Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- India can transform and become the global leader, exporter, producer of electrolyzer and global champion of green hydrogen, but for that, multilateral institutions must also finance our entrepreneurs said India’s G20 Sherpa Amitabh Kant.
Electrolyzer
- The electrolyser is an apparatus that produces hydrogen through a chemical process (electrolysis) capable of separating the hydrogen and oxygen molecules of which water is composed using electricity.
- One of the world's largest electrolysers is located in Fukushima, Japan, at the site of the well-known nuclear disaster, symbolising a paradigm shift in energy productionas it is powered by solar panels.
.jpg)
How does an Electrolyzer work?
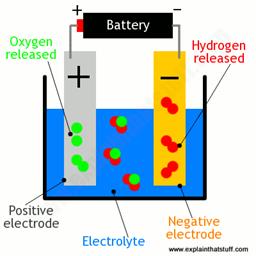
- Electrolysis was first discovered in 1800.After the invention of the electric battery by Alessandro Volta in the same year, other chemists tried connecting their poles in a container of water. They discovered that the current flowed through the water and that hydrogen and oxygen were separated at the electrodes.
- An electrolyser consists of a conductive electrode stack separated by a membrane to which a high voltage and current is applied. This causes an electric current in the water which causes it to break down into its components: hydrogen and oxygen.The complete system also includes pumps, power electronics, gas separator and other auxiliary components such as storage tanks.
- The oxygen generated in parallel is released into the atmosphere or can be stored for later use as a medical or industrial gas in some cases. The hydrogen is stored as a compressed gas or liquefied for use in industry or in hydrogen fuel cells,which can power transport vehicles such as trains, ships and even aircraft.
Types of Electrolyzers
- Although several types of electrolyzers are in use today, the most common ones are polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) electrolyzers and alkaline electrolysis cells (AECs).
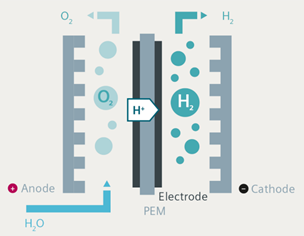
- In a polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) electrolyzer, the electrolyte is a solid specialty plastic material. Water reacts at the anode to form oxygen and positively charged hydrogen ions (protons). The electrons flow through an external circuit and the hydrogen ions selectively move across the PEM to the cathode.
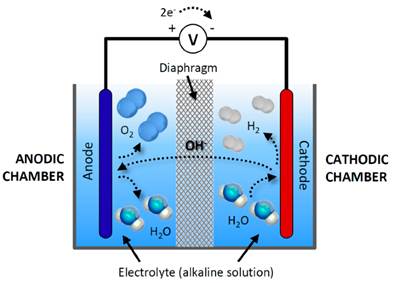
- Alkaline water electrolysis is a type of electrolyzer that is characterized by having two electrodes operating in a liquid alkaline electrolyte solution of potassium hydroxide (KOH) or sodium hydroxide (NaOH). These electrodes are separated by a diaphragm, separating the product gases and transporting the hydroxide ions (OH−) from one electrode to the other.
.jpg)
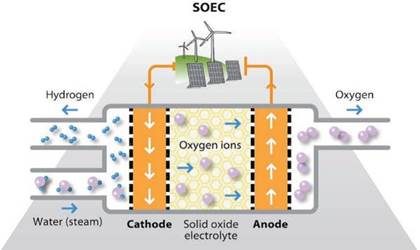
- Another technology - Solid oxide electrolysis cells (SOECs) - is less mature but has the potential to offer up to 80 per cent efficiency. A solid oxide electrolyzer cell (SOEC) is a solid oxide fuel cell that runs in regenerative mode to achieve the electrolysis of water (and/or carbon dioxide) by using a solid oxide, or ceramic, electrolyte to produce hydrogen gas (and/or carbon monoxide) and oxygen.
India and Electrolysers
- India is emerging as one of the world’s most important electrolyser manufacturing centres, with 8GW of factories due to come on line by 2025, according to analysis from Norwegian research house Rystad Energy.
- Green hydrogen is fast emerging as the next mega-industry in the clean energy space. Hydrogen, both a feedstock and an energy carrier, is considered a critical factor in the decarbonization of the hard-to-abate sectors. Apart from decarbonization, hydrogen can play an integral role in increasing India's energy self-reliance and reducing oil and gas import bills. Thus, over 50 countries have announced or are working on a national hydrogen policy roadmap.
- Under the first phase of its hydrogen policy, India plans to manufacture 5 million tonnes (Mt) of green hydrogen per annum by 2030, translating to an electrolyzer demand of 50GW–60GW.Electrolyzers being the key component in the green hydrogen value chain, their market is expected to grow exponentially in the next 3-5 years.
Present Scenario
- Currently, there are only a few electrolyzer OEMs with extensive production facilities and advanced technologies, presenting a significant opportunity for India to become a global electrolyzer manufacturing hub that caters to domestic as well as international demands.
- However, keeping a sharp eye on emerging technologies and the upcoming demand trends is necessary for electrolyzer OEMs to scale up domestic manufacturing and make the most of this million-billion-dollar opportunity.
Untapping the opportunity: Key Steps
- The industry needs to focus on two key pillars to make the most of this opportunity. One is the scale-up of domestic manufacturing capabilities, and the other is the R&D of technology. Scaling up the production of available technologies will help ensure the supply of critical components and bring down the cost of electrolyzers.
- Currently, the cost to produce and operate electrolyzers is high due to the inefficiency of technology and the end-to-end support systems. Increasing the overall efficiency will provide a significant opportunity for OEMs. For instance, the efficiency of PEM electrolyzers can be boosted by 60-70 per cent just by improving the materials used in the stack.
- Electrolyzers have three key subsections – power electronics, stack, and balance of stack. Stack and power electronics determine the electrolyzers' performance and contribute to their cost as they consist of high-value components. Manufacturing and supply of these components are confined to a few geographies and are practically non-existent in India, adding to the cost factor.
- Thus, India must consider end-to-end manufacturing to truly bring down costs and create value in the manufacturing space. The policy incentives should facilitate the creation of an end-to-end electrolyzer manufacturing ecosystem and domestic supply chain of critical high-value subcomponents.
- While scaling up the production of advanced technology should be the first step, research to improvise other technologies, such as alkaline and PEM, to boost efficiency, increase reliability and reduce costs is equally important.
- In addition, research to develop disruptive technologies is paramount for India to emerge as a global leader in the green hydrogen industry.
- As the demand for electrolyzers is expected to increase in the next few years, the players must consider partnerships with energy and utility players as renewable power hubs are better suited for green hydrogen production due to access to renewable electricity. These partnerships will play an integral role in supporting the development of a green hydrogen ecosystem.
Significance of Electrolysers
- Hydrogen produced in this sustainable way, i.e. without emitting carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, can be the basis for a decarbonised economy.
- Apart from decarbonization, hydrogen can play an integral role in increasing India's energy self-reliance and reducing oil and gas import bills.
The way forward
- India has a huge opportunity to become the global hub for electrolyzers' design, technology, and manufacturing.
- However, the country must learn from the lessons of the semiconductor and solar boom periods and seize this emerging opportunity with innovation, the right push from the government and a synchronized response from the industry players.
Read all about Green Hydrogen: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/green-hydrogen-47
https://www.thehindu.com/business/india-can-be-a-global-leader-in-electrolyzer-green-hydrogen-says-g20-sherpa-amitabh-kant/article66255448.ece






.jpg)









