Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Elon Musk’s Starlink has lost dozens of satellites that were caught in a geomagnetic storm a day after they were launched.
- Up to 40 of the 49 satellites were impacted, causing them to fall from orbit before they could be commissioned.
Solar storms/flares
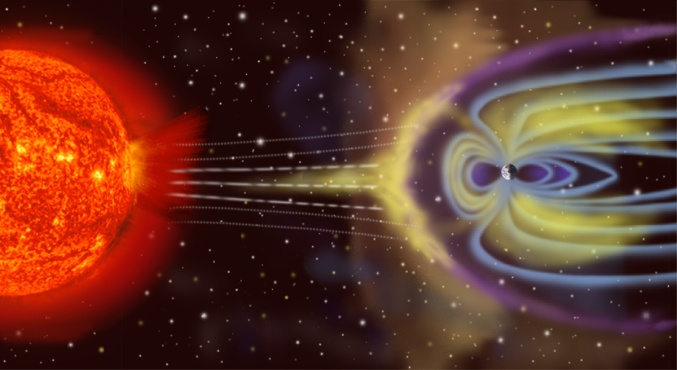
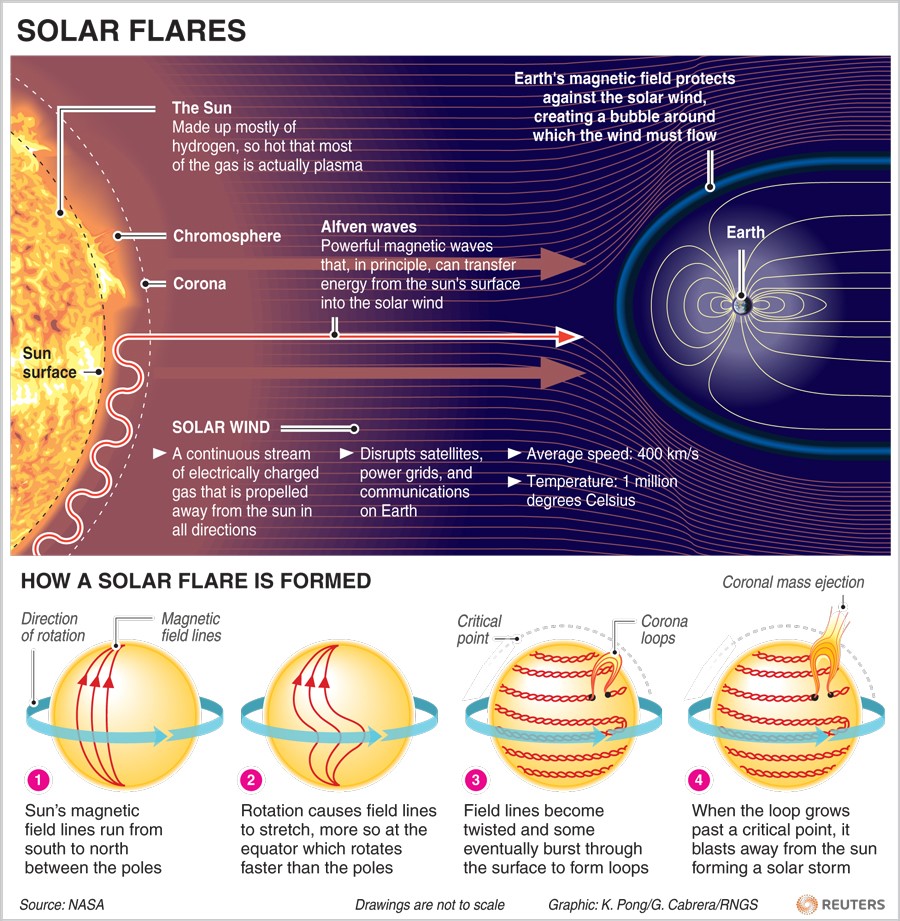
- About: Solar storms are magnetic plasma ejected at great speed from the solar surface.
- Occurrence: They occur during the release of magnetic energy associated with sunspots (‘dark’ regions on the Sun that are cooler than the surrounding photosphere), and can last for a few minutes or hours.
|
What is a sunspot?
It’s an area of intense magnetic activity on the surface of the Sun—a storm—that appears as an area of darkness.
Sunspots are indicative of solar activity, giving birth to solar flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs).
Sunspots have been continuously counted each day since 1838.
This has allowed solar scientists to describe a repeating pattern in the wax and wane of activity on the Sun’s surface—the solar cycle.
|
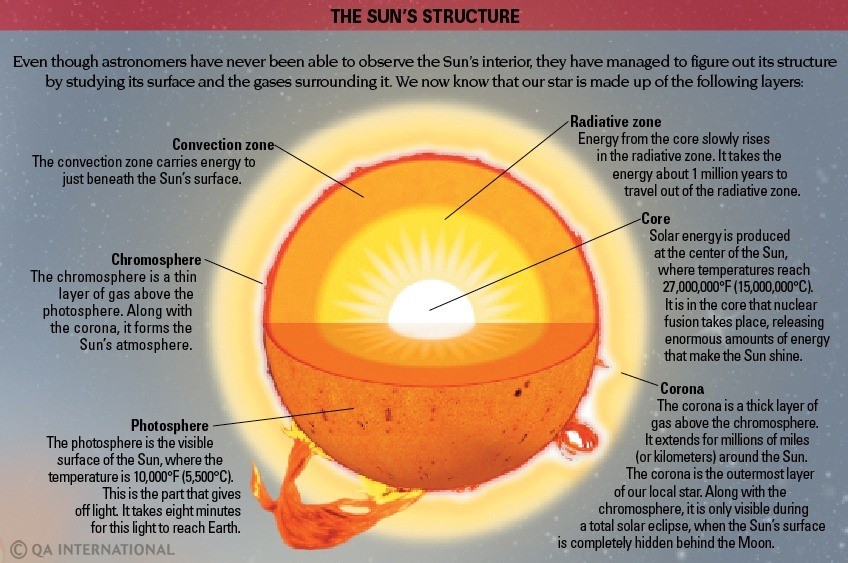
To read more about the sun, visit: https://www.iasgyan.in/blogs/structure-of-the-sun
Impact of Solar Flares on Earth
Not all solar flares reach Earth, but solar flares/storms, solar energetic particles (SEPs), high-speed solar winds, and coronal mass ejections (CMEs) that come close can impact space weather in near-Earth space and the upper atmosphere.
- Space-dependent services: Solar storms can hit operations of space-dependent services like global positioning systems (GPS), radio, and satellite communications.
- Radio communication: Geomagnetic storms interfere with high-frequency radio communications and GPS navigation systems.
- Magnetosphere: CMEs, with ejectiles loaded with matter travelling at millions of miles an hour, can potentially create disturbances in the magnetosphere, the protective shield surrounding the Earth.
- Astronauts: Astronauts on spacewalks face health risks from possible exposure to solar radiation outside the Earth’s protective atmosphere.
- Other: Aircraft flights, power grids, and space exploration programmes are vulnerable.
|
Do you know?
A solar storm in March 1989 caused a nine-hour blackout Hydro-Québec's electricity transmission system in Canada.
|
Final Thought
- With the increasing global dependence on satellites for almost every activity, there is a need for better space weather forecasts and more effective ways to protect satellites.
https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/geomagnetic-storm-that-killed-starlink-sats-7764995/
















