Description
Context
- Green hydrogen can drive India’s transition to clean energy, combat climate change
What is green hydrogen?
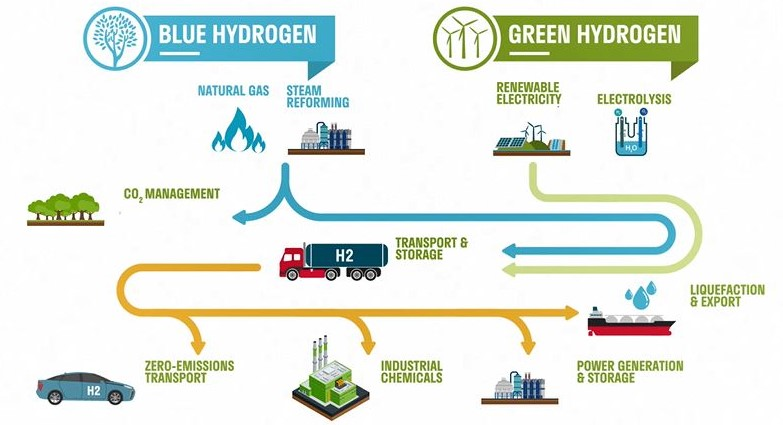
- Green hydrogen is produced by electrolysis of water using renewable energy and has a lower carbon footprint.
- By 2030, the cost of green hydrogen is expected to compete with that of hydrocarbon fuels.
- Hydrogen will make up 12 per cent of the energy mix by 2050, according to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA).
- At present, less than 1 per cent of hydrogen produced is green hydrogen, according to IRENA's World Energy Transitions Outlook.
India and green hydrogen
- Under the Paris Climate Agreement, India pledged to reduce the emission intensity of its economy by 33-35 per cent from 2005 levels by 2030.
- India consumes about six million tonnes of hydrogen every year for the production of ammonia and methanol in industrial sectors, including fertilisers and refineries.
- India has favourable geographic location and abundance of sunlight and wind for the production of green hydrogen.
- Green hydrogen production will reduce the country’s dependence on imports while also staving off climate change.
- India will become a net exporter of green hydrogen by 2030 due to its cheap renewable energy tariffs, according to the Global Hydrogen Council.
- The Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE) has circulated a draft to establish a hydrogen ecosystem in the country.
- In some sectors, the purchase of green hydrogen can be made mandatory, similar to renewable purchase obligations.
Why to opt for Green Hydrogen?
- Adoption of Green hydrogen technologies are favorable in those sectors where direct electrification isn't feasible for ex in Heavy duty, long-range transport and long-term storage in the power sector.
- With technological improvements, green hydrogen will become more affordable and accessible.
- It can be used in a wide range of existing applications such as fertilisers, mobility, power, chemicals and shipping.
- It can be blended up to 10 per cent by city gas distribution networks for wider acceptance.
- It is a cross-cutting solution that may reduce emissions across a range of sectors.
What can be done to build a global-scale green hydrogen industry?
- As with renewable energy, India should announce ambitious national targets for green hydrogen and electrolyser capacity by 2030.
- Launch an incentive programme for the production of electrolysers.
- Implementing complementary solutions that create virtuous cycles for ex. building the hydrogen infrastructure for refueling, heating and generating electricity at airports.
- Optimising distribution networks to decarbonise the gas grid.
https://www.downtoearth.org.in/blog/pollution/green-hydrogen-can-drive-india-s-transition-to-clean-energy-combat-climate-change-77685





