Description
Copyright infringement not intended
Context: A public health alert has been issued for Burney, a small city in California (USA), after a surge of E. coli infections among its residents. The Los Angeles Times reported that many people, especially children and the elderly, have been suffering from symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhoea, and fever, and some have been hospitalized or needed medical care.
Details
- A report by the Los Angeles Times revealed that Burney, a small city in California (USA), is facing a serious public health crisis due to an outbreak of E. coli infections. Several residents, especially children and the elderly have been hospitalized or sought medical attention after experiencing symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhoea, and fever.
- According to the authorities, they have detected E. coli in the water supply, which could indicate a possible leakage of sewage or animal waste into the system.
- Escherichia coli, commonly known as E. coli, is a type of bacteria that can be found naturally in the intestines of humans and many other animals. While most strains of E. coli are harmless and even beneficial, some strains can cause illness and infections.
- Pathogenic E. coli strains are the ones that can lead to various health issues, ranging from mild gastrointestinal problems to severe and life-threatening conditions.

coli outbreak
About
- coli is a type of bacteria that normally lives in the intestines of humans and animals. However, some strains of E. coli can cause serious illness, such as diarrhoea, urinary tract infections, and pneumonia and kidney failure. In recent months, there has been a surge of E. coli infections in several countries, affecting thousands of people and causing several deaths.
What are the reasons for the E. coli outbreak?
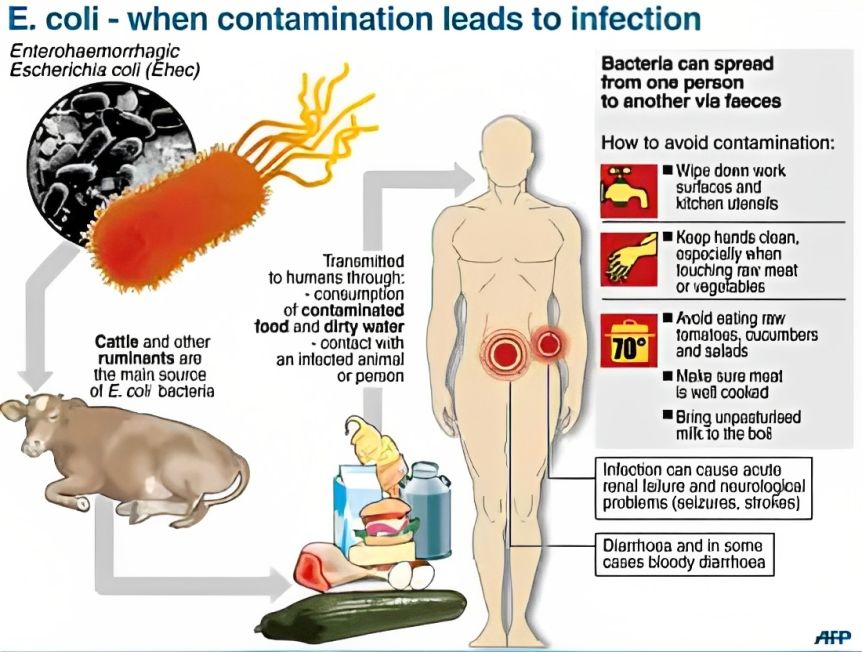
- Contaminated food or water: coli can spread through raw or undercooked meat, unpasteurized milk, fresh produce, or water that has been contaminated by animal or human faeces.
- Poor hygiene: coli can also spread through contact with infected people or animals, especially if proper handwashing is not practised.
- Antibiotic resistance: Some strains of E. coli have developed resistance to common antibiotics, making them harder to treat and more likely to cause severe complications.
What are the impacts of the E. coli outbreak?
- Health risks: coli infection can cause symptoms such as abdominal cramps, diarrhoea, vomiting, fever and blood in the stool. In some cases, it can lead to hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS), a life-threatening condition that damages the kidneys and other organs.
- Economic losses: The E. coli outbreak has affected the food industry, especially the meat and dairy sectors, as consumers lose confidence in the safety and quality of their products. It has also increased the costs of health care, testing and surveillance.
- Social disruption: The E. coli outbreak has caused fear and anxiety among the public, as well as social stigma and discrimination against certain groups or regions that are perceived to be associated with the outbreak.
What are the challenges in dealing with the E. coli outbreak?
- Identifying and tracing the source: The E. coli outbreak involves multiple countries, regions and products, making it difficult to pinpoint the origin and transmission routes of the bacteria.
- Preventing and controlling the spread: The E. coli outbreak requires coordinated efforts from various sectors, such as agriculture, health, environment and education, to implement preventive measures, such as improving sanitation, hygiene and food safety standards, as well as raising public awareness and providing timely information.
- Treating and supporting the patients: The E. coli outbreak demands adequate resources and facilities to diagnose, treat and monitor the patients, especially those who develop severe complications or require dialysis or transplantation.
The E. coli outbreak is a complex and evolving situation that requires continuous vigilance and collaboration from all parties involved.
Some possible steps for the way forward include
- Strengthening surveillance and reporting systems: The E. coli outbreak calls for improved surveillance and reporting systems that can detect and track outbreaks quickly and accurately, as well as share data and information across borders and sectors.
- Developing new technologies and strategies: The E. coli outbreak urges the development of new technologies and strategies that can prevent, diagnose and treat E. coli infections more effectively and efficiently, such as vaccines, rapid tests and novel antibiotics.
- Enhancing cooperation and communication: The E. coli outbreak highlights the need for enhanced cooperation and communication among governments, organizations, industries and communities that can foster trust, transparency and coordination in responding to the outbreak.
- Implement stricter standards and regulations for the production, processing, distribution and handling of fresh produce and other foods, based on scientific evidence and risk assessment, and enforce them through regular audits and inspections.
- Invest in research and innovation to develop new technologies and methods that can prevent or reduce the contamination of fresh produce and other foods, such as biocontrol agents, irradiation, packaging and sanitation.
- Educate consumers and food handlers about the risks of foodborne illnesses, the symptoms and treatment of E. coli infection, and the proper ways to wash, store and prepare fresh produce and other foods.

Conclusion
- coli outbreaks are a significant public health concern with potentially serious consequences. Preventing and managing these outbreaks require a multi-faceted approach involving enhanced food safety measures, effective surveillance, education, and collaboration among various stakeholders. By addressing the challenges and adopting a proactive approach, the impact of E. coli outbreaks can be minimized, safeguarding public health and well-being.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. How are E. coli outbreaks commonly transmitted?
A) Through mosquito bites
B) By inhalation of contaminated air
C) By contact with infected individuals or animals
D) By consuming undercooked meat or contaminated food and water
Answer: D
Explanation: By consuming undercooked meat or contaminated food and water. E. coli outbreaks often occur due to the consumption of undercooked or raw meat, contaminated vegetables, unpasteurized dairy products, and contaminated water used during food processing.
|
https://www.news18.com/world/e-coli-outbreak-in-california-los-angeles-find-out-what-is-e-coli-infection-and-how-serious-it-is-8390959.html












