Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Goa has achieved a significant milestone by becoming the first Indian state to offer free in vitro fertilization (IVF) treatment, in addition to assisted reproductive technology (ART) and intrauterine insemination (IUI).
- This move not only marks a vital stride in healthcare accessibility but also sheds light on the expanding fertility industry in India.
Details
- Chief Minister inaugurated the IVF service, ART, and IUI at Goa Medical College (GMC) in Bambolim.
- IVF treatment in India typically costs between Rs 70,000 to Rs 3 lakh per cycle, varying based on the hospital and the type of treatment.
- The newly introduced IVF service at GMC has already garnered a strong response, with approximately 100 parents registering to access the facility located within the hospital's super-speciality block.
- The fertility business in India has expanded at a rate of 15-20% annually over the last five years, according to Ernst & Young's Call to Action report.
Underlying Surge in Infertility
- Fertility Issues in India: Infertility has become a significant concern in India, affecting around 15% of Indian couples. An estimated 2.75 crore Indian couples face fertility disorders.
- Factors Contributing to Infertility: Lifestyle factors like sedentary routines, stress, obesity, and various medical conditions have contributed to the increasing prevalence of infertility.
Accessibility and Affordability Challenges
- High Costs: Fertility treatments are often perceived as financially burdensome, restricting access for many, especially those from middle and lower income groups.
- Loan Burden: Many couples resort to personal loans with high interest rates to cover the expenses of fertility treatments.
- Lack of ART Insurance: Despite the growing demand for fertility services, ART insurance coverage remains limited in India.
- Pricing Transparency Issues: A lack of pricing transparency makes it difficult for patients to estimate the total cost of treatment, leading to financial uncertainties.
Consequences and Barriers
- Stuck in the Middle: Some individuals find themselves at a crossroads where they cannot proceed due to financial constraints, nor can they turn back.
Significance of Goa's Initiative
- Addressing Financial Barriers: Goa's move to provide free IVF treatment addresses the financial barriers that hinder many from accessing fertility services.
- Impact on Healthcare Equity: This initiative contributes to a more equitable healthcare system by extending infertility treatment to a wider demographic.

About IVF
- In-Vitro Fertilization (IVF) stands as one of the most transformative achievements in modern medicine, offering hope and solutions to couples struggling with infertility.
- This groundbreaking assisted reproductive technology has revolutionized the way we perceive conception, pregnancy, and parenthood.
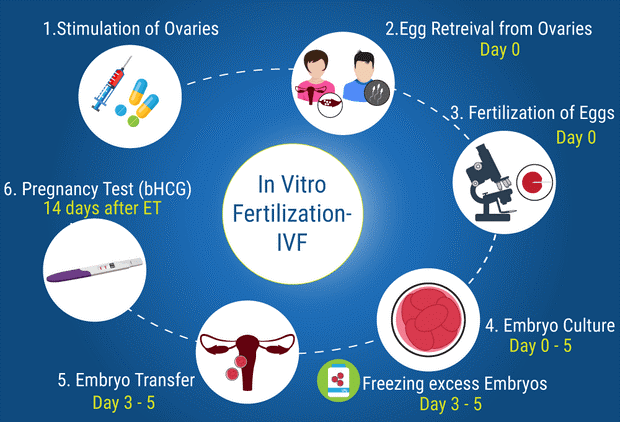
Understanding IVF
- IVF is a medical procedure wherein an egg is fertilized by sperm outside the body, in a controlled laboratory environment. The resulting embryo is then implanted into the uterus.
Procedure
- Ovulation Induction: Hormones stimulate the ovaries to produce multiple eggs.
- Egg Retrieval: Mature eggs are collected through a minimally invasive procedure.
- Sperm Collection: Sperm is obtained from the partner or a donor.
- Fertilization: Eggs and sperm are combined in a lab dish to facilitate fertilization.
- Embryo Culture: Embryos are cultured and monitored for a few days.
- Embryo Transfer: The healthiest embryos are transferred to the uterus.
- Implantation: Successful embryos attach to the uterine lining, leading to pregnancy.
Applications and Advancements
- Infertility Solutions: IVF provides hope to couples dealing with male infertility, tubal damage, ovulatory disorders, and unexplained infertility.
- Fertility Preservation: IVF allows individuals to freeze eggs, sperm, or embryos for future use, preserving fertility before medical treatments that could affect reproductive health.
- Pre-implantation Genetic Diagnosis (PGD): Embryos can be screened for genetic disorders before implantation, reducing the risk of passing on hereditary conditions.
Ethical Considerations
- Multiple Pregnancies: IVF increases the likelihood of multiple pregnancies, which can pose health risks to both the mother and babies.
- Embryo Selection: Ethical debates arise over embryo selection based on genetic characteristics, raising concerns about designer babies and eugenics.
Success Rates and Challenges
- Success Rates: IVF success rates vary based on factors like age, underlying fertility issues, and the quality of embryos transferred.
- Emotional and Financial Strain: IVF can be emotionally and financially taxing due to the uncertainty of outcomes and the need for multiple attempts.
Social and Cultural Impact
- Changing Perceptions: IVF challenges traditional notions of conception, parenthood, and biological relationships.
- Legal and Social Debates: Legal frameworks vary across countries, influencing debates around surrogacy, donor anonymity, and parental rights.
Future Prospects
- Advancements in Reproductive Medicine: Innovations in embryo selection, genetic editing, and artificial wombs could shape the future of IVF and assisted reproduction.
- Global Accessibility: Strides in affordability and accessibility could make IVF more accessible to a wider range of individuals and couples.
About Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)
- Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART) encompass a range of medical procedures designed to help individuals and couples achieve pregnancy when natural conception becomes challenging or impossible.
