Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context: A new strain of the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) was identified in the United Kingdom last month.
About the new variant
- It has been named the 5.1 variant, code-named Eris.
- It is a strain of Omicron
Geographical Spread
- Patients in the United States, Europe and Asia have also been found infected with Eris.
- In the UK, about 39.4 per cent of the cases are due to the 1.16 strain, also known as Arcturus.
- It is currently not clear whether any EG.5.1 variants have been reported in India and as per scientists there is no concern due to the nature of the virus and the country’s past exposure.

Symptoms
- The symptoms include a runny nose, headache, fatigue, sneezing and a sore throat.
- Present Covid-19 status in India
- There were 1,543 active COVID cases in India on August 8, 2023, according to the website of the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Cause of concern
- There was a continued rise in COVID-19 cases over the week in the UK.
- It accounts for 14.6 per cent of all cases in the UK.
- There’s nothing to connect the dots between EG.5.1 and the wave of rising Covid-19 cases in the UK.
- However, it is concerning that it is not anything like Omicron as the latter's prevalence is less than 10 per cent.
- We don’t know when this wave will peak and whether the rise of EG.5.1 is contributing. However, the higher cases signify that the strain certainly does not look benign.
SARS-CoV-2 Variant Classifications and Definitions
- Viruses like SARS-CoV-2 continuously evolve as changes in the genetic code (caused by genetic mutations or viral recombination) occur during the replication of the genome.
- SARS-CoV-2 has consistently mutated throughout the pandemic, resulting in variants that are different from the original SARS-CoV-2 virus.
Key Definitions and Points for Prelims
- Mutation: A mutation refers to a single change in a virus’s genome (genetic code). Mutations happen frequently, but only sometimes change the characteristics of the virus.
- Lineage: A lineage is a group of closely related viruses with a common ancestor. SARS-CoV-2 has many lineages; all cause COVID-19.
- Sublineage: A term used to define a lineage as it relates to being a direct descendent of a parent lineage. For example, BA.2.75 is a sublineage of BA.2.
- Variant: A variant is a viral genome (genetic code) that may contain one or more mutations. In some cases, a lineage or group of lineages with similar genetic changes may be designated by the World Health Organization (WHO) or the U.S. SARS-CoV-2 Interagency Group (SIG) as a Variant of Interest (VOI), Variant of Concern (VOC), Variant of High Consequence (VOHC) or Variant Being Monitored (VBM) due to shared attributes and characteristics that may require public health action.
- Recombination: A process in which the genomes of two SARS-CoV-2 variants combine during the viral replication process to form a new variant that is different from both parent lineages. This may occur when a person is infected with two variants at the same time. The lineage that results from recombination is called a “recombinant.”
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Consider the following statements pairs
Variant Origin
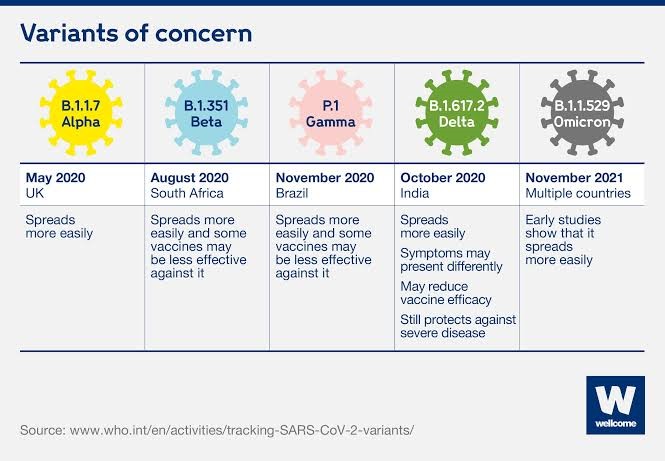
- Alpha variant India
- Beta variant South Africa
- Gamma Variant Brazil
- Delta India
How many of the above statements are correctly matched?
- Only one
- Only Two
- Only Three
- Al Four
Ans: C
|

https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/health/new-covid-strain-in-circulation-may-not-be-a-concern-for-india-91063












