Description

Copyright infringement not intended
In News
- The Chief Election Commissioner has suggested 6 key electoral reforms to the Union Law Ministry.
- Issue guidelines for the linking of Aadhaar with voter IDs.
- The election commission has asked the Powers to deregister political parties.
- Mandatory disclosure of all donations above Rs 2,000.
- Empowers the commission to register associations and bodies as political parties.
- Restrict the number of seats a candidate can contest from.
- Ban on exit polls and opinion polls
Important Reforms Taken in Electoral System
- The right to vote irrespective of Caste, Creed, Religion or Gender.
- Lowering the voting age from 21 to 18 through the 61st Amendment Act of 1988.
- Provision was made for voting by Certain Classes of Persons through Postal ballot.
- A facility for voting through Proxy was provided to the Service voters belonging to the Armed forces.
- Rajya Sabha elections were reformed by removing the domicile of the Contesting Candidate and the Introduction of an open ballot system was introduced.
- Exemption of travelling expenditure from being included in the election expenses of the Candidate was made.
- Restrictions were imposed on conducting exit Polls and Publishing the results of exit Polls.
- Provision was made for the disqualification of a Person found guilty of Corrupt Practices.
- Appointment of appellate authorities within the district.
- Voting rights for Citizens of India living abroad were provided in 2010.
- The ceiling on election expenditure was increased.
- Those who are deemed unsound of mind and People Convicted of Certain Criminal offences are not allowed to vote.
- Introduced Electoral Photo Identity Card, also allows certain alternative documents like government I-Cards, Passports, PAN Cards, driving license, bank/Post office account Passbook, Property documents, SC/ST/OBC Certificate, Pension documents, Job cards issued under NREGA and Health insurance Scheme Smart Cards to establish the identity of the electors in the Polling Stations.
- Introduced by 52nd Amendment Act, for the disqualification of the members of Parliament and the State legislatures on the ground of defection from one Political Party to another.
- Disqualification on grounds of defection is not to apply in the case of a Split.
- Model Code of Conduct evolved by Election Commission based on a consensus among political parties.
- All Recognised National and State Parties have been allowed free access to the State-owned electronic media: AIR and Doordarshan.
- NOTA Option - In its efforts of Cleansing the Political System, Supreme Court upheld the right of voters to reject all candidates contesting the elections.
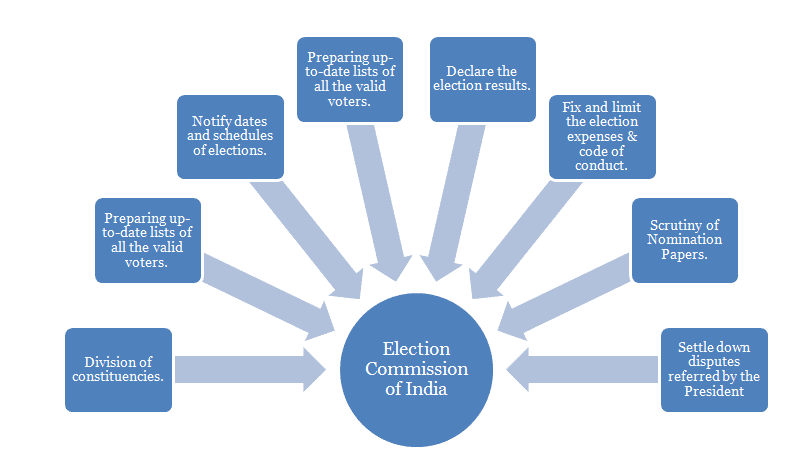
Election Commission of India
- It is a permanent constitutional body.
- Article 324 of the constitution establishes the Election Commission of India.
- It was established on 25th January 1950.
- It supervises the conduct of elections to Parliament and Legislature of every State and elections to the offices of President and Vice-President of India.
- It consists of the Chief Election Commissioner and two Election Commissioners.
- Originally, there was only Chief Election Commissioner, there were no Election Commissioners.
Copyright infringement not intended
Appointment of Election Commissioners
- The President appoints Chief Election Commissioner and Election Commissioners.
- Tenure of 6 years, or up to the age of 65 years, whichever is earlier.
- The status, salary and perks of election commissioners are equivalent to Judges of the Supreme Court of India.
- The Chief Election Commissioner can be removed from office only through impeachment by
- Other members can be removed by the President in consultation with the Chief Election Commissioner.
- The President may appoint Regional Election Commissioners in consultation with the CEC before elections to the Parliament or Assemblies.
- The Chief Election Commissioner cannot hold any office of profit after retirement.
- The Chief Election Commissioner cannot be reappointed to the post.
https://indianexpress.com/article/india/ec-govt-chief-election-commissioner-rajiv-kumar-seats-contest-opinion-exit-polls-7966453/
1.png)
https://t.me/+hJqMV1O0se03Njk9

















