Description

Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://nsidc.org/learn/ask-scientist/what-are-glacial-lakes
Context: The recent announcement by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) about the huge growth of glacier lakes in the Himalayas is an important development that provides information about the changing landscape of this environmentally sensitive region.
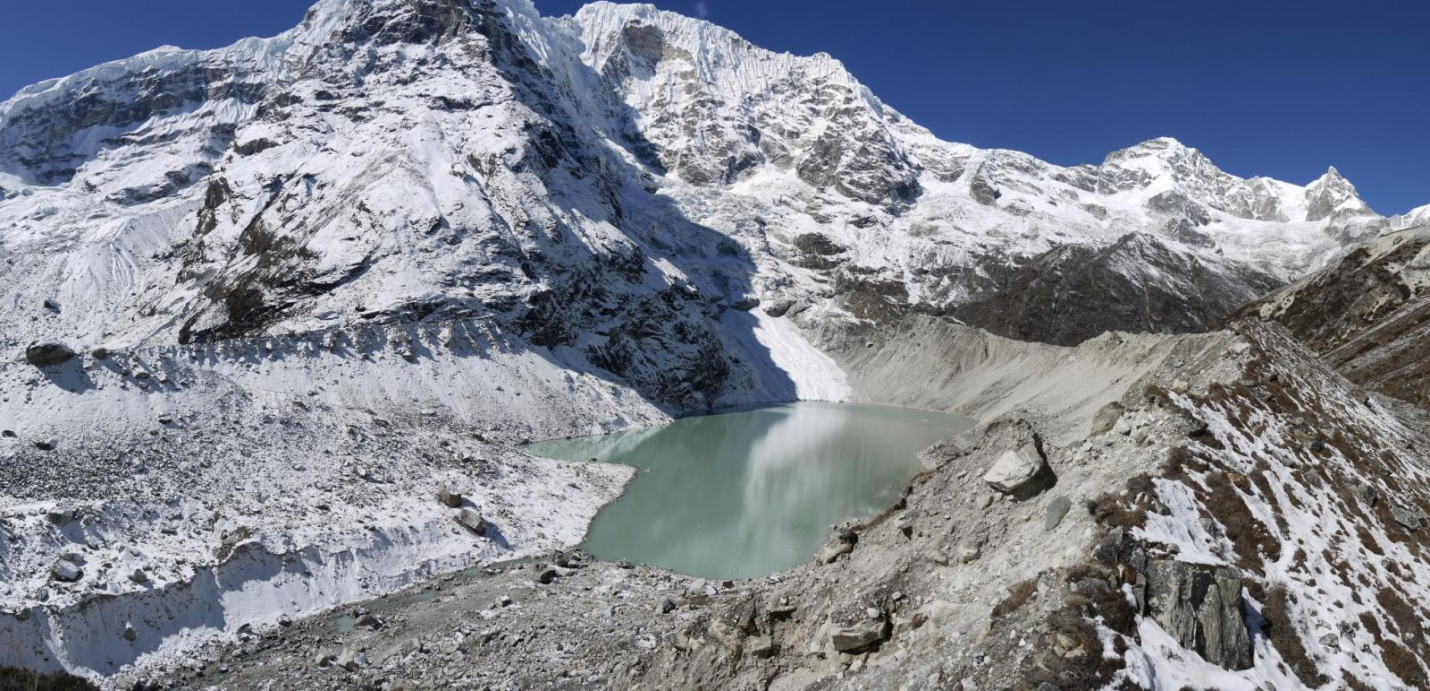
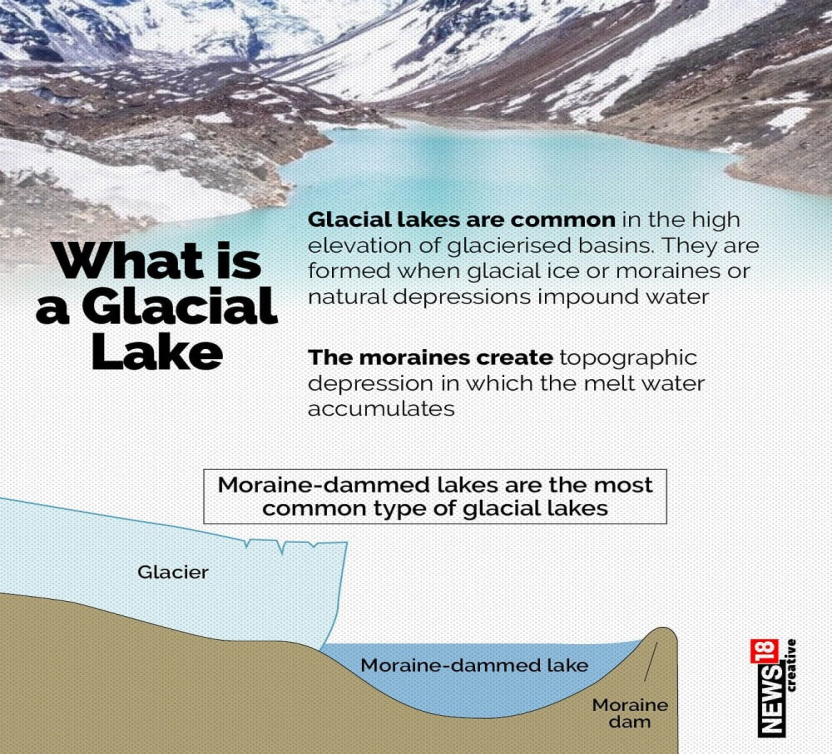
About Glacial Lakes
- Glacial lakes are bodies of water that originate from glacial activity. They form when glaciers erode the land and subsequently melt, filling depressions created by glacial movements.
- The formation of these lakes is a direct result of the retreat of glaciers that occurred near the end of the last glacial period, approximately 10,000 years ago.
- As glaciers receded, they left behind large deposits of ice in hollows between drumlins or hills. The melting of these ice deposits led to the formation of glacial lakes.
Scope of the Study and Findings
- ISRO's study covered a substantial period from 1984 to 2023, utilising long-term satellite imagery to monitor changes in glacial lakes across the Indian Himalayan river basins.
- The study identified a notable expansion in more than 27% of the identified glacial lakes since 1984, with 130 of these lakes situated within India.
- Among the lakes larger than 10 hectares identified during 2016-17, 676 glacial lakes have shown significant expansion, with 601 lakes having grown more than twice their original size.
Distribution and Characteristics of Glacial Lakes
- The expanding glacial lakes are distributed across different river basins, including the Indus, Ganga, and Brahmaputra basins.
- Elevation-based analysis revealed that a significant number of expanding lakes are situated in the higher altitude ranges, particularly in the 4,000-5,000-metre and above 5,000-metre categories.
Formation and Types of Glacial Lakes
- Glacial lakes are categorised based on their formation process, including moraine-dammed, ice-dammed, erosion, and other glacial lakes.
- The majority of the expanding lakes are moraine-dammed, followed by erosion and other types.
|
Case Study: Ghepang Ghat Glacial Lake (Indus Basin)
●ISRO highlighted the significant expansion of the Ghepang Ghat glacial lake in Himachal Pradesh, showing a 178% increase in size between 1989 and 2022.
●This case study exemplifies the rate of growth of glacial lakes in the region, with the lake expanding at approximately 1.96 hectares per year.
|
Implications of Glacial Lake Expansion
- The expansion of glacial lakes in the Himalayas is due to glacier retreat caused by climate change.
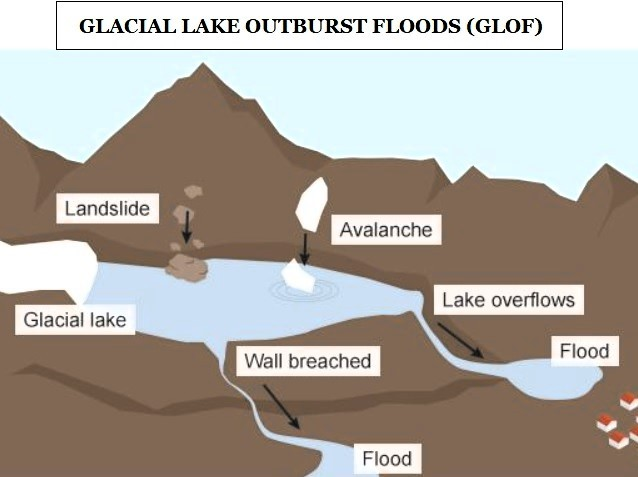
- Glacial lake expansion poses risks such as Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs), as observed in the case of South Lhonak Lake in Sikkim, where a burst resulted in casualties and extensive damage.
- Monitoring and understanding glacial lake dynamics are critical for assessing GLOF risks, evaluating glacier retreat rates, and comprehending the broader impacts of climate change on the Himalayan ecosystem.
Role of Satellite Remote Sensing
- Satellite remote sensing plays a pivotal role in monitoring and studying glacial lakes due to the challenging terrain and inaccessible nature of the Himalayan region.
- Remote sensing technology offers wide coverage and revisit capabilities, enabling researchers to assess long-term changes in glacial lakes and gain insights into climate change impacts.
Policy and Research Implications
- ISRO's findings highlight the urgency of addressing climate change impacts on the Himalayan region through robust policy interventions.
- Continued research and monitoring of glacial lakes are essential for developing adaptive strategies to mitigate risks associated with glacial lake expansion and glacier retreat.

Conclusion
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) study offers insight into the changing dynamics of Himalayan glacial lakes, highlighting the connection of climate change, glacier retreat, and glacial lake extension. The study underlines the importance of using a multimodal approach that includes scientific research, policy initiatives, and community participation to protect the region's environmental integrity and reduce dangers to human populations downstream.
Must Read Articles:
GLACIAL LAKE OUTBURST FLOOD (GLOF)
Source:
Indian Express
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Mountain glaciers act as natural reservoirs, storing and releasing freshwater throughout the year. How will the loss of glaciers impact regional and global water cycles, particularly in arid regions that rely on meltwater for irrigation and drinking water? What are the potential solutions and adaptation strategies for managing water resources in a future with shrinking glaciers?
|


















