Description
Context:
- Recently, the Ministry of Civil Aviation has launched the e-Governance for Civil Aviation (e-GCA) online platform.
About E-Governance:
- E-governance is the public sector’s use of ICTs with the aim to improve information and service delivery, encourage citizen participation in decision-making and make government more accountable, transparent and efficient.
- It far beyond mere computerisation of stand alone back office operations.
- It implies fundamental changes in government operations; and new set of responsibilities for the legislature, executive, judiciary and citizens.
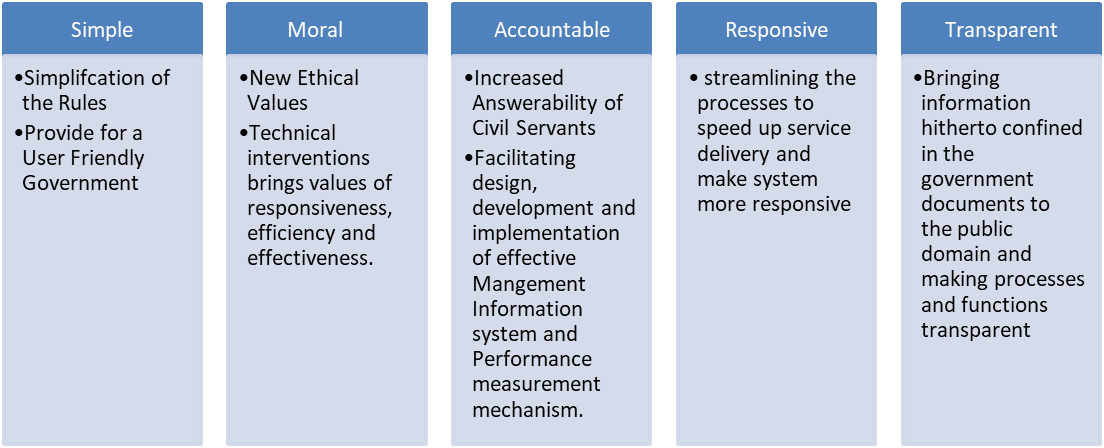
- E-governance is the application of ICT in government functioning to bring in SMART governance implying: simple, moral, accountable, responsive and transparent governance.
Figure 4: Smart Governance
Stages of E-Governance:
- Simple information dissemination (one-way communication)- is considered as the most basic form, as it is used for merely disseminating information;
- Two-way communication (request and response)- is characterised with e-mail system and information and data-transfer technologies in the form of website;
- Service and financial transactions- is online services and financial transactions leading to web based self-services;
- Integration (both vertical and horizontal)- in this stage the government would attempt inter and intra-governmental integration;
- Political participation- this stage means online voting, online public forums and opinion surveys for more direct and wider interaction with the government.
Difference Between E-Government and E-Governance:
|
BASIS FOR COMPARISON
|
E-GOVERNMENT
|
E-GOVERNANCE
|
|
Meaning
|
The application of ICT, with the aim of supporting government operations, aware citizens and deliver services is called as e-Government.
|
e-Governance refers to the use of ICT in enhancing the range and quality of information and services delivered to the public, in an effective manner.
|
|
What it it?
|
System
|
Functionality
|
|
Communication Protocol
|
One way communication protocol
|
Two way communication protocol
|
Legal and Policy Framework:
Information Technology Act 2000
It aims to provide for the legal framework so that legal sanctity is accorded to all electronic records and other activities carried out by electronic means.
Report of the Working Group on Convergence and E-governance 2002-07:
- It felt the need to set up a central body for taking stock of the total IT picture in the country.
- This central body could be a ‘Council for E-governance’ or an adhoc ‘Commission on Reengineering Administrative Procedures for E- governance.’
- Another alternative it suggested was to set up a National Institute of Smart Governance.
National E-Governance Plan;
The 10-point agenda of the Department of Information Technology announced for growth of ICT in the country includes expeditious implementation of a ‘National E-Governance Plan’ to bring about transparency and citizen centric approach in administration.
Digital India Program:
- Digital India is a programme launched in 2015 to transform India into digital empowered society and knowledge economy.
- It would also bring in public accountability through mandated delivery of government’s services electronically.
9 Pillars of Digital India:
- Broadband Highways
- Universal Access to Mobile Connectivity
- Public Internet Access Programme
- e-Governance: Reforming Government through Technology
- e-Kranti - Electronic Delivery of Services
- Information for All
- Electronics Manufacturing
- IT for Jobs
- Early Harvest Programmes
Significance of E-governance:
- Automation of Administrative Processes : Software has been built and designed around government departments ensuring efficiency in operations. The departments have launched individual websites carrying information of their respective departments. This has enabled online carrying of operations and file movements.
- Paper Work Reduction: Paperwork is reduced to a greater extent with communication being enabled via electronic route and storage and retrieval of information in the electronic form.
- Quality of Services: ICT helps governments to deliver services to the citizens with greater accountability, responsiveness and sensitivity. Quality of services improves, as now the people are able to get services efficiently and instantaneously
- Elimination of Hierarchy: ICT has reduced procedural delays caused by hierarchical processes in the organisation. Through Intranet and LAN, it has become possible to send information and data across various levels in the organisation at the same time.
- Change in Administrative Culture: With e-governance, public actions coming under public glare would certainly induce norms and values of accountability, openness, integrity, fairness, equity, responsibility and justice in the administrative culture. Rather, administration would become efficient and responsive.
- Transparency: easy access to information and subsequently makes the system publicly accountable. Also as web enables free flow of information, it can be easily accessed by all without any discrimination
- Social Development: The access to information empowers the citizens. Informed citizenry can participate and voice their concerns, which can be accommodated in the programme/ project formulation, implementation, monitoring and service delivery.











