Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- India's ethanol production program has seen significant progress in the last five years.
- Quantities supplied by sugar mills/distilleries to oil marketing companies (OMCs) have increased substantially.
- The program has diversified its raw material sources from cane molasses and juice to rice, damaged grains, maize, and millets.
Details
Ethanol and its Blending
- Ethanol is a high-purity alcohol that can be blended with petrol for fuel purposes.
- It differs from rectified spirit (94%) used in industries and extra neutral alcohol (96%) for potable liquor.
PM Modi's Announcement
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi announced that India has achieved 20% ethanol-blended petrol and aims for nationwide coverage by 2025.
- This move is part of India's efforts to promote ethanol as an eco-friendly and renewable fuel.
Cane Options and Ethanol Production
- Sugar mills traditionally produced ethanol from 'C-heavy' molasses, containing around 40-45% sugar.
- Mills can optimize sugar extraction to produce ethanol from 'B-heavy' molasses (50%-plus sugar) or ferment the entire cane's fermentable sugars into ethanol.
Diversification of Feedstocks
- Ethanol supplies have surged from 38 crore liters in 2013-14 to an estimated 559 crore liters in 2022-23.
- Feedstocks have diversified, including B-heavy molasses, direct sugarcane juice, rice, maize, and other foodgrains.
Ethanol Yields from Grains
- Ethanol yields from grains are higher than from molasses.
- Rice (450-480 liters/tonne), broken/damaged grains (450-460 liters/tonne), maize (380-400 liters/tonne), jowar (385-400 liters/tonne), and millets (365-380 liters/tonne) contribute to higher ethanol production.
Challenges in Grain Ethanol Production
- Ethanol production from grains involves a longer process of converting starch into sucrose and simpler sugars before fermentation.
- Molasses already contain sugars and are more straightforward to convert into ethanol.
Year-round Production with Multiple Feedstocks
- Leading sugar companies have installed distilleries that can operate on multiple feedstocks, enabling year-round production.
- This flexibility ensures a consistent ethanol supply throughout the year.
Differential Pricing Policy
- The government's policy of differential pricing incentivizes the use of various feedstocks by fixing higher prices for ethanol produced from B-heavy molasses and sugarcane juice/syrup.
- This compensates mills for reduced sugar production.
Boost in Ethanol Blending
- The policy boost has resulted in a significant increase in ethanol blending with petrol, reaching 11.75% in 2022-23 compared to 1.6% in 2013-14.
New Demand for Grains
- The incorporation of new feedstocks can create additional demand for grains like rice, barley, and millets.
- States like Uttar Pradesh and Bihar, known for sugarcane and maize, respectively, can contribute to "fueling India" with ethanol.
Byproduct Benefits
- Molasses-based distilleries have multi-effect evaporator (MEE) units that help in treating liquid effluent (spent wash).
- The concentrated wash can be used as boiler fuel, and the ash contains potash suitable for fertilizers.
- Grain distilleries produce distillers' dried grain with solubles (DDGS), a valuable animal feed product.
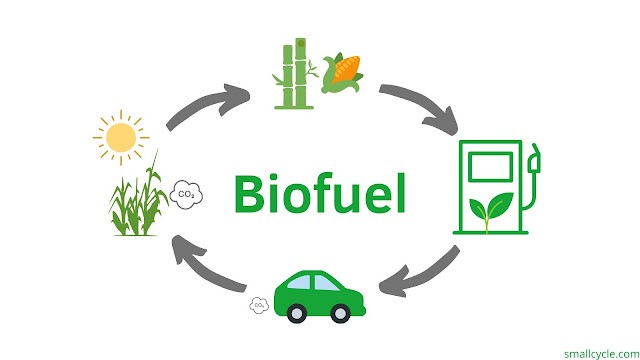
Biofuel
Definition
- Biofuels are renewable fuels derived from organic materials, such as plants and animal waste, rather than fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas.
- They are considered a greener alternative to conventional fuels because they reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote sustainability.
Purpose
- The main purpose of biofuels is to provide a cleaner and more sustainable source of energy to replace fossil fuels, which contribute significantly to climate change and environmental degradation.
- Biofuels also aim to reduce the dependence on imported oil and enhance energy security.
