




Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: www.alzheimercalgary.ca
Context: An international team of researchers, which includes specialists from Indiana University School of Medicine, has discovered a protein that is present in the brains of patients with frontotemporal dementia (FTD). This discovery reveals a new potential target for developing treatments for FTD.
Details
Key Points
Implications
Frontotemporal dementia
Diagnosis
Cure
|
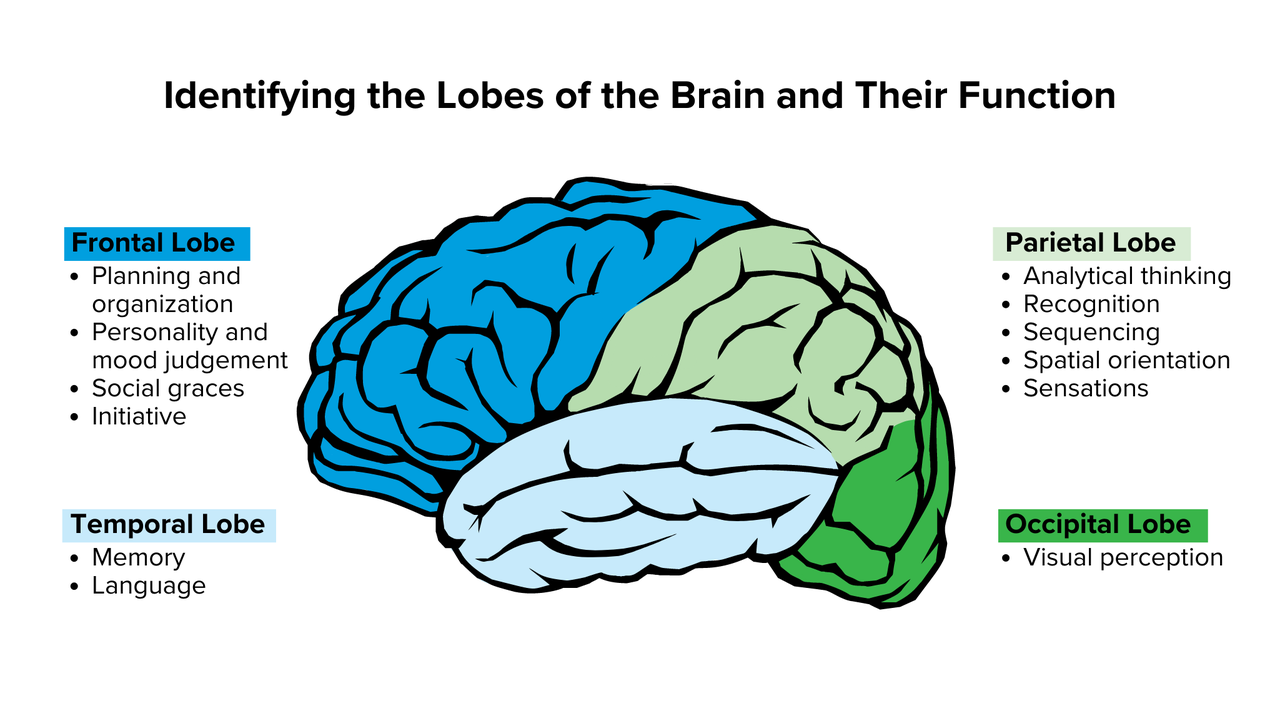
Human Brain ●The human brain can be divided into three main parts: the cerebrum, the cerebellum, and the brainstem. Each part has a different role and is made up of several subparts. Cerebrum ●The cerebrum is the largest and most visible part of the brain. It occupies the upper part of the skull and consists of two hemispheres (left and right) that are connected by a bundle of nerve fibres called the corpus callosum. ●It is covered by a thin layer of grey matter called the cerebral cortex, which has many folds and grooves to increase its surface area. ●The cerebral cortex is responsible for higher cognitive functions such as reasoning, language, creativity, and problem-solving. It also processes sensory information from the eyes, ears, nose, skin, and other organs. Cerebellum ●The cerebellum is located at the lower back of the brain, below the cerebrum. It is smaller than the cerebrum but has more neurons (nerve cells). ●It is responsible for coordinating movement, balance, posture, and fine motor skills. It also plays a role in learning and memory. Brainstem ●The brainstem is located at the base of the brain, where it connects to the spinal cord. It consists of three parts: the midbrain, the pons, and the medulla oblongata. ●The brainstem is responsible for controlling vital functions such as breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, swallowing, coughing, sneezing, and vomiting. It also regulates sleep cycles and consciousness.
|
Conclusion
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. What is the role of the TAF15 protein in Frontotemporal Dementia (FTD)? A) It causes vascular abnormalities in the brain. B) It forms amyloid filaments in nerve cells. C) It regulates neurotransmitter release. D) It induces inflammation in the brain. Answer: B Explanation: Research indicates that TAF15 protein plays a role in the development of amyloid filaments in individuals with FTD. |






© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved