





Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Content
What are GM Crops?
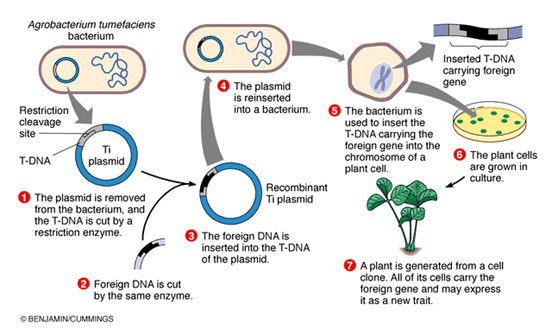
Read about the pros and cons of GM Crops over here: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/gm-crops-40
Bt Cotton
Description
Bt Cotton in India
Concerns raised
The recent nod to Pink Bollworm-Resistant GM Cotton trials
Significance
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q) Resistance to insecticides and to Bt toxins in pink bollworm are running havoc on Indian cotton industry. Comment. |






© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved