



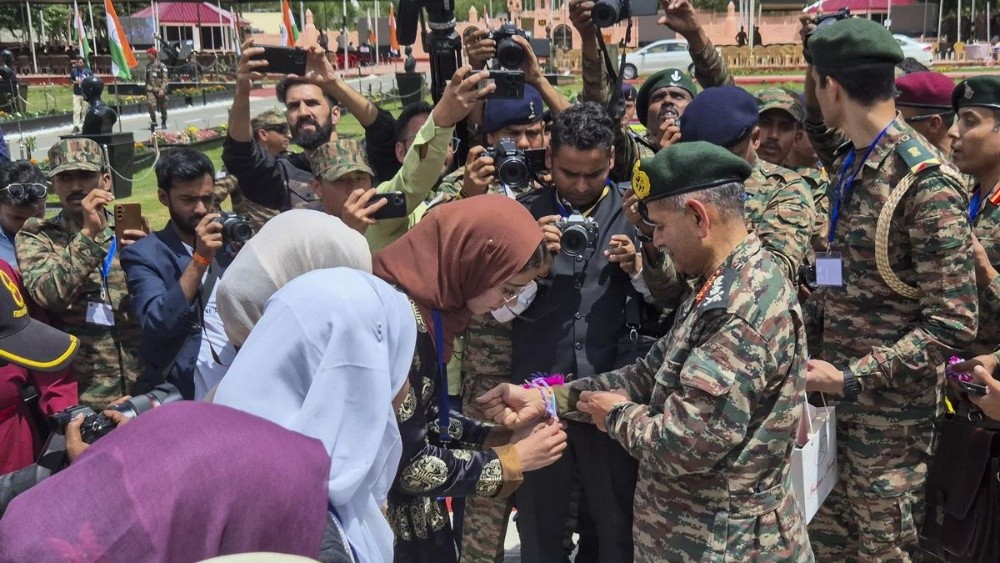
Exercise Surya Kiran is an annual joint military exercise between the Indian and Nepalese Armies, enhancing interoperability in jungle warfare, counter-terrorism, and disaster relief. The 18th edition, held in Saljhandi, Nepal, involves India's 11th Gorkha Rifles and Nepal's Srijung Battalion, reflecting robust defense ties and fostering bilateral relations.

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
The Indian Army contingent comprising more than 300 personnel departed for Nepal today to participate in the India-Nepal joint military exercise Surya Kiran.
Area |
Details |
|
Trade and Development |
Trade and Investment: India is Nepal's largest trading partner and source of foreign direct investment. Bilateral trade crossed $7 billion in 2019–2020 with a trade deficit in favor of India. |
|
Connectivity and Development Partnership: India supports Nepal's infrastructure development, including border infrastructure and cross-border rail links. |
|
|
$680 million line of credit from India for three major transmission corridors: Bheri Corridor, Nijgadh Inaruwa Corridor, and Gandak Nepalgunj Corridor. |
|
|
Dual Integrated Checkpoints (ICP) established at Rupaidiha, India, and Nepalgunj, Nepal in 2023. |
|
|
Revised transit treaty provides Nepal access to India's inland waterways. |
|
|
Political and Security |
Political Cooperation: Regular high-level visits and Nepal as a priority partner under India's "Neighbourhood First" policy. |
|
Defense Cooperation: Recruitment of Nepalese soldiers into the Indian Army's Gorkha regiments. |
|
|
Annual joint military exercise Surya Kiran conducted alternately by both countries. |
|
|
Multilateral Cooperation: Joint participation in BBIN, BIMSTEC, Non-Aligned Movement, SAARC, and the International Solar Alliance (ISA). |
|
|
Energy |
Energy Exchange Agreement: Since 1971, India and Nepal have exchanged energy to meet border area requirements. |
|
In 2023, India enabled the first tripartite electricity trade, allowing Nepal to export up to 40 MW of electricity to Bangladesh through India. |
|
|
Hydropower Cooperation: Long-standing collaboration in hydropower development. |
|
|
Other Areas |
Culture: Deep interpersonal relationships, especially along the border. Buddhist and Ramayana circuits under the Swadesh Darshan scheme connect Lumbini and Janakpur with Indian religious cities. |
|
Disaster Management: India conducted Operation Maitri as the first responder to Nepal's 2015 earthquake. |
|
|
Under the Vaccine Maitri Initiative, India supplied Covishield to Nepal. |
Source:
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q.India and Nepal share a unique defense relationship characterized by historical ties and strategic interests. Discuss the key features of this relationship and analyze its role in strengthening regional security and bilateral cooperation. (250 words) |










© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved