Description

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://www.thehindu.com/news/national/on-fire-safety-regulations-in-india-explained/article68226258.ece
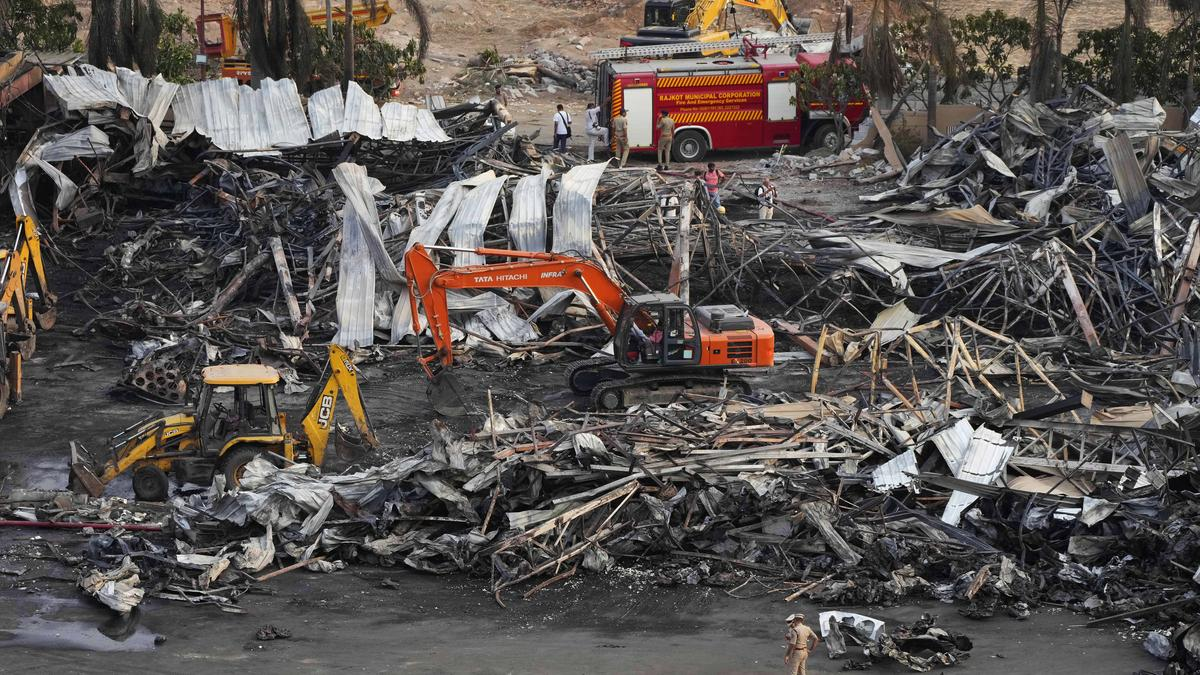
Context: The recent fires in Rajkot and Delhi highlight the urgent need for robust enforcement of fire safety regulations and compliance to prevent future tragedies.
Details
- A fire at the TRP Game Zone in Rajkot, Gujarat, killed at least 32 people, including children. The structure's metal frame and sheets contributed to the rapid spread of the fire, trapping many victims.
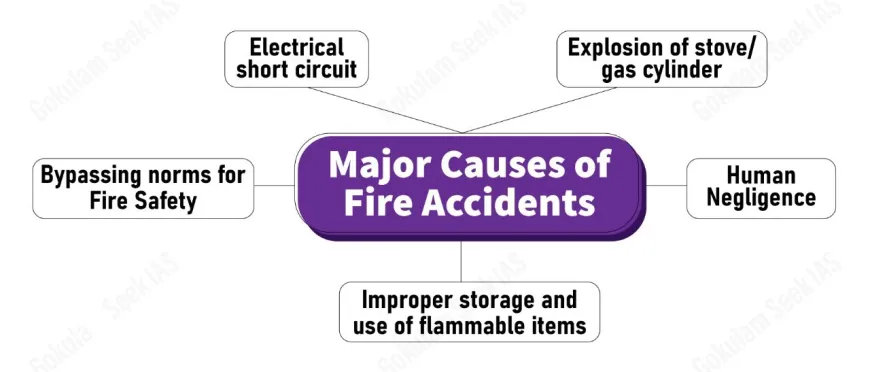
Fire Safety Importance
- Fire safety regulations are crucial in managing fire risks across various industry sectors, especially in a densely populated country like India. With daily reports of fire incidents causing loss of life, injuries, and property damage, these regulations play a significant role in ensuring public safety and mitigating potential hazards.
