





Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
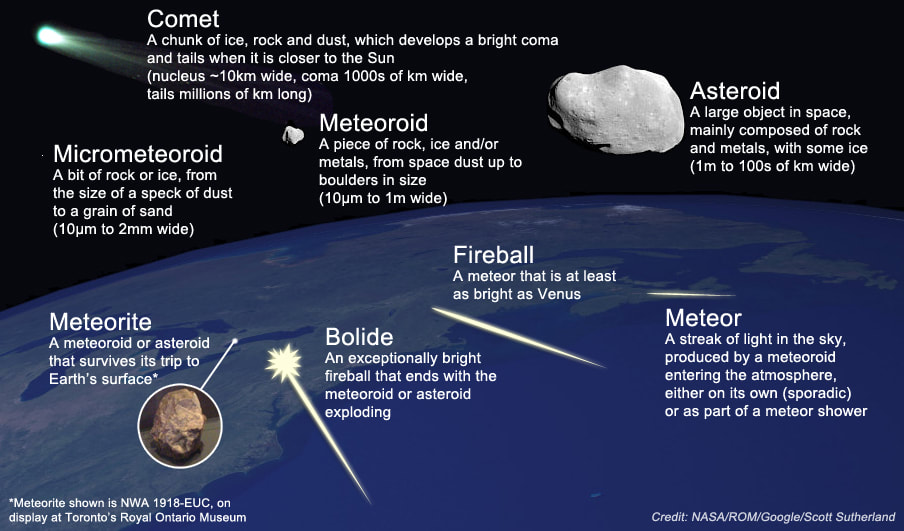
Meteor Shower
.jpg)
Geminids
https://indianexpress.com/article/technology/science/geminids-geminid-meteor-shower-2022-8322005/






© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved