Description

Copyright infringement not intended.
Context:
- India’s largest floating solar power project, spanning over 600 acres, is now fully operational at Ramagundam in Peddapalli district of Telangana.
Floatovoltaics:
- Floating solar or floating photovoltaics (FPV), sometimes called floatovoltaics, is solar panels mounted on a structure that float on a body of water, typically a reservoir or a lake. The costs for a floating system are 20-25% higher than for ground-mounted systems.
- The first floating photovoltaic system was built in Japan in 2007. Currently, the world’s largest floating solar farm is in Shandong, China.
Floating Solar Power Plants in India:
- In recent years, floating solar power plants have become part of India’s plans to achieve a national target of 100 GW solar capacity by 2022.
- According to a 2020 study by think tank The Energy and Resources Institute (TERI), reservoirs cover 18,000 square kilometres in India and can generate 280 GWthrough floating solar panels.
- India launched the National Solar Mission in 2010 to tap sources of renewable energy. According to a study done by TERI in association with the Energy Transmission Commission India programme, 7 MW capacity floatovoltaic projects were in operation as of 2019, while over 1.7 GW were in various stages of development. The Government plans to establish a renewable energy capacity of 500 GW by 2030.
|
NTPCS FLOATING SOLAR PROJECTS:
The NTPC, with a target to produce 60 GW capacity through renewable sources by 2032, said it already commissioned 222 MW of floating solar projects, with another 40 MW in the construction stage. So far, the NTPC has installed floating solar plants on reservoirs at Kayamkulam in Kerala (92 MW) and Simhadri in Andhra Pradesh (25 MW). The world’s largest floating 600 MW solar energy project is being constructed on the Omkareshwar dam in the Khandwa district of Madhya Pradesh, covering approximately 2000 hectares. Projects at Getalsud in Jharkhand, Rihand reservoir in UP, and Vaitarna in Maharashtra have also been cleared. The project in Ramagundam, Telangana is the country’s largest floating solar power project.
|
.jpeg)
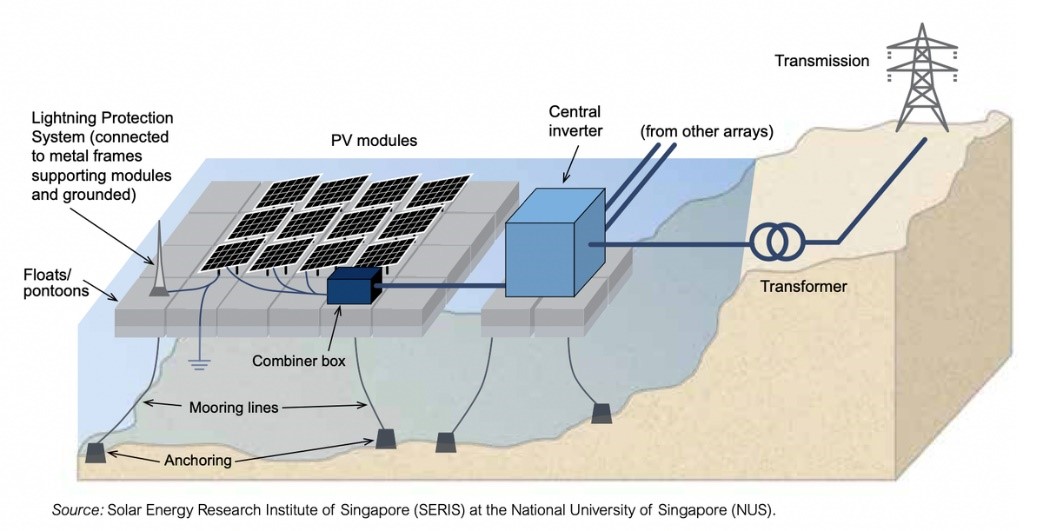
Working of a Floating Solar Plant
- A network of floating solar panels, or photovoltaics/floatovoltaics are mounted on a structure that is made to float on the surface of a water body. This could be a reservoir, lake, irrigation canal, or pond.
- Usually, a floating solar plant will have :-
-a floating system,
-a mooring structure to prevent panels from moving freely in water and to keep it near the shore,
-a photovoltaic system to generate electricity using thermal energy, and
-an underwater cable to transfer the generated power to a substation.
Advantages of Floating Solar Panel Farms
- Solar power is the cheapest electricity in history, as per an International Energy Agency (IEA) report.
- Besides constraints pertaining to land, scientists feel that ground-mounted solar panels are unable to function at their full potential as they heat up. This is where the floating solar technology has an edge even though such farms are comparatively more expensive.
Some advantages of floating solar power projects include
- No land occupancy: The main advantage of floating PV plants is that they do not take up any land, except the limited surfaces necessary for electric cabinet and grid connections. Their price is comparable with land-based plants, but floatovoltaics provide a good way to avoid land consumption.
- Installation and decommissioning: Floating PV plants are more compact than land-based plants, their management is simpler and their construction and decommissioning straightforward. The main point is that no fixed structures exist like the foundations used for a land-based plant so their installation can be totally reversible.
- Water conservation and water quality: Partial coverage of water basins can reduce water evaporation. This result depends on climate conditions and on the percentage of the covered surface. In arid climates such as parts of India, this is an important advantage since about 30% of the evaporation of the covered surface is saved.
- Increased panel efficiency due to cooling: the cooling effect of the water close to the PV panels leads to an energy gain that ranges from 5% to 15%. Natural cooling can be increased by a water layer on the PV modules or by submerging them, the so-called SP2 (Submerged Photovoltaic Solar Panel). In these cases, the global PV module's efficiency rises thanks to the absence of thermal drift.
- Tracking: Large floating platforms can easily be rotated horizontally and vertically to enable Sun-tracking (similar to sunflowers). Moving solar arrays uses little energy and doesn't need a complex mechanical apparatus like land-based PV plants. Equipping a floating PV plant with a tracking system costs a little extra while the energy gain can range from 15% to 25%.
- Higher efficiency: Like any other electrical equipment, solar panels operate more efficiently when kept cold. According to the Environmental and Energy Study Institute, floating solar farms can be up to 15 percent more efficient than those on the ground due to the cooling effect of the water beneath the panels. As a coolant, water maintains the temperature of solar panels which eventually prevents loss of energy due to higher temperatures. Also, since they are deployed on the water's surface, it is convenient to clean and move the network in the direction of sunlight.
- Reduces Environment Threats: Floating solar farms, if designed and deployed appropriately, reduce the threat posed by climate change to water bodies. Floating panels can offset climate change by 10 years, according to the WEF report. A floating solar farm that reduces wind speed and solar radiation by 10 percent across the entire lake could offset a decade of warming from climate change. Designs that shaded the lake more than sheltered it, by reducing sunlight more than wind, had the greatest cooling effect. Evaporation fell and the lake was mixed more frequently, which helps oxygenate the deeper water. Also, solar panels prevent the growth of algae in the water, which improves its quality. Algal blooms, a serious problem in industrialized countries, may be reduced. The partial coverage of the basins and the reduction of light on biological fouling just below the surface, together with active systems, can solve this problem.
Conclusion
- More and more countries are switching to eco-friendly methods of producing electricity to make their energy portfolio cleaner and greener to tackle climate change.
- Power generation technology using floating solar panels has proved to be an efficient and fast-growing approach toward clean energy, especially in countries where land is scarce.
.jpeg)
https://www.thehindu.com/sci-tech/science/a-clear-picture-of-how-mercury-becomes-a-superconductor/article66346400.ece