- These innovative techniques have revolutionized the field of reproductive medicine, offering hope to those facing infertility and redefining the boundaries of parenthood.
Understanding Assisted Reproductive Technologies
- ART refers to medical interventions that assist in achieving pregnancy by manipulating eggs, sperm, embryos, or the uterus.
- ART includes procedures like In-Vitro Fertilization (IVF), Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI), gamete and embryo cryopreservation, surrogacy, and pre-implantation genetic testing.
Applications and Techniques
- IVF and ICSI: IVF involves fertilizing eggs with sperm in a laboratory dish before implanting the embryo into the uterus. ICSI is used when male infertility is a concern, as a single sperm is directly injected into an egg.
- Gamete and Embryo Cryopreservation: Eggs, sperm, or embryos can be frozen and stored for future use, allowing fertility preservation before medical treatments or for family planning.
- Surrogacy: A surrogate mother carries a pregnancy for intended parents who may be unable to carry a pregnancy themselves.
- Pre-Implantation Genetic Testing (PGT): Embryos can be screened for genetic disorders before implantation, reducing the risk of passing on hereditary conditions.
Benefits and Impact
- Overcoming Infertility: ART provides hope to couples dealing with various fertility challenges, including ovulatory disorders, tubal damage, and male infertility.
- Fertility Preservation: ART enables individuals to preserve their fertility before medical treatments that could impact reproductive health.
- Same-Sex Couples and Single Individuals: ART allows non-traditional families, such as same-sex couples and single parents, to have biological children.
Ethical and Legal Considerations
- Multiple Pregnancies: Some ART procedures increase the likelihood of multiple pregnancies, which can have health risks for both the mother and babies.
- Egg and Sperm Donation: The use of donor gametes raises questions about donor anonymity, genetic inheritance, and disclosure to children.
- Surrogacy: Ethical dilemmas arise concerning the compensation of surrogates, the potential exploitation of vulnerable individuals, and the legal rights of the child and surrogate.
Challenges and Controversies
- Cost and Access: ART procedures can be financially burdensome, limiting access for individuals with limited resources.
- Emotional Strain: The emotional rollercoaster of ART, with its uncertain outcomes and multiple attempts, can be mentally taxing.
- Designer Babies and Genetic Manipulation: The ability to select genetic traits in embryos raises ethical concerns about creating "designer babies."
Future Developments and Social Impact
- Advancements in Reproductive Medicine: Innovations like artificial wombs, genetic editing, and improved embryo selection techniques could shape the future of ART.
- Legal and Societal Changes: Continued debates about donor rights, surrogacy regulations, and parental rights may lead to evolving legal frameworks and societal perceptions.
Three-Parent Babies: Exploring Mitochondrial Replacement Therapy
- The concept of "three-parent babies" refers to a groundbreaking medical technique known as mitochondrial replacement therapy (MRT).
- This innovative procedure involves combining genetic material from three individuals to prevent the transmission of certain genetic diseases caused by faulty mitochondria.
- While offering hope for families affected by mitochondrial disorders, three-parent babies also raise ethical, scientific, and societal considerations.
Mitochondrial Disorders and MRT
- Mitochondria and Genetic Diseases: Mitochondria are organelles responsible for energy production within cells. Mutations in mitochondrial DNA can lead to various disorders affecting energy production and cellular functions.
- Inherited Disorders: Mitochondrial disorders are often inherited from the mother due to the maternal transmission of mitochondria. These disorders can result in serious health issues, including muscular dystrophy and organ dysfunction.
- MRT to Prevent Transmission: Mitochondrial replacement therapy involves replacing defective mitochondria in a mother's egg with healthy mitochondria from a donor egg, thereby preventing the transmission of mitochondrial disorders to the offspring.
Types of MRT
- Pronuclear Transfer: This technique involves transferring the nucleus of the mother's fertilized egg (zygote) into a donor egg with healthy mitochondria, after removing the nucleus.
- Maternal Spindle Transfer: In this approach, the nucleus is removed from the mother's egg before fertilization and transferred into a donor egg that has had its nucleus removed.
Ethical and Regulatory Considerations
- Genetic Modification: MRT involves genetic modification, as it alters the genetic material of embryos. This raises ethical concerns about the potential long-term effects on future generations.
- Designer Babies: Critics argue that the ability to manipulate genetic material for preventing diseases could open the door to "designer babies," where genetic enhancements are made for non-medical reasons.
Regulatory Landscape
- Global Variations: Different countries have varying regulations regarding MRT. Some countries permit it only for research purposes, while others have approved it for clinical use under strict conditions.
- UK's Regulatory Pathway: The UK became the first country to approve MRT for clinical use in specific cases where mitochondrial diseases pose a significant risk.
Social and Cultural Perspectives
- Religious and Cultural Beliefs: Three-parent babies can pose ethical dilemmas in communities with strong religious or cultural beliefs about human conception and genetic manipulation.
- Parental Identity: Questions about parental identity may arise due to the involvement of genetic material from three individuals.
.jpg)
Conclusion
- Goa's pioneering step in offering free IVF treatment signifies a positive stride toward making fertility services accessible and affordable. While the Indian fertility industry continues to expand due to increasing infertility rates, addressing financial hurdles and ensuring transparency in pricing remain crucial to ensuring that individuals and couples can make informed decisions about their reproductive health.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Discuss the significance, applications, ethical considerations, and challenges associated with Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART) in the context of modern reproductive medicine. How have these technologies revolutionized the way we perceive fertility, parenthood, and family structures? (250 Words)
|
https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/india/in-a-first-in-india-goa-to-give-free-ivf-treatment-in-govt-hospital/articleshow/102744887.cms?from=mdr











