Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
The challenges faced by the Ghaggar River and its tributaries.
Details
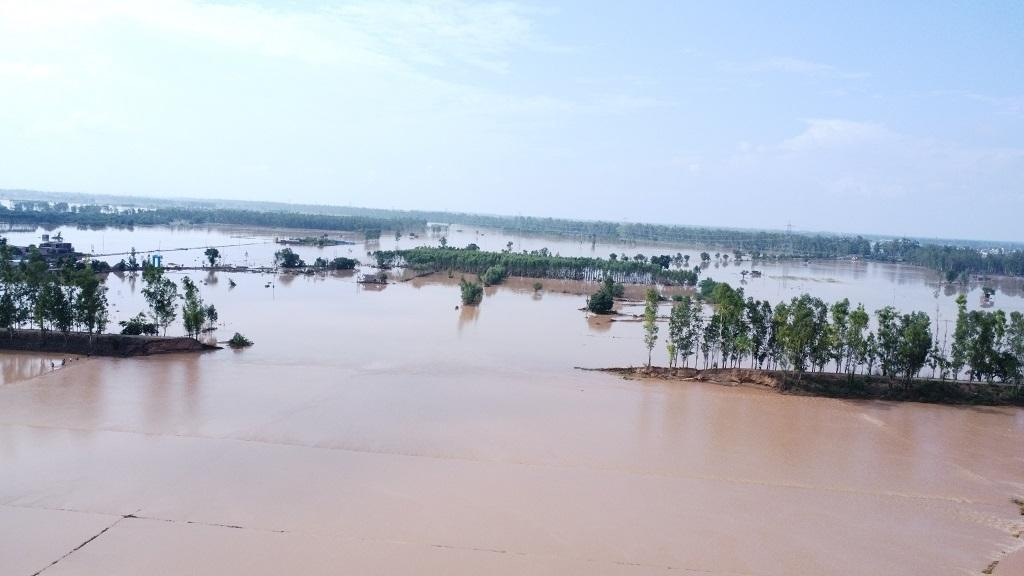
- The Ghaggar River and its tributaries, including Tangri and Markanda rivers, have faced significant flooding issues in Haryana, Punjab, and Rajasthan.
- Encroachment and lack of maintenance of river embankments contribute to the severity of the problem.
Impact of Tangri River Flooding
- Tangri River breached its embankment, causing flooding in approximately 50 villages in Ambala district, Haryana.
- Neglecting small rivers like Tangri and poor embankment maintenance leads to avoidable problems.
Ghaggar River and Its Tributaries
- The Ghaggar River and its tributaries, including Kaushalya, Tangri, Markanda, Beghna, and Sukhna, originate in the Shivalik foothills of Haryana, Punjab, and Chandigarh.
- Encroachment and reduced floodplain areas have transformed these perennial rivers into seasonal ones.
Flooding and River Erosion
- Heavy monsoon rains in the Shivalik hills result in flash floods in the Ghaggar River and its catchment areas.
- Floods have affected cities such as Panchkula, Derabassi, Ambala, and Shahabad, leading to infrastructure damage and displacement of people.
Encroachment and Urbanization
- The Ghaggar River is heavily encroached upon as it passes through rural areas of Haryana and urban areas like Panchkula and Derabassi.
- Settlements and residential colonies have encroached upon riverbanks, obstructing the natural flow of water.
Damage and Impact
- The Ghaggar River has transformed into a drain due to encroachment and lack of maintenance.
- Flooding and erosion have caused significant damage to villages along the Punjab-Haryana border, affecting both states.
- Infrastructure, including the National Highway connecting Sangrur to Delhi, has been affected by the river's waters.
Environmental Consequences
- Unscientific and illegal mining activities have also harmed the Ghaggar River and its ecosystem.
- Absence of embankment construction in recent years and unregulated mining have disrupted the natural balance of the rivers.
Urgent Need for Restoration and Management
- To mitigate flooding and erosion, restoration of the rivers' natural flow and floodplains is necessary.
- Measures must be taken to address encroachment, maintain embankments, and regulate mining activities.
- Stakeholders should focus on sustainable management and the preservation of the Ghaggar River basin.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q) Examine the causes and consequences of flooding and encroachment in the Ghaggar River basin. (150 words)
|

https://www.downtoearth.org.in/news/natural-disasters/a-dead-ghaggar-and-its-tributaries-wrought-havoc-in-haryana-early-july-here-is-how-90671