
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- The National Statistical Office (NSO), Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation released estimates of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) for the April-June quarter (Q1) of 2022-23, both at Constant (2011-12) and Current Prices.
Findings
- Real GDP or Gross Domestic Product (GDP) at Constant (2011-12) Prices in Q1 2022-23 is estimated to attain a level of Rs 36.85 lakh crore, as against Rs 32.46 lakh crore in Q1 2021-22, showing a growth of 13.5 percent as compared to 20.1 percent in Q1 2021-22.
- Nominal GDP or GDP at Current Prices in Q1 2022-23 is estimated at Rs 64.95 lakh crore, as against Rs 51.27 lakh crore in Q1 2021-22, showing a growth of 26.7 percent as compared to 32.4 percent in Q1 2021-22.
What is GDP of a country?
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the final monetary value of the goods and services produced within the country during a specified period of time, normally a year.
- In simple terms, GDP is the measure of the country's economic output in a year. In India, contributions to GDP are mainly divided into three broad sectors — agriculture, industry, and services.
- GDP is measured over market prices and there is a base year for the computation. The GDP growth rate measures how fast the economy is growing. It does this by comparing the country's gross domestic product in one quarter with that in the previous one, and with the same quarter of the previous year.
- Thus, GDP is measured over specific time frames, such as a quarter or a year.
- GDP as an economic indicator is used worldwide to show the economic health of a country.
- For low-income or middle-income countries, high year-on-year GDP growth is essential to meet the growing needs of the population. Hence, the GDP growth rate of India is an essential indicator of the country’s economic development and progress.
- Besides measuring the health of the economy and helping the government is framing policies, the GDP growth rate numbers are also useful for investors in better decision-making related to investments.
- Different countries have different methods to calculate GDP.
Components
- The GDP growth rate is driven by GDP’s four components. The main driver is personal consumption, which includes the critical sector of retail sales.
- The second component is business investment, including construction and inventory levels.
- The third is government spending whose largest categories are social security benefits, defence spending, and medicare benefits.
- The government often increases spending to jump-start the economy during a recession. The fourth is net trade.
- When the economy is expanding, the GDP growth rate is positive. If the economy grows, so do businesses, jobs and personal income. If it contracts, then businesses hold off investing in new purchases. They delay hiring new employees until they are confident that the economy will improve. Those delays further depress the economy. Without jobs, consumers have less money to spend. If the GDP growth rate turns negative, the country's economy is said to be in a state of recession.
- The GDP growth rate is the most important indicator of economic health. It changes during the four phases of the business cycle — peak, contraction, trough, and expansion.
Nominal vs Real
- Nominal GDP is the value of all final goods and services that an economy produces during a given year; it is not adjusted for inflation. It is calculated by using the prices that are current in the year in which the output is produced. Nominal GDP takes into account all of the changes that occurred for all goods and services produced during the year. If prices change from one period to the next and the output does not change, the nominal GDP would change even though the output remained constant.
- Real GDP, on the other hand, is the total value of all final goods and services that the economy produces during a given year, accounting for inflation. It is calculated using the prices of a selected base year. To calculate Real GDP, you must determine how much of GDP has been changed by inflation since the base year, and divide out the inflation each year. Real GDP, therefore, accounts for the fact that if prices change but output doesn’t, nominal GDP would change.
- In January 2015, the government moved to the new base year of 2011-12 from the earlier base year of 2004-05 for national accounts. The base year of national accounts had previously been revised in January 2010.
- In the new series, the Central Statistics Office (CSO) did away with GDP at factor cost and adopted the international practice of valuing industry-wise estimates in gross value added (GVA) at basic prices.
How is GDP calculated in India?
- The Central Statistical Office, or CSO,is responsible for compiling data for calculating GDP.
- It aggregates the GDP data by coordinating with several federal and state-run agencies.
- Once the data collection process is completed, the task of calculating the GDP begins. There are two methods to arrive at the GDP number:
- Known as GDP at factor cost, the first method looks at the economic activity.
- The second method is the expenditure-based method (at market prices).
- Further, the nominal GDP is calculated using the current market price, and real GDP is arrived after adjusting inflation.
