Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
India's monsoon weather patterns and their impact during the months of August and September.
Details
- India experienced above-average rainfall in July despite the emergence of El Nino.
- August, however, saw the adverse impacts of El Nino, making it the driest August in over a century.
- The outlook for September is uncertain, with hopes of a revival in monsoon activity.
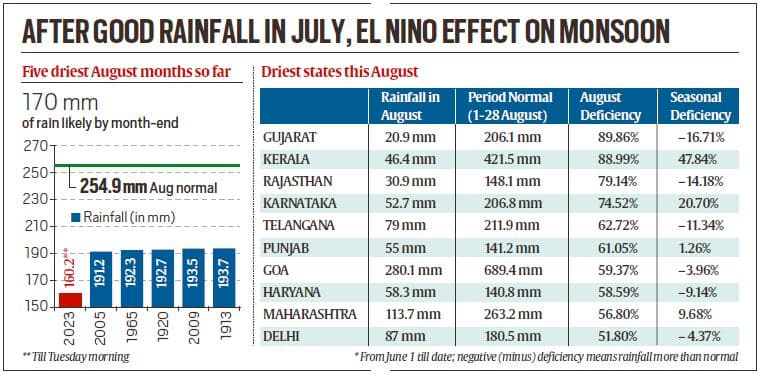
Driest August on Record
- August is typically the second rainiest month in India, accounting for about 22% of the annual rainfall.
- August 2023 is set to be the driest since 1901, with a deficit of about 33%.
- States like Gujarat and Kerala had nearly 90% rainfall deficit, while others like Karnataka, Telangana, and Andhra Pradesh had over 50% deficiency.
- Tamil Nadu, relying on winter rainfall, had a shortfall of 23%.
El Nino Impact
- El Nino, the warming of the equatorial Pacific Ocean, suppresses monsoon rainfall in India.
- The Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD) didn't compensate for El Nino's impact this year.
- The relationship between IOD and the Indian monsoon remains uncertain.
Regional Variances
- East and northeast India received good rainfall in August after deficits in June and July.
- However, this rainfall couldn't fully offset the seasonal deficit.
Possible Monsoon Revival
- Experts predict a potential monsoon revival in the first or second week of September.
- It's uncertain how much rainfall this revival will bring, but El Nino's influence may still lead to a deficiency in September.
Reservoir Levels and Concerns
- Monsoon provides 75% of India's annual rainfall, crucial for reservoirs.
- As of last week, major reservoirs were at 94% of normal levels, but this may decline.
- Some states already have critically low reservoir levels (e.g., Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Bihar).
- A dry September could worsen the situation.
Impact on Crops
- Winter crops and standing kharif crops are under stress due to inadequate rainfall.
- Soybean, a relatively low water-intensive crop, requires immediate rain for sustainability.
- The extent of yield loss will depend on the monsoon's behavior in the next 45 days.

About El Nino
- El Nino, Spanish for "the boy child," is a climate phenomenon characterized by the abnormal warming of sea surface temperatures in the equatorial Pacific Ocean.
- It is part of the broader El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) climate pattern, which also includes La Nina.
Causes of El Nino
- El Nino occurs irregularly, typically every 2 to 7 years, and is driven by complex interactions between the ocean and the atmosphere.
- It is triggered when the trade winds that usually blow from east to west weaken or reverse direction, allowing warm water to move eastward.
Key Characteristics of El Nino
- Elevated Sea Surface Temperatures: The central and eastern Pacific Ocean experiences unusually warm sea surface temperatures during El Nino events.
- Disruption of Normal Weather Patterns: El Nino disrupts typical climate patterns worldwide, affecting weather systems and precipitation.
- Global Impact: The effects of El Nino are felt globally, influencing weather events, agriculture, ecosystems, and economies.
Impacts of El Nino
On Weather Patterns
- Reduced Rainfall: El Nino tends to suppress rainfall in regions that normally receive it, leading to droughts and water shortages.
- Increased Rainfall: Conversely, it can result in excessive rainfall and flooding in other areas.
On Agriculture and Food Security
- Crop Failures: Droughts or floods caused by El Nino can lead to crop failures, impacting food production.
- Food Price Volatility: Reduced agricultural output can cause food prices to rise, affecting food security.
On Ecosystems
- Marine Ecosystems: El Nino can disrupt marine ecosystems, leading to coral bleaching and changes in fish migration patterns.
- Terrestrial Ecosystems: Forest fires and altered vegetation patterns may occur due to changed precipitation patterns.
On Economics
- Economic Disruption: Industries such as agriculture, fisheries, and insurance can be negatively affected by El Nino-induced weather extremes.
- Costly Disasters: The economic costs of responding to El Nino-related disasters, such as floods and wildfires, can be substantial.
El Nino's Counterpart: La Nina
- La Nina is the opposite phase of ENSO, characterized by cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures in the equatorial Pacific.
- It often leads to contrasting weather patterns, such as increased rainfall in some regions and more active hurricane seasons.
Prediction and Monitoring
- Scientists use various tools, including ocean buoys and climate models, to monitor and predict El Nino events.
- Early detection and prediction are essential for preparedness and mitigation efforts.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q) Discuss the causes, characteristics, and global impacts of El Nino, and elucidate the strategies that governments and organizations can adopt to mitigate its adverse effects. (150 words)
|

https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-climate/staring-at-driest-ever-august-8915316/
