Types of Biofuels
- Ethanol: Produced from fermenting sugars and starches found in crops like corn, sugarcane, and wheat.
- Biodiesel: Made from vegetable oils, animal fats, or recycled cooking oil through a chemical process called transesterification.
- Biogas: Generated from the anaerobic decomposition of organic matter, such as agricultural waste, sewage, and landfill gas.
- Bioethanol: Derived from cellulosic biomass, such as wood, grasses, and agricultural residues, using advanced technologies.
.jpg)
Ethanol Blending
Meaning
- Ethanol blending refers to the practice of mixing a certain percentage of ethanol with conventional gasoline or petrol to create blended fuels.
- It is an effective way to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, improve air quality, and promote renewable energy usage in the transportation sector.
How it is done?
- Ethanol blending is achieved by mixing ethanol with gasoline in specific proportions.
- The most common blend is E10, which contains 10% ethanol and 90% gasoline.
- Blends like E15 (15% ethanol), E85 (85% ethanol), etc., are also used in certain regions depending on the suitability of vehicle engines.
Different Generations of Biofuels
- First Generation Biofuels
- Derived from food crops, such as sugarcane, corn, soybeans, and vegetable oils.
- Widely used and easily available, but criticized for potential competition with food production.
- Examples: Biodiesel, bioethanol, and vegetable oil-based fuels.
- Second Generation Biofuels
- Produced from non-food feedstocks like agricultural residues, woody biomass, and waste materials.
- Address concerns about food competition and offer more sustainable options.
- Examples: Cellulosic ethanol, biobutanol, and biofuels from algae.
- Third Generation Biofuels
- Focus on using microorganisms and algae to convert sunlight into biofuels through photosynthesis.
- Highly efficient in terms of land use and resource utilization.
- Examples: Algal biofuels and cyanobacterial biofuels.
- Fourth Generation Biofuels
- Utilize advanced technologies to engineer microorganisms for biofuel production.
- Aim for higher yields and cost-effectiveness compared to previous generations.
- Examples: Synthetic biology-based biofuels and genetically engineered biofuels.
Ethanol Blended Petrol (EBP) Programme
Implementation Scope
- The EBP Programme is implemented across India, except in the Union Territories of Andaman Nicobar and Lakshadweep islands.
- Oil Marketing Companies (OMCs) sell petrol blended with 10% ethanol to promote eco-friendly and renewable fuel.
Government Interventions for Increased Ethanol Production
- Since 2014, the government has taken multiple measures to boost indigenous ethanol production.
- These interventions include reintroducing the administered price mechanism, opening alternate routes for ethanol production, amending the Industries (Development & Regulation) Act for smooth ethanol movement, reducing GST on ethanol for EBP, differential pricing based on raw material, extending EBP nationwide, and interest subvention schemes.
Expanded Raw Materials for Ethanol Production
- In 2018-19, the EBP Programme allowed new raw materials for ethanol production, including B heavy molasses, sugarcane juice, sugar, sugar syrup, and damaged food grains (unfit for human consumption) like wheat and rice.
- Different ex-mill prices of ethanol were fixed based on the raw material used.
Increase in Ethanol Procurement
- The government's actions led to a significant increase in ethanol procurement by PSU OMCs.
- Ethanol procurement increased from 38 crore litres in ESY 2013-14 to 188.6 crore litres in ESY 2018-19, achieving an average blend percentage of 5.00% in ESY 2018-19.
Addressing Ethanol Distillation Capacity Constraint
- To achieve the target of 20% by 2030, the government identified a constraint in available ethanol distillation capacity.
- The Department of Food and Public Distribution (DFPD) introduced a Scheme to extend financial assistance to sugar mills for enhancing and augmenting ethanol production capacity.
Long Term Ethanol Procurement Policy
- The Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas (MoP&NG) issued a Long Term Ethanol Procurement Policy under the EBP Programme on 11th October 2019 to provide a strategic roadmap for achieving higher ethanol blending in petrol.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. How has the government's intervention and policy measures contributed to the increase in ethanol production? (150 Words)
|

https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-economics/the-ethanol-impetus-8856449/












