Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Free Courses Sale ends Soon, Get It Now


Context
Gravitational Waves
What causes gravitational waves?
How do we know that gravitational waves exist?
How are gravitational waves detected?

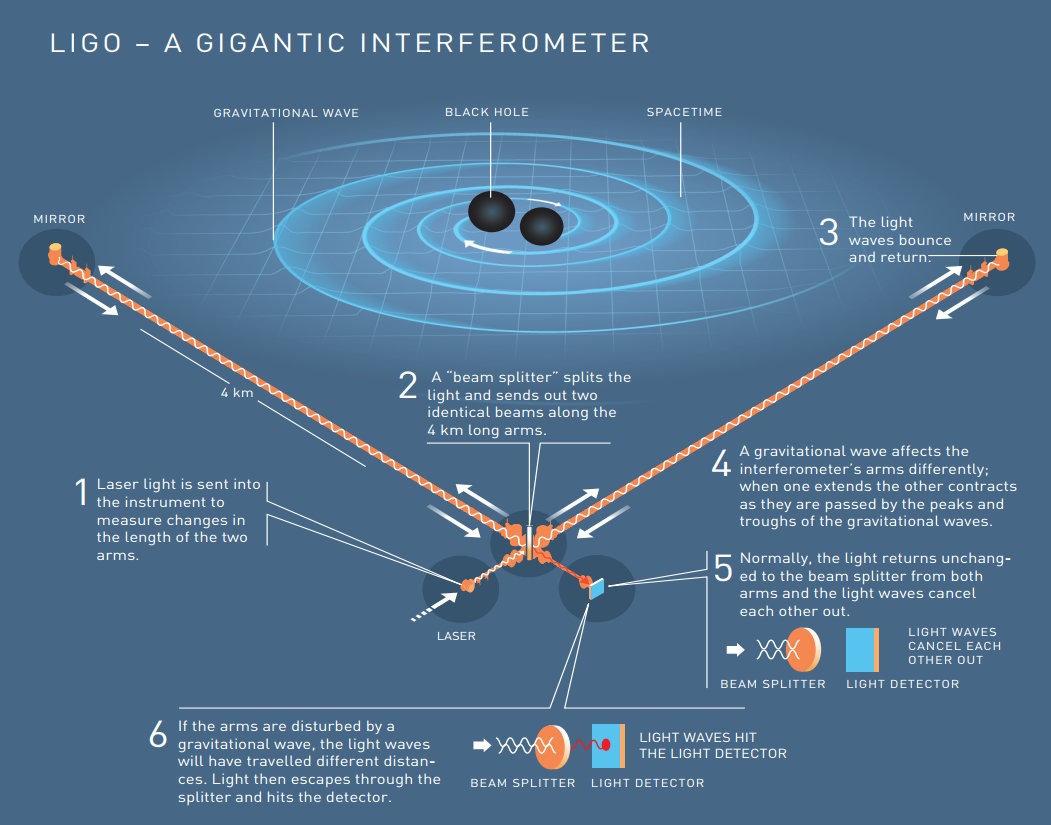
|
Neutron Stars · Neutron stars are formed when a massive star runs out of fuel and collapses. · The very central region of the star – the core – collapses, crushing together every proton and electron into a neutron. · If the core of the collapsing star is between about 1 and 3 solar masses, these newly-created neutrons can stop the collapse, leaving behind a neutron star. Once formed, they no longer actively generate heat, and cool over time. · Neutron stars are the smallest and densest currently known class of stellar objects. · Since neutron stars began their existence as stars, they are found scattered throughout the galaxy in the same places where we find stars. And like stars, they can be found by themselves or in binary systems with a companion. · Many neutron stars are undetectable because they simply do not emit enough radiation. A handful of neutron stars have been found sitting at the centers of supernova remnants quietly emitting X-rays. · In binary systems, some neutron stars can be found accreting materials from their companions, emitting electromagnetic radiation powered by the gravitational energy of the accreting material. · The two general classes of non-quiet neutron stars are – pulsars and magnetars. |
https://www.sciencenews.org/article/gravitational-waves-ligo-first-black-hole-neutron-star-merger









© 2024 iasgyan. All right reserved