




Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
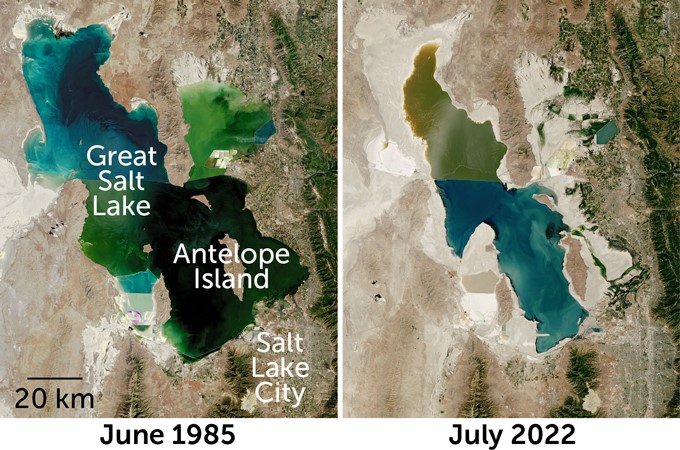
Drying of Great Salt Lake and its implications
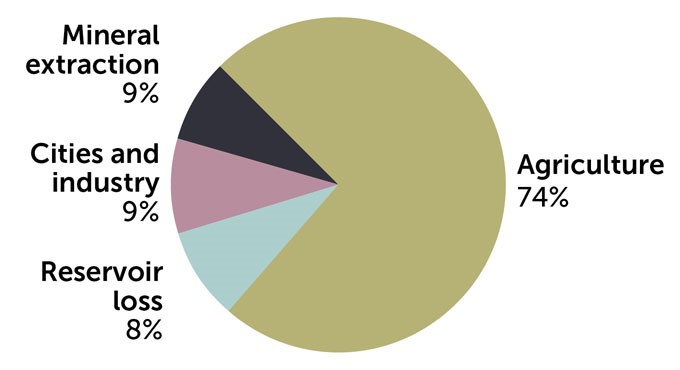
Terminal lakes, like the Great Salt Lake, are ones where water can flow into but not out of the basin. And when strong winds blow over a drying lake bed, they kick up tiny particles that can be inhaled and damage the lungs and exacerbate other respiratory illnesses. These pollutants have been linked to health complications such as asthma, heart disease and chronic bronchitis.
Great Salt Lake
About
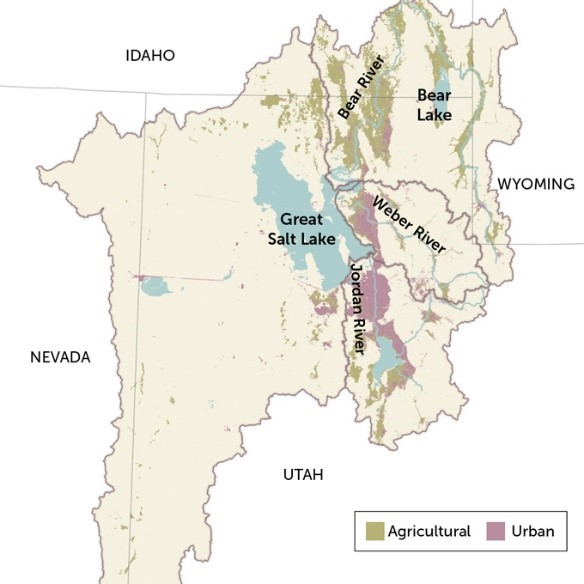
Location
Source
Tributaries
Salinity
Importance
|
TERMINAL LAKES/ ENDORHEIC LAKES Endorheic lakes are a type of lake that has no outlet. You can find them typically at the terminal end of a water system. They are usually fed by rivers and rainfall, and in most cases, water only leaves the lake through evaporation. In some cases, water may also leave the lake through the bottom by sinking underground into aquifers or going into the groundwater supply. Some endorheic lakes also drain into nearby swamps or marshes. However, water from a true endorheic lake never makes it into the ocean. An endorheic lake that drains into a swamp or marsh that eventually drains into the ocean is called a cryptorheic lake. Most endorheic lakes are saltwater lakes. In other types of lakes, minerals such as salt get washed away into the outlet of the lake, such as a river or the ocean. In an endorheic lake, the minerals are left behind in the evaporation process. Some endorheic lakes also have high levels of other minerals such as fluoride. |
Trivia

|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Which one of the following is the correct arrangement of lakes from West to East direction? a) Lake Michigan- Great Salt lake- Lake Ontario- Lake Huron. b) Great Salt lake - Lake Michigan - Lake Ontario- Lake Huron. c) Great Salt lake - Lake Michigan - Lake Huron Lake Ontario. d) Lake Ontario- Lake Huron-Lake Michigan- Great Salt lake. Correct Answer: Option c |
https://edition.cnn.com/2023/04/16/us/great-salt-lake-water-level-climate/index.html






© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved