Description
 Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- An assessment of climate change over the Indian subcontinent, published by the Ministry of Earth Sciences in 2020, said annual mean temperatures had risen by 0.7 degree Celsius from 1900.
- This is significantly lower than the 1.59 degree Celsius rise for land temperatures across the world.
Details
Global rise of temperature
- The annual mean temperature of the world is known to have increased by 1.1 degree Celsius from the average of the 1850-1900 period. But this increase, as can be expected, is not uniform.
- It varies in different regions and also at different times of the year.
- Temperature rise over land is much higher than over oceans.
- Over land, the annual mean temperatures have risen by as much as 1.59 degree Celsius.
- Oceans, in contrast, have warmed by about 0.88 degree Celsius.
Warming in India
- The lower warming could give the impression that the problem of climate change over India was not as acute as other parts of the world. But that is not entirely accurate.
Why is warming over India lower?
Location
- The increase in temperatures is known to be more prominent in the higher altitudes, near the polar regions, than near the equator.
- This is attributable to a complex set of atmospheric phenomena, including heat transfers from the tropics to the poles through prevailing systems of air circulation.
- India happens to be in the tropical region, quite close to the equator.

Tropical location
- A major part of India’s relatively lesser warming can be attributed to its location in the lower latitudes.
- A majority of the global landmass is concentrated in the northern latitudes.
- In the tropics and along the equator, it is mostly oceans.
- Land areas are also prone to faster, and greater, heating.
- Because of both these reasons — that lands heat up more, and most of the land is located in northern latitudes — the average warming over global land areas has become more pronounced.
- For a country like India, located in the tropics, the deviation in temperature rise from the global average is not surprising.
Albedo effect
- It denotes how much sunlight a surface reflects.
- The ice cover in the Arctic is melting, because of which more land or water is getting exposed to the Sun.
- Ice traps the least amount of heat and reflects most of the solar radiation when compared with land or water.
- More recent research suggests that the higher warming in the polar region could be attributed to a host of factors, including the albedo effect, changes in clouds, water vapour and atmospheric temperatures.
- The warming in the polar regions account for a substantial part of the 1.1 degree Celsius temperature rise over the entire globe.
Impact of aerosols
- Aerosols refer to all kinds of particles suspended in the atmosphere.
- These particles have the potential to affect the local temperature in multiple ways.
- Many of these scatter sunlight back, so that lesser heat is absorbed by the land.
- Aerosols also affect cloud formation. Clouds, in turn, have an impact on how much sunlight is reflected or absorbed.
- Aerosol concentration over the Indian region is quite high, due to natural as well as man-made reasons.
- A reduction in warming could be an unintended but positive side-effect.
Land vs Ocean
- Land areas have a tendency to get heated faster, and by a larger amount, than oceans.
- Oceans have a higher capacity to cool themselves down through the process of evaporation. The warmer water evaporates, leaving the rest of the ocean relatively cooler.
Mapping Climate Change in India
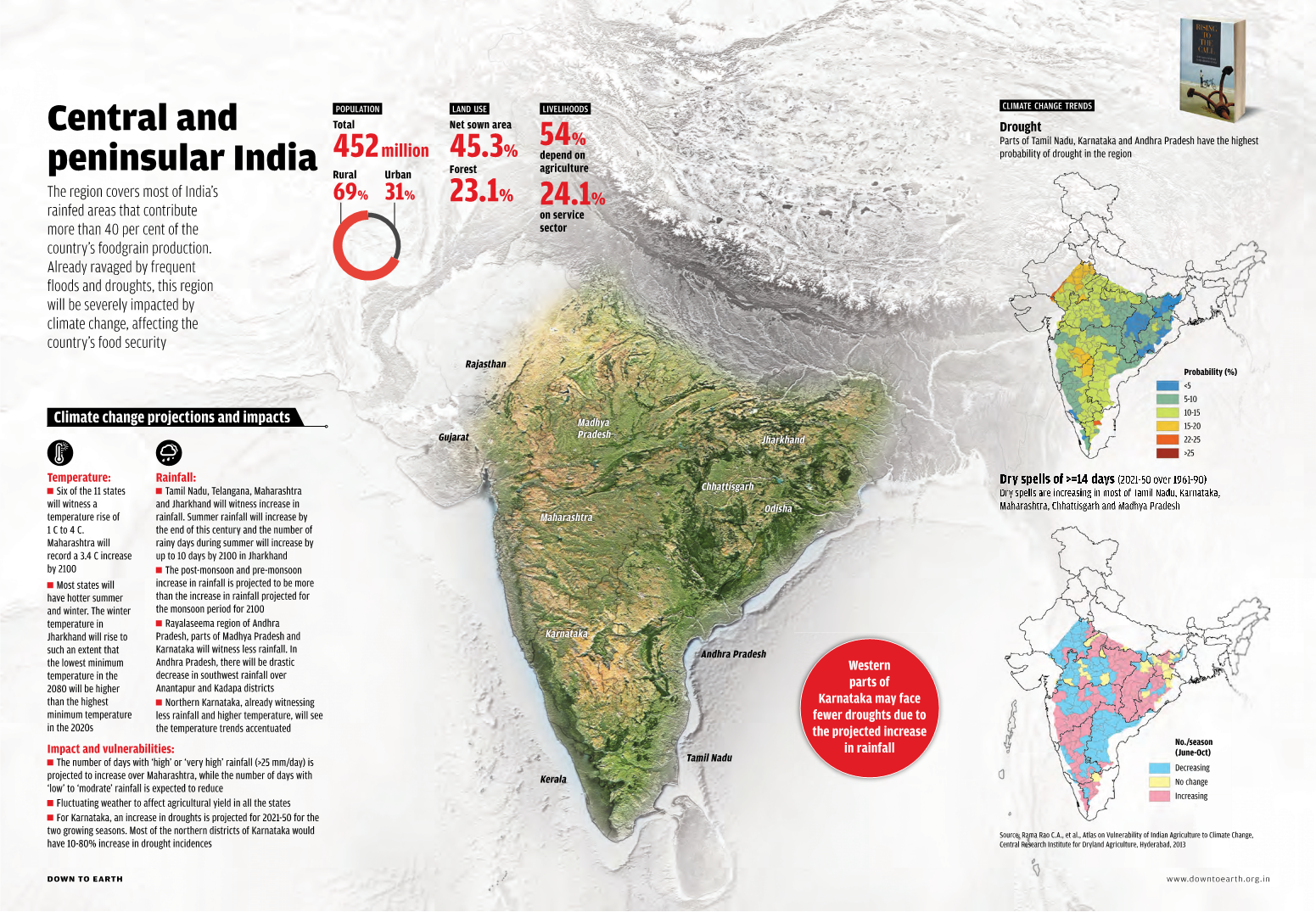
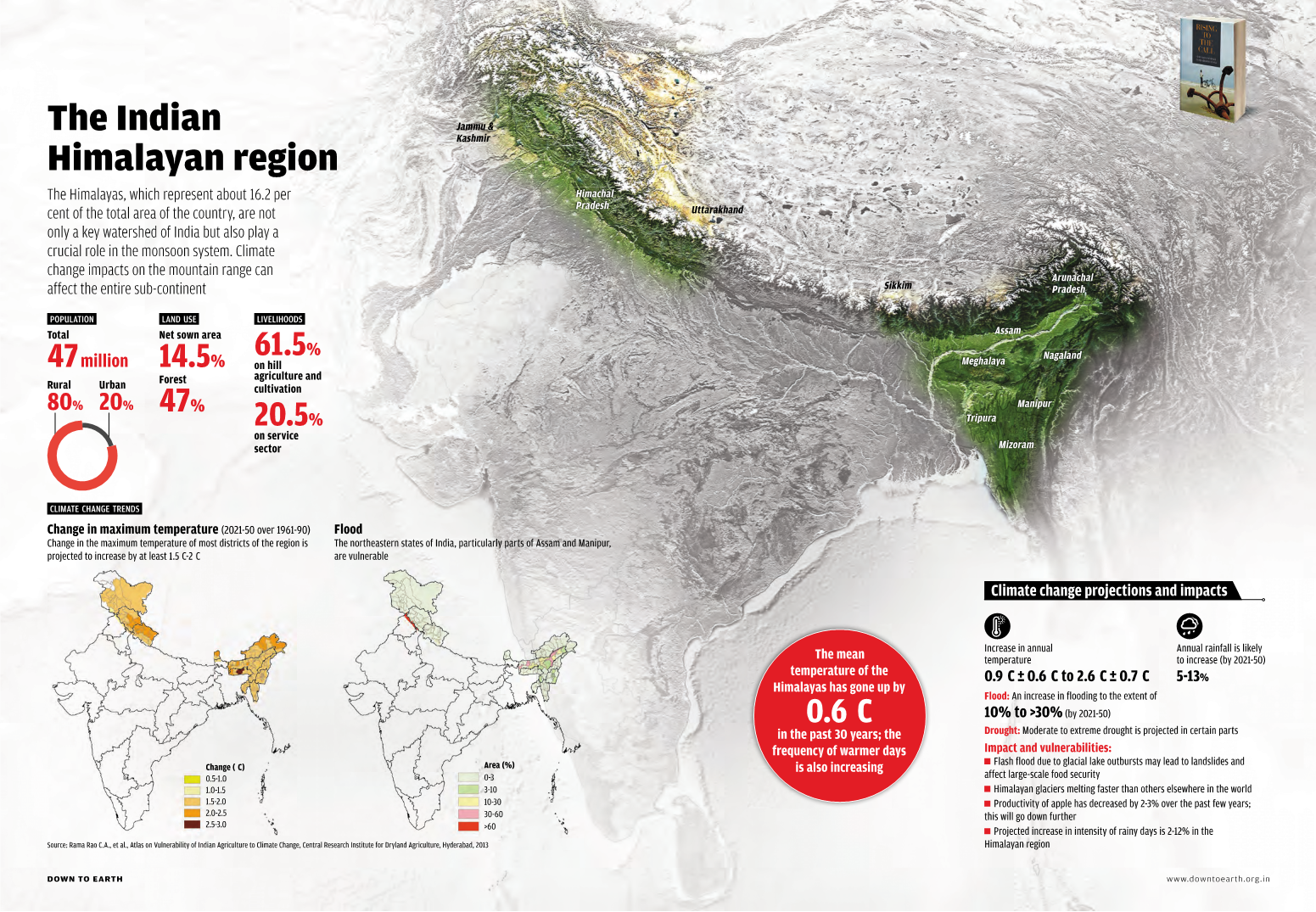
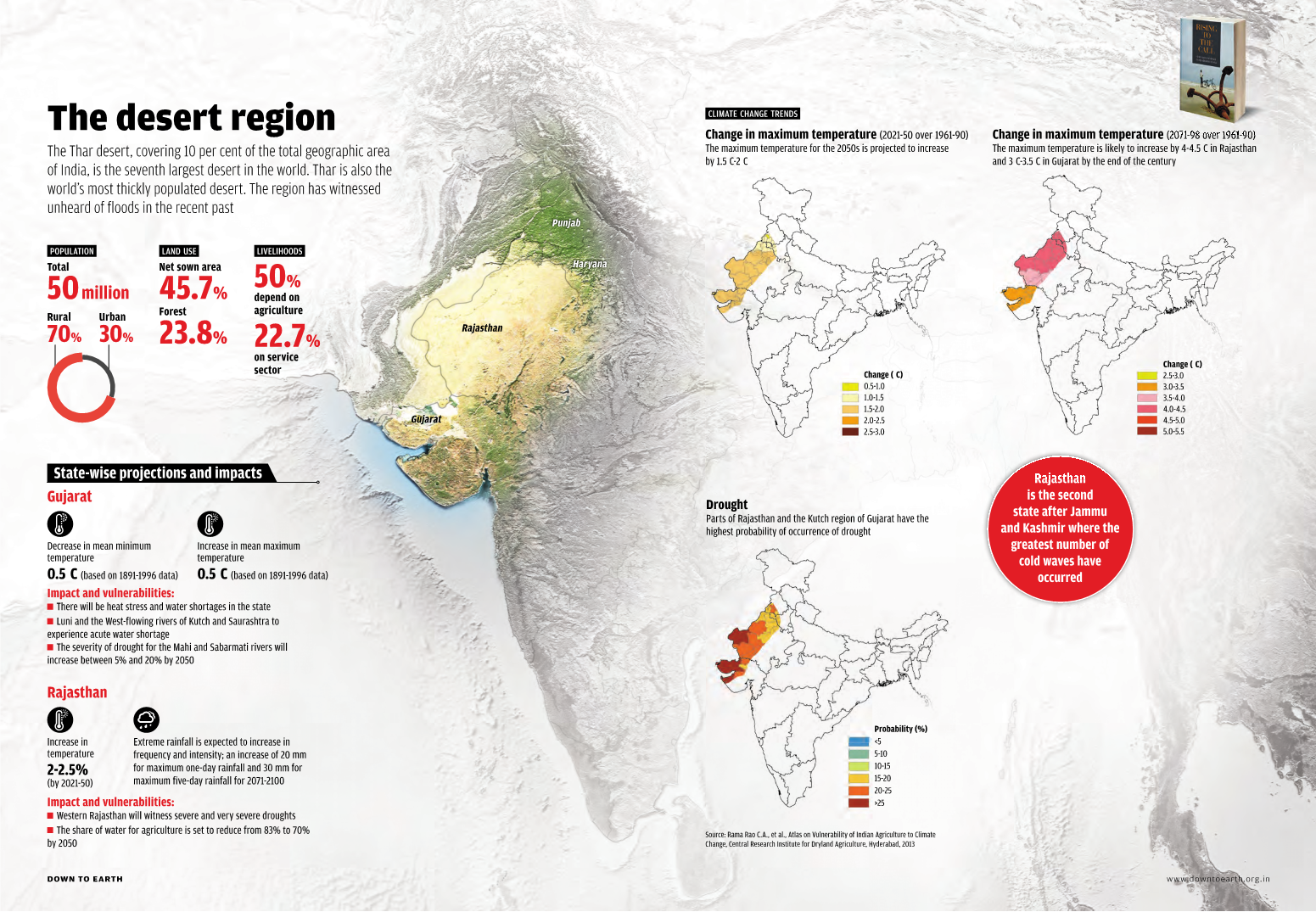
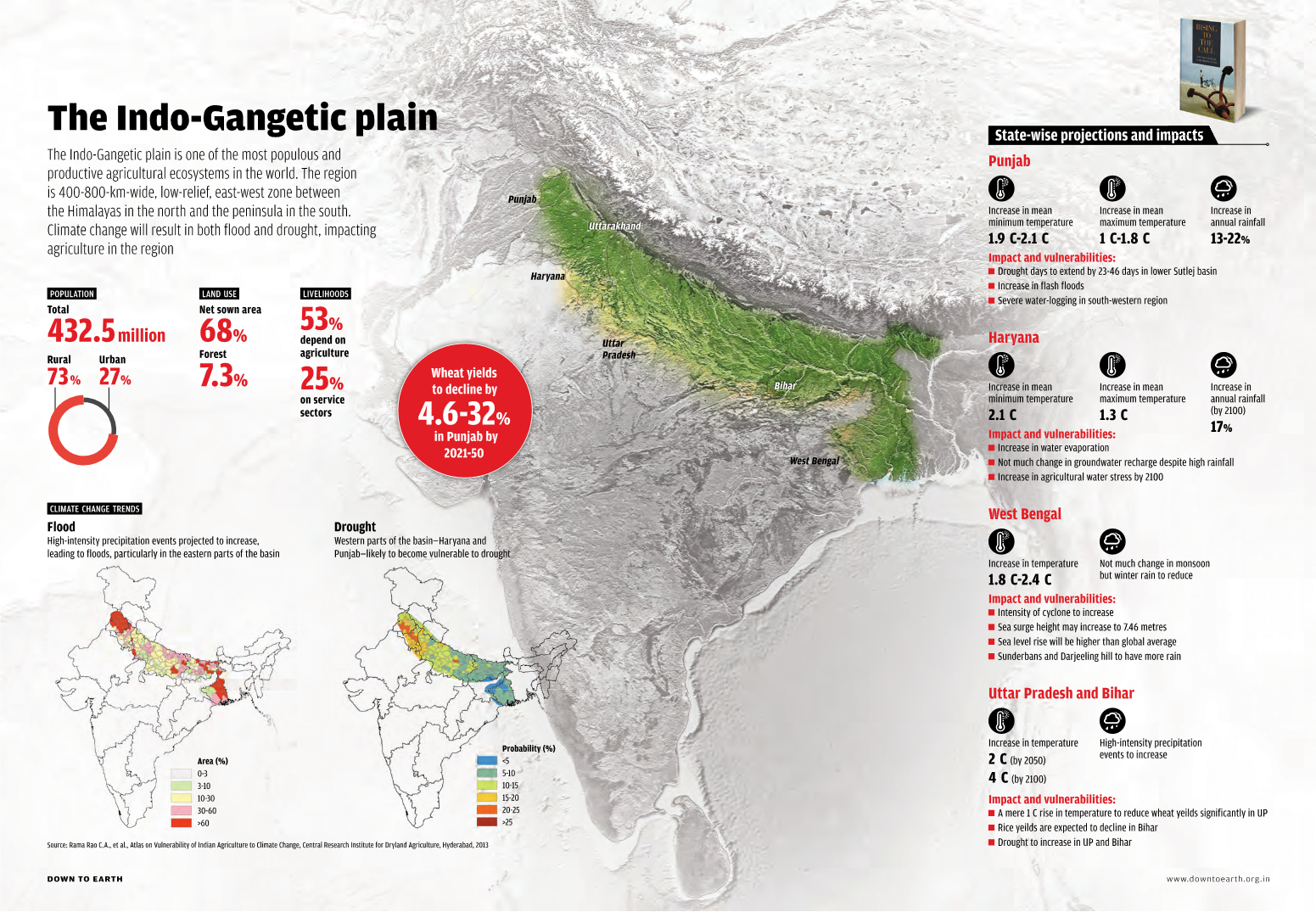
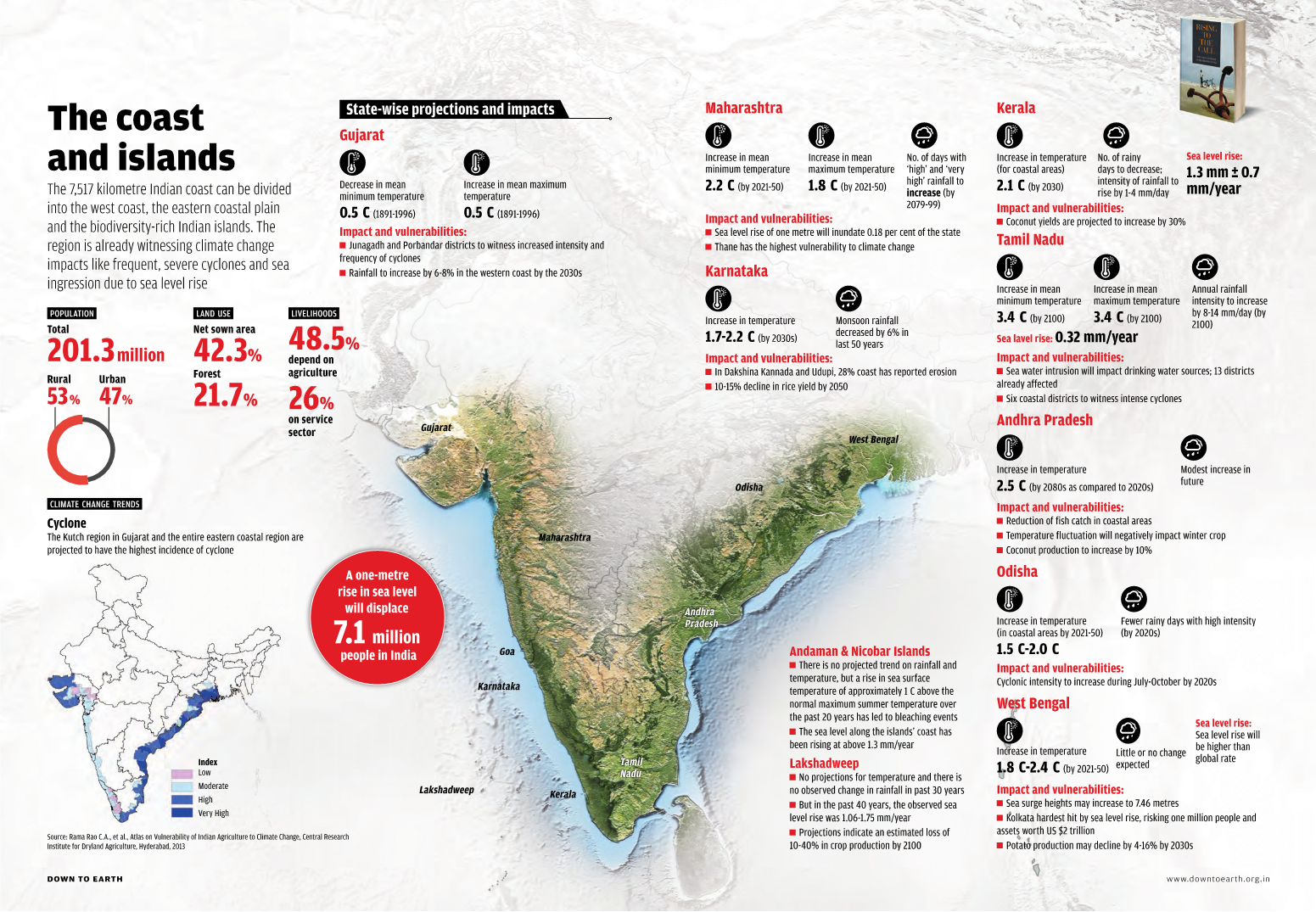
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q) An assessment of climate change over the Indian subcontinent, published by the Ministry of Earth Sciences in 2020, said annual mean temperatures had risen by 0.7 degree Celsius from 1900. This is significantly lower than the 1.59 degree Celsius rise for land temperatures across the world. Discuss the various factors which can be attributed to be responsible for this phenomenon. (250 words)
|

https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-climate/climate-change-why-india-is-heating-up-slower-than-the-world-average-8602414/





 Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.