Growth in Construction and Fire Risks
- Over the past two decades, there has been significant growth in construction activities in India, particularly high-rise buildings. Fires in these structures are more complex to handle, complicating rescue and salvage operations and often resulting in higher casualties and property losses.
- Rapid industrial modernization has further complicated the fire safety scenario, highlighting the need for increased awareness and stringent safety measures.
Importance of Fire Safety Regulations
- Risk Management: Fire safety regulations are vital for managing the risk of fire incidents, which can result in loss of life, injuries, and significant property damage.
- Public Safety: With a dense population, India faces unique challenges in ensuring public safety. Fire safety regulations aim to mitigate these risks and protect individuals and communities.
- Property Protection: Fires can cause substantial damage to buildings, infrastructure, and assets. Regulations help minimise property losses and preserve economic resources.
- Complexity of High-Rise Fires: The growth of high-rise buildings presents specific challenges in fire management. Fires in these structures are more complex to handle, requiring specialised measures for rescue, salvage, and evacuation.
- Industrial Modernization: Rapid industrialization has increased the complexity of fire safety requirements. Regulations need to keep pace with technological advancements to address emerging risks.
Key Regulatory Frameworks
National Building Code (NBC), 2016
- The NBC, published by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), is the primary framework for fire safety regulations in India.
Important Features of NBC 2016
- Integrated Multidisciplinary Approach: Emphasises collaboration from conceptual stages through to construction and maintenance.
- Building Permit Reforms: Includes two-stage permits for high-rises and special buildings.
- Safety Certifications: Mandates periodic renewal certificates for structural, fire, and electrical safety.
- Empowering Engineers and Architects: Allows them to sanction plans for residential buildings up to 500 m².
- Town Planning Norms: Provides detailed guidelines for various public amenities.
- Parking Requirements: Revised for metro and megacities.
- Accessibility Provisions: Updated requirements for buildings and facilities for physically challenged individuals.
- Fire Safety Norms: Comprehensive updates on fire prevention, life safety, and fire protection.

Specific Provisions in NBC 2016
- Fire Zones: Demarcates zones and restricts construction to minimise fire risks.
- Building Classification: Based on occupancy type, height, and floor area.
- Fire Resistance: Requirements for structural and non-structural components.
- Means of Escape: Details on stairwells, fire escapes, and emergency exits.
- Fire Detection and Alarm Systems: Specifications for installation and maintenance.
- Firefighting Equipment: Standards for extinguishers, sprinklers, and hydrants.
- Handling Hazardous Materials: Regulations for storage and handling.
- Emergency Preparedness: Includes drills, training, and signage.
Other Provisions under different rules and regulation
- Factories Act and Rules (State-specific)
- Section 38: Obliges occupiers to prevent fire outbreaks, provide safe escape means, maintain firefighting equipment and train workers.
- Section 37: Details of measures to prevent explosion hazards.
- Petroleum and Explosives Safety Organization (PESO): Oversees safe handling, storage, and transportation of hazardous materials.
- Electrical Rules: Contain fire and safety requirements to prevent electrical fire-related accidents.
- Environment Protection Act of 1986: Indirectly addresses fire safety due to its impact on environmental safety.
- Chemical Accidents Rules, 1996: Provide guidelines for emergency planning, preparedness, and response for industries dealing with chemicals.
- Explosives Act and Rules: Regulate handling, storage, and transportation of explosives
- Disaster Management Act: Mandates fire safety measures in public buildings.
|
Fire safety audits are crucial for assessing and enhancing fire safety standards in buildings and workplaces. They help identify potential fire hazards, ensure compliance with the NBC and state-specific rules, and validate adherence to fire safety norms.
|
Conclusion
- India has a comprehensive set of fire safety rules and regulations aimed at preventing fire accidents. These regulations, covering various sectors such as factories, industries, schools, and hospitals, ensure that safety measures are in place to protect lives and property. Regular updates and adherence to these guidelines are crucial for maintaining high safety standards and preventing fire-related disasters.
Source:
The Hindu
consultivo
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. A wildfire is raging through a protected forest area, threatening the lives of both wildlife and nearby communities. As a member of the disaster management team, you have the authority to decide on the course of action. What ethical considerations should guide your decisions?
A) Utilitarianism: Maximise the overall well-being by prioritising human lives and property
B) Environmental ethics: Prioritise the protection of the natural habitat and wildlife
C) Justice: Ensure fair distribution of resources and assistance to affected communities
D) Beneficence: Act in the best interests of all stakeholders, including humans and animals
Answer: D
|















