Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Ernst & Young (EY) in collaboration with GIZ India, organized a panel at TERI School of Advanced Studies (TERI SAS) to discuss the future of floating solar photovoltaic (FSPV) technology in India.
Understanding Floating Solar PV Technology
- Floating solar PV plants represent an innovative approach to solar power generation, where photovoltaic panels are mounted on floating structures deployed on inland waterbodies like lakes, reservoirs, and ponds.
- This novel setup offers several advantages over traditional land-based solar installations. Notably, it minimizes land requirements by utilizing existing water surfaces and benefits from ambient cooling, which enhances the performance and efficiency of the solar panels.
Methodology for Assessing FSPV Potential in India:
- The methodology involves identifying perennial waterbodies characterized by year-round water availability, covering an estimated area of 30,404 square kilometers.
- Certain criteria, such as the proximity to 132 kilovolt substations and exclusion of waterbodies located in protected zones, are applied to determine suitable sites. This process results in an estimated resource area of approximately 7,751 square kilometers.
- The installation density for FSPV is calculated, with each megawatt peak (MWp) requiring a surface area of 0.015 square kilometers. Based on this density, the estimated FSPV potential for India is around 206 gigawatts (GW).
Environmental Considerations:
- Environmental concerns, particularly regarding biodiversity and aquatic life, are taken into account in the methodology.
- To minimize ecological disruption, the area allocated for FSPV installations is limited to 40% of the total waterbody area. This approach aims to ensure sustainable development while maximizing the potential for renewable energy solutions.
Advantages & Challenges of Floating Solar PV Technology
Advantages of Floating Solar PV:
- Leveraging waterbodies for solar power generation provides a dual land use solution, optimizing space utilization and minimizing environmental impact.
- The natural cooling effect of water enhances energy efficiency, leading to higher generation compared to land-based installations.
- Potential benefits include reducing water evaporation and preserving aquatic ecosystems, making floating solar a sustainable and environmentally friendly energy solution.
Challenges Facing Floating Solar:
- Despite its promise, floating solar encounters several challenges that require attention.
- Technological feasibility, site selection criteria, environmental impact assessments, regulatory frameworks, and financing constraints emerged as key hurdles.
- Addressing these challenges necessitates parallel interventions through policy measures, technological improvements, and studies on the impact on aquatic life. This comprehensive approach is vital for fostering the widespread adoption of floating solar in India's renewable energy landscape.
Floating Solar PV Technology in India
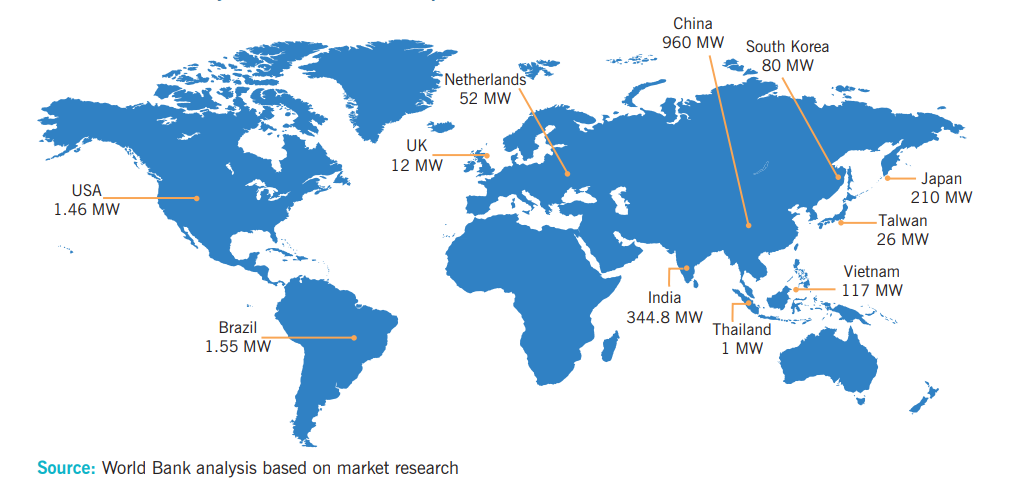
- India boasts of the potential capacities of 280-300 GW in floating solar power. However, only a small fraction of its estimated potential has been installed in the states of Madhya Pradesh, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, Telangana, Bihar and Rajasthan.
Overcoming Barriers
- At present, the cost of generating floating solar power in India is higher than from ground-mounted installations due to several reasons.
- The eligibility criteria for a floating solar site are unclear and manufacturing capacity for floating solar equipment is limited. In addition, the standards and certifications required to install a plant are not comprehensive.
How can we accelerate the pace of adoption and maximize the benefits of floating solar?
- Firstly, establish clear targets for floating solar capacity to establish the country's overall solar energy goals.
- Create a repository of potential sites for floating solar projects to give a positive signal to the market and streamline the project development process.
- Promote the manufacturing of floating solar equipment and standardize procedures and certifications to ensure quality.
- Invest in institutions to conduct reliable feasibility surveys for successful floating panel projects.
Policy & Technological Perspectives on Floating Solar PV
Policy Frameworks and Regulatory Processes:
- Clear policy frameworks and streamlined regulatory processes are crucial for floating solar deployment.
- There is huge importance of comprehensive policies incentivizing investment in floating solar while ensuring environmental sustainability and stakeholder engagement.
- Suggestions included integrating floating solar targets into national and state-level renewable energy policies, streamlining approval processes, and providing financial incentives to boost investment in floating solar infrastructure.
Technological Innovation:
- Ongoing research and development initiatives are essential for advancing floating solar photovoltaic technology.
- Focus areas include improving efficiency, durability, cost-effectiveness, and minimizing maintenance of FSPV systems.
- Key technological advancements needed encompass floating platform design, solar panel technology, mooring systems, and environmental monitoring tools.
- Pre-feasibility studies and accurate data on wind, solar resources, water levels, and quality are crucial for informed decision-making and project planning.
Towards the future
- As costs continue to decline and technological advancements improve efficiency, we can anticipate a significant uptick in floating solar projects across India, driving a greener future for generations to come.
- Globally, deploying floating solar panels on existing hydropower reservoirs could meet 50% of the world’s total demand for electricity. Realizing this, several countries have started deploying this technology. However, floating solar still has a long way to go. W
- hile the global installed capacity of ground mounted solar is more than 1,000 GW, it is less than 10 GW for floating solar.
- India’s experience as a pioneer in floating solar technology in South Asia could thus provide valuable lessons for other countries to follow.

Conclusion:
- FSPV technology holds significant promise for India's renewable energy future, offering unique advantages and solutions to energy and environmental challenges.
- Realizing its potential requires collaborative efforts from policymakers, industry stakeholders, researchers, and the community to overcome barriers and unlock its full benefits.
- With concerted efforts, floating solar can contribute substantially to meeting India's growing energy needs in a sustainable manner, paving the way for a brighter energy future.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Evaluate the potential and challenges of floating solar photovoltaic (FSPV) technology in India. Discuss its significance for India's energy transition and propose strategies to overcome obstacles to its adoption.
|
SOURCE: DOWN TO EARTH















