




Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://ponce.sdsu.edu/groundwater_utilization_and_sustainability.html
Context: The National Green Tribunal (NGT) has raised concerns that the problem of toxic arsenic and fluoride contamination in groundwater across different areas of India is not being effectively addressed by the Central Ground Water Authority (CGWA).
Key Highlights
|
National Green Tribunal (NGT) |
|
|
Established |
Established under the National Green Tribunal Act, 2010. It was enacted under India's constitutional provision Article 21. |
|
Purpose |
Effective and expeditious disposal of cases related to: ●Environmental protection ●Conservation of forests and other natural resources ●Enforcement of environmental laws |
|
Jurisdiction |
Covers civil cases with substantial environmental questions arising from the implementation of various environmental laws listed in Schedule I of the NGT Act, 2010. These include: ●The Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974 ●The Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981 ●The Environment (Protection) Act, 1986 ●The Forest (Conservation) Act, 1976 |
|
Composition |
One Chairperson with expertise in judicial administration or environmental law. Ten Expert Members with experience in environmental science, forest management, pollution control, or social sciences. Ten Judicial Members with judicial experience of at least 10 years. |
|
Sittings |
Principal Bench: New Delhi Zonal Benches: Bhopal, Pune, Kolkata, and Chennai |
|
Powers |
Can entertain appeals against orders passed by any authority under various environmental laws. Can hear original applications from individuals or organizations affected by environmental violations. Can pass orders for: ●Stopping environmental violations ●Compensation and restoration for environmental damage ●Granting interim relief |
|
Procedure |
Less formal than regular courts, focusing on the speedy disposal of cases. Guided by principles of natural justice (fairness and due process). Allows filing of applications without a lawyer (though legal representation is encouraged). |
|
Significance |
Provides a specialized forum for handling environmental disputes with dedicated expertise. Ensures prompt and effective legal recourse for environmental protection and restoration. Empower citizens to seek redressal for environmental damage they have suffered or witnessed. |
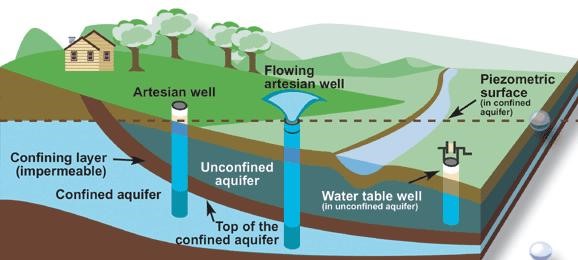
Groundwater Contamination in India
Factors contribute to groundwater contamination
Types of Contaminants
Impacts
Government Initiatives
Challenges
Possible Solutions
Conclusion
Must Read Articles:
NATIONAL GROUNDWATER MANAGEMENT IMPROVEMENT SCHEME: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/national-groundwater-management-improvement-scheme
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. How can India ensure equitable access to safe groundwater for all citizens, particularly considering the vast rural-urban divide and marginalized communities, while simultaneously addressing the challenges of overexploitation and contamination? Answer Structure: ●Briefly introduce the situation of groundwater in India, highlighting the importance of safe water access and the challenges of overexploitation and contamination. ●Discuss the rural-urban divide in water access. Mention government initiatives like the Har Ghar Jal Mission and the need for decentralized water treatment systems in rural areas. Address the challenges faced by marginalized communities like lack of infrastructure and affordability. ●Explain the causes of overexploitation, including agricultural practices, industrial water demands, and lack of awareness. ●Briefly explain the sources of groundwater contamination in India (industrial waste, agricultural runoff, improper sanitation). ●Discuss measures to control contamination: Regulation and enforcement of environmental laws for industries and waste management. Improving sanitation infrastructure in urban and rural areas to prevent sewage contamination. Promoting sustainable agricultural practices that minimize the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides. ●Summarize the key points and emphasize the need for a holistic approach that balances equitable access, sustainable management, and pollution control. Mention the role of technology and community participation in achieving these goals. |






© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved