




Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
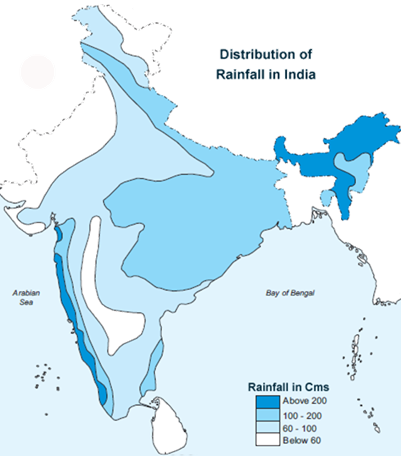
Rainfall Distribution
The distribution of yearly rainfall in various pieces of India shows below:
The normal rainfall in India is 120 cm as per yearly information from the Meteorological/Climatological Department.
The areas of rainfalls are classified in India are below, there are four regions of rainfalls in India as follows:
Areas of Inadequate Rainfall in India
Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka and Maharashtra, Ladakh, and a large portion of western Rajasthan get rainfall below 50 cm. Jaisalmer in Rajasthan is the spot in India that gets the least rainfall.
Low Rainfall Areas in India
Maharashtra, Gujarat, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, and Western Uttar Pradesh are regions having 50 to 100 cm of rainfall.
Medium Rainfall Areas in India
Gujarat, east Tamil Nadu, northeastern Peninsula covering Odisha, Jharkhand, Bihar, eastern Madhya Pradesh, northern Ganga plain along the sub-Himalayas, and the Sachar Valley and Manipur, Rainfall between 100-200 cm.
Areas of high rainfall in India
The most noteworthy rainfall happens along the west coast, on the Western Ghats, as well as in the sub-Himalayan regions in the upper east and the slopes of Meghalaya. Northeastern locales and the windward side of the Western Ghats experience a normal 400 cm of yearly rainfall. In the Brahmaputra valley and the connecting slopes, the rainfall is less than 200 cm.
The areas encountering 200-300 cm rainfalls have a place within this zone. Eastern India majorly covers this zone.
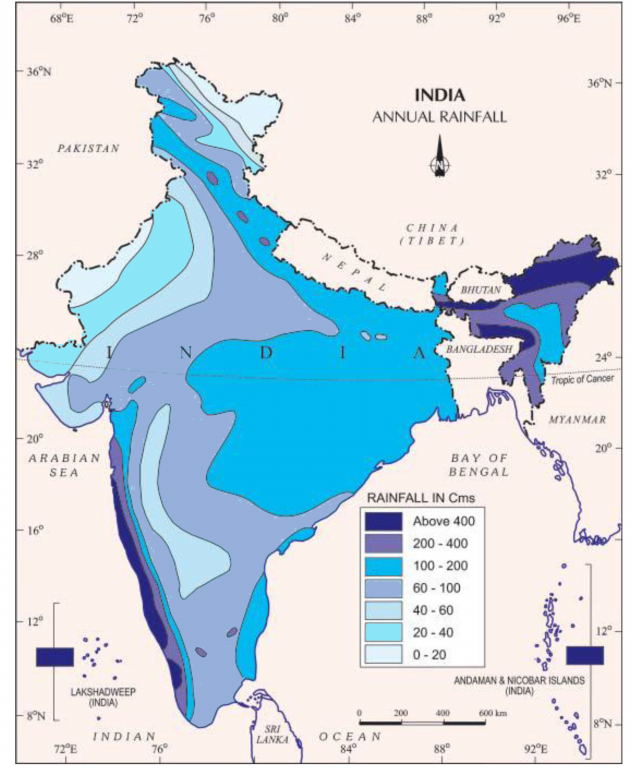
Pattern of yearly rainfall
Attributable to the idea of rainstorms, the yearly rainfall is exceptionally factored from one year to another. Fluctuation is high in the districts of low rainfall like pieces of Rajasthan, Gujarat and the leeward side of the Western Ghats. The rainfall dispersion in India is affected by the Thar Desert and the Himalayas. Temperature and strain changes over the Indian Ocean, the Arabian Sea, the Bay of Bengal and the southern piece of the Pacific Ocean likewise assume a critical part in the monsoon downpours over the country.
Area that receives 400 cm of rainfall in India
Mawsynram town of Meghalaya gets rainfall over 400cm. Northeastern districts and the windward side of the Western Ghats experience a normal of 400cm of yearly precipitation. Regions like Assam, Meghalaya, Arunachal Pradesh and sloping lots of the Western Ghats are host to tropical rainforests.
Distribution of rainfall regions in India
The average annual rainfall in India is 120 cm and the rainfall regions in India are classified in 4 regions:
Medium Rainfall Region
Gujarat, east Tamil Nadu, northeastern Peninsula covering Odisha, Jharkhand, Bihar, eastern Madhya Pradesh, northern Ganga plain along the sub-Himalayas, and the Sachar Valley and Manipur, Rainfall between 100-200 cm.
Types of rainfalls in India
Rainfalls are classified into three main types based on Origin, they are
Convectional rainfall, Orographic or relief rainfall, Cyclonic or frontal rainfall. And another rainfalls are classified in three types based on Intensity, they are
Reasons behind distribution of rainfall in India
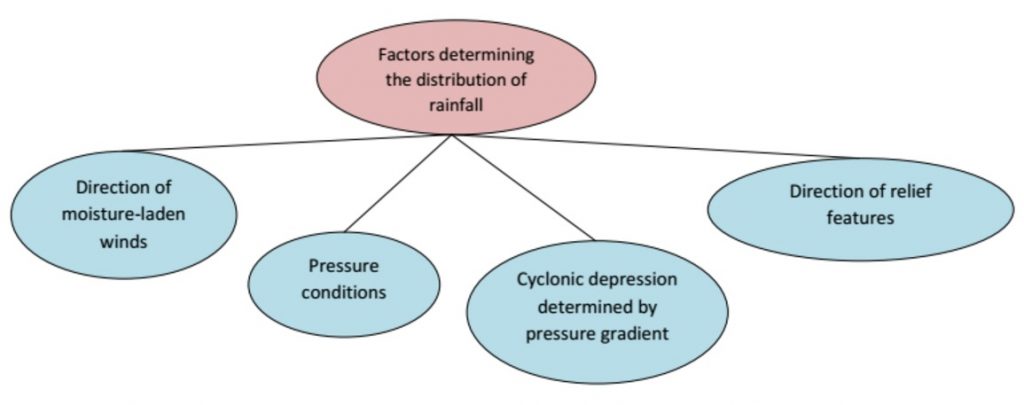
The rainfall distribution in India will occur due to these reasons stated below:
Type of monsoons in India
In India the monsoons are classified into two types
Southwest monsoons
The Southwest monsoons are the primary monsoon, roll in from the ocean and fires advancing up India’s west coast toward the beginning of June. By mid-July, the greater part of the nation is shrouded in downpour. This progressively begins clearing from most places in northwest India by October.
Northeast monsoons
The northeast monsoons influences India’s east coast during November and December. It’s a short however extraordinary storm. The provinces of Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Kerala get the greater part of their rainfall from the upper east storm, while the remainder of the nation gets the majority of its rainfall from the southwest rainstorm.
Read more about Monsoon in India: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/monsoon
https://epaper.thehindu.com/Home/ShareArticle?OrgId=GO09QQ564.1&imageview=0






© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved