Copyright infringement not intended
Context: Prime Minister Narendra Modi is in Germany to attend the Group of Seven (G7) Summit at Schloss Elmau, a century-old retreat in a nature reserve in the Bavarian Alps. The Prime Minister is expected to speak in two sessions that include Environment, Energy, Climate, Food Security, Health, Gender Equality, and Democracy, the Ministry of External Affairs said earlier this week. He will also hold bilateral meetings with leaders of some of the participating countries.
About:
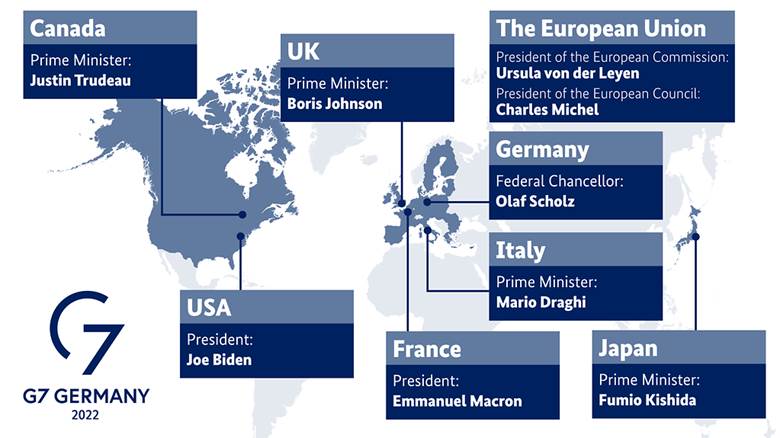
- The G-7 or ‘Group of Seven’ are Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
- It is an intergovernmental organisation that was formed in 1975 by the top economies of the time as an informal forum to discuss pressing world issues.
- Canada joined the group in 1976, and the European Union began attending in 1977.
- Initially formed as an effort by the US and its allies to discuss economic issues, the G-7 forum has deliberated about several challenges over the decades, such as the oil crashes of the 1970s, the economic changeover of ex-Soviet bloc nations, and many pressing issues such as financial crises, terrorism, arms control, and drug trafficking.
- The G-7 was known as the ‘G-8’ for several years after the original seven were joined by Russia in 1997.
- The Group returned to being called G-7 after Russia was expelled as a member in 2014 following the latter’s annexation of the Crimea region of Ukraine.
- The G-7 does not have a formal constitution or a fixed headquarters.
- The decisions taken by leaders during annual summits are non-binding.
- The rise of India, China, and Brazil over the past few decades has reduced the G-7’s relevance, whose share in global GDP has now fallen to around 40%.
- The G-7 nations meet at annual summits that are presided over by leaders of member countries on a rotational basis.
- The summit is an informal gathering that lasts two days, in which leaders of member countries discuss a wide range of global issues.
- The host country typically gets to invite dignitaries from outside the G-7 to attend the Summit.
G-20
- The G-20 is a larger group of countries, which also includes G7 members.
- The G-20 was formed in 1999, in response to a felt need to bring more countries on board to address global economic concerns.
- Apart from the G-7 countries, the G-20 comprises Argentina, Australia, Brazil, China, India, Indonesia, Mexico, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, South Korea, and Turkey.
- Together, the G-20 countries make up around 80% of the world’s economy.
- Deliberations at the G-20 are confined to those concerning the global economy and financial markets.
- India is slated to host a G-20 summit in 2022.
GROUP OF TEN
- The Group of Ten (G10) refers to the group of countries that have agreed to participate in the General Arrangements to Borrow (GAB), a supplementary borrowing arrangement that can be invoked if the IMF’s resources are estimated to be below a member’s needs.
- The G10 was also the forum for discussions that led to the December 1971 Smithsonian Agreement following the collapse of the Bretton Woods system.
- G10: Belgium, Netherlands, Canada, Sweden, France, Switzerland, Germany, United Kingdom, Italy, United States, Japan
GROUP OF FIFTEEN
It was established at the Ninth Non-Aligned Summit Meeting in Belgrade, then Yugoslavia, in September 1989. It is composed of countries from Latin America, Africa, and Asia with a common goal of enhanced growth and prosperity. The G15 focuses on cooperation among developing countries in the areas of investment, trade, and technology. The membership of the G15 has since expanded to 17 countries but the name has remained unchanged.
G15 Members: Algeria, Indonesia, Nigeria, Argentina, Iran, Islamic Republic of Senegal, Brazil, Jamaica, Sri Lanka, Chile, Kenya, Venezuela, República Bolivariana de, Egypt, Malaysia, Zimbabwe, India, Mexico
G24
Originally a chapter of the G77, was established in 1971 to coordinate the positions of emerging markets and developing countries on international monetary and development finance issues and to ensure that their interests were adequately represented at the Bretton Woods Institutions, particularly in the IMFC and Development Committee meetings of the IMF and World Bank. The group—officially called the Intergovernmental Group of Twenty-Four on International Monetary Affairs and Development—is not an organ of the IMF but the IMF provides secretariat services for the Group.
Members: Algeria, Egypt, Iran, Islamic Republic of Peru, Argentina, Ethiopia, Kenya, Philippines, Brazil, Gabon, Lebanon, South Africa, Colombia, Ghana, Mexico, Sri Lanka, Congo, Dem. Rep. of , Guatemala, Morocco, Syrian Arab Republic, Côte d’Ivoire, Haiti, Nigeria, Trinidad and Tobago ,Ecuador, India, Pakistan, Venezuela, ,República Bolivariana de
G77
- It was established in 1964 at the end of the first session of the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) in Geneva.
- It was formed to articulate and promote the collective economic interests of its members and to strengthen their joint negotiating capacity on all major international economic issues in the United Nations system.
- The membership of the G77 has since expanded to 134 member countries but the original name has been retained because of its historical significance.
G33
- Friends of Special Products in agriculture is a coalition of developing countries, established prior to the 2003 Cancun ministerial conference, that have coordinated during the Doha Round of World Trade Organization negotiations, specifically in regard to agriculture.
- Dominated by India, the group has "defensive" concerns regarding agriculture in relation to World Trade Organization negotiations, and seeks to limit the degree of market opening required of developing countries.
https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/everyday-explainers/explained-g7-summit-germany-india-invitation-7992746/
1.png)












