Description

Figure 1: No Copyright Infringement Intended
Context:
- Recently, government has announced the fortification of rice distributed under various government schemes, including the public distribution system (PDS) and midday meals in schools, by 2024.
Details:
- Government has issued uniform parameters for fortified rice kernels (FRK) for grade ‘A’ and common rice.
- The specifications for fortified rice have been issued by the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution.
- The department issued the uniform specifications of food grains for Central Pool procurement for the ensuing Kharif Marketing Season (KMS) 2020-21.
- The State Governments are requested to ensure that wide publicity of the Uniform Specifications is made among the farmers to ensure that they get due price for their produce and any rejection of the stocks is completely avoided.
Need for Fortified Rice:
- Fortified rice helps in tackling Malnutrition and lack of essential nutrients in poor women and poor children.
- It will also help in mitigating global hunger index.
Process of Fortification of Rice:
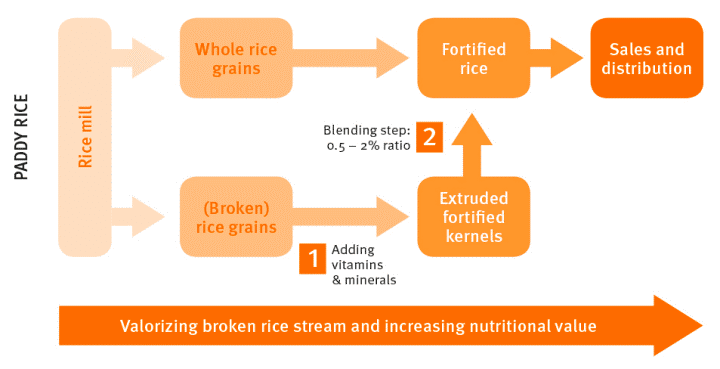

About Fortification:
FSSAI defines fortification as “deliberately increasing the content of essential micronutrients in a food so as to improve the nutritional quality of food and to provide public health benefit with minimal risk to health”.
About Fortified Rice:
- 1 kg fortified rice will contain iron (28 mg-42.5 mg), folic acid (75-125 microgram) and Vitamin B-12 (0.75-1.25 microgram).
- In addition, rice may also be fortified with micronutrients, singly or in combination, with zinc(10 mg-15 mg), Vitamin A (500-750 microgram RE), Vitamin B1 (1 mg-1.5 mg), Vitamin B2 (1.25 mg-1.75 mg), Vitamin B3 (12.5 mg-20 mg) and Vitamin B6 (1.5 mg-2.5 mg) per kg.
About FSSAI:
- Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) is an autonomous body established under the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India.
- The FSSAI has been established under the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006, which is a consolidating statute related to food safety and regulation in India.
- FSSAI is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the regulation and supervision of food safety.