- Among the four sets of GDP numbers, GDP at factor costis the most commonly used figure and reported in the media.
- While the GDP at factor cost reveals which industry sector is doing well, the expenditure-based GDP is indicative of the status of different areas of the economy; how the trade is doing or whether investments are on the decline.
GDP can be measured by three methods, namely,
Output Method
This measures the monetary or market value of all the goods and services produced within the borders of the country. In order
to avoid a distorted measure of GDP due to price level changes, GDP at constant prices o real GDP is computed. GDP (as per
output method) = Real GDP (GDP at constant prices) – Taxes + Subsidies.
Expenditure Method
This measures the total expenditure incurred by all entities on goods and services within the domestic boundaries of a country.
GDP (as per expenditure method) = C + I + G + (X-IM) C: Consumption expenditure, I: Investment expenditure, G: Government
spending and (X-IM): Exports minus imports, that is, net exports.

Income Method
It measures the total income earned by the factors of production, that is, labour and capital within the domestic boundaries of a
country. GDP (as per income method) = GDP at factor cost + Taxes – Subsidies.
From where is the GDP data sourced?
- For the calculation of GDP at factor cost, data is taken from eight sectors, namely agriculture; mining and quarrying; manufacturing; forestry and fishing; electricity and gas supply; construction, trade, hotel, transport and communication; financing, real estate and insurance; and business services and community, social and public services.
- For the calculation of expenditure-based GDP, all the spending incurred on final goods and services are addedthat include consumer spending, government spending, business investment spending, and net exports.
- The government releases quarterly GDP numbersevery two months, and the final numbers for the whole year are issued on May 31.
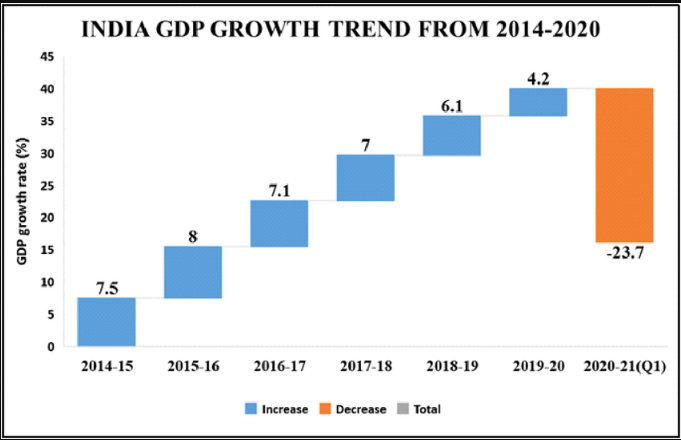
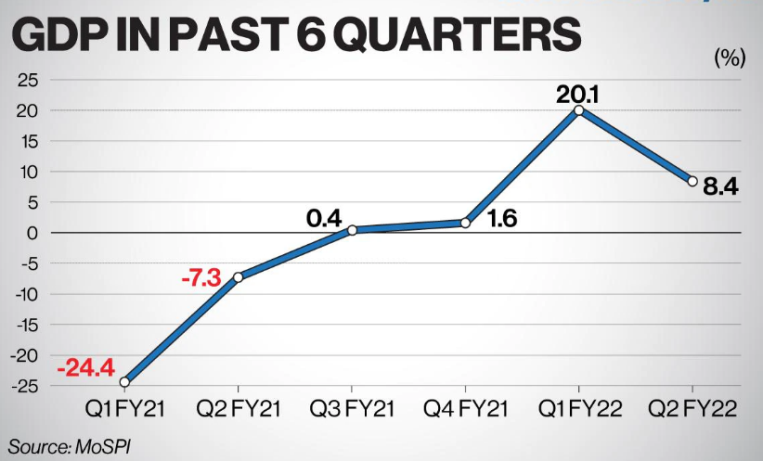
National Statistical Office (NSO) pegged the country's growth for 2021-22 at 8.9 per cent.
National Statistical Office (NSO) pegged the country's growth for 2021-22 at 8.9 per cent.
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1855789















