for Knowledge Sharing, is a national platform for school education in India.
- It is an initiative led by the National Council for Educational Research and Training (NCERT) under the Ministry of Education (MoE), Government of India.
- Launched in 2017 by the Honourable Vice President of India, Shri M. Venkaiah Naidu, DIKSHA has been widely adopted across all states, union territories, central autonomous bodies/boards, including CBSE.
Purpose and Development
- DIKSHA was developed based on the Strategy and Approach Paper for the National Teacher Platform, as released by the then Honourable Minister for Human Resource Development, Shri Prakash Javdekar in September 2017.
- This platform serves as a digital education resource accessible to both learners and teachers nationwide.
- DIKSHA currently supports 36 Indian languages.
Customization and Usage
- Each state and union territory has the autonomy to leverage the DIKSHA platform according to its unique needs.
- This includes utilizing the platform's various capabilities and solutions to design and execute educational programs for teachers, learners, and administrators.
- DIKSHA policies and tools enable the participation and contribution of a wide range of stakeholders in the education ecosystem, including experts, organizations, institutions (government, autonomous, non-government, and private), with the common goal of achieving scalable learning outcomes for the country.
Content Licensing
- NCERT textbooks are licensed under CC BY NC-ND, and all the resources on DIKSHA are licensed under CC BY NC-SA.
One Nation, One Digital Platform
- Under the PM eVidya initiative of the Government of India, which is part of the Atma Nirbhar Bharat initiative, DIKSHA has been designated as 'One Nation, One Digital Platform.'
Solutions and Features
- DIKSHA is built on open-source technology, tailored for India and made in India. It incorporates internet-scale technologies and offers a diverse range of solutions for teaching and learning.
- The platform is constructed using MIT licensed open source technology called Sunbird, which provides over 100 microservices as building blocks for the development of platforms and solutions.
- DIKSHA aligns with the National Digital Education Architecture (NDEAR) launched by the Honourable Prime Minister of India in July 2021. It includes building blocks for the development of federated and interoperable systems by states and union territories.
- Key building blocks of DIKSHA include energized textbooks, online courses, content authoring, content sourcing, interactive quizzes, question banks, chatbot, analytics, and dashboard.
Impact During COVID-19 Pandemic
- During the COVID-19 pandemic, DIKSHA experienced a significant increase in usage by learners and teachers across the country.
- The platform played a crucial role in facilitating online learning and professional development for educators.
Additional Initiatives and Resources
- DIKSHA hosts a rich repository of digital content contributed by schools, individual teachers, content partners, NGOs, and corporates under CSR to meet the content requirements of NCERT, CBSE, and various states.
- To support Children With Special Needs (CWSN), DIKSHA offers a wide range of resources, including audio books, Indian Sign Language (ISL) videos, and dictionaries.
- The platform also serves as a hub for various teacher professional development programs, including NISHTHA (National Initiatives for School Heads and Teacher’s Holistic Advancement) for different grade levels.
- NCERT delivers content to students on a 24x7 basis through PM eVIDYA DTH-TV channels, linked to DIKSHA through QR codes, ensuring accessibility anytime, anywhere.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. What is the primary aim of integrating Personalised Adaptive Learning (PAL) into the Digital Infrastructure for Knowledge Sharing (DIKSHA) platform by the National e-Governance Division (NeGD)?
Options:
A. To provide content for students with visual or hearing challenges.
B. To create a static content repository for educational resources.
C. To offer individualized learning experiences based on students' unique needs and abilities.
D. To facilitate teacher training in IT applications for the classroom.
Correct Answer: C.
|

https://epaper.thehindu.com/ccidist-ws/th/th_delhi/issues/50436/OPS/GBTBN25AC.1+GAOBN3260.1.html















