Description
Copyright infringement not intended
Context - The Union Government has released the ‘Guidelines on Prevention of Misleading Advertisements and Endorsements for Misleading Advertisements, 2022’.
Details
- The Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA) under the Department of Consumer Affairs has announced the ‘Guidelines for Prevention of Misleading Advertisements and Endorsements for Misleading Advertisements, 2022’.
- The main objective of the guidelines is to regulate advertisements and protect consumers from misleading advertisements.
- The Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA) has stated that misleading advertisements violate several rights of consumers.
- The CCPA has been established under the Consumer Protection Act, of 2019.
- Misleading advertisement has already been defined under the Consumer Protection Act, 2019.
- The current guidelines define “bait advertisement”, and “surrogate advertisement” and provide what comprises “free claim advertisements”.
- The guidelines have been formed by keeping in view the sensitiveness and vulnerability of advertisements in the Children’s minds.
Key points of the Guidelines
- It prohibited advertisements from magnifying the features of a product or service in such a manner that promotes unrealistic expectations.
- Prohibited the advertisements of such products or services that claim any health or nutritional benefits without being scientifically recognized by an authentic body.
- Advertisements targeting children should not show any personalities from the field of sports, music or cinema for products that require a health warning or cannot be purchased by children.
- Disclaimers in advertisements must not hide any information about the products and services.
- Clear Guidelines are laid for manufacturers, service providers, advertisers and advertising agencies.
- It aims to protect consumers’ interests by ensuring more transparency and clarity in published advertisements, so that, consumers could make informed decisions based on facts rather than wrong narratives and exaggerations.
- CCPA can impose a penalty of up to 10 lakh rupees on manufacturers, advertisers and endorsers for any misleading advertisements.
- It may increase a penalty up to 50 lakh rupees for repetitive violation of the guidelines.
- It can prohibit the endorser of a misleading advertisement.
Consumer Protection Act, 2019
- The Act defined a consumer as a person who buys any goods or avails of service for final use.
- It does not include a person who buys a good for resale or a good or service for commercial purposes.
- It covers transactions through all modes including offline, and online.
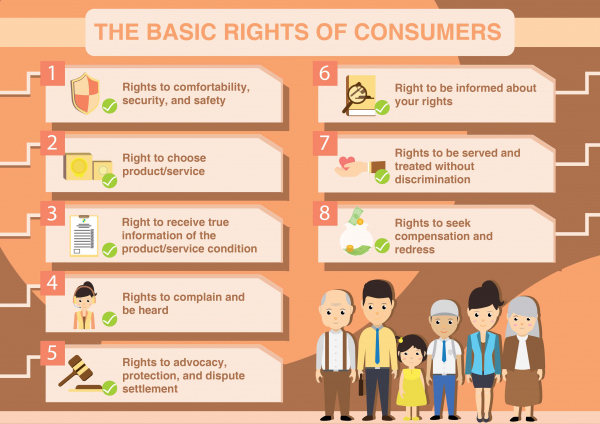
- The Act clearly defined 6 Rights of consumers:
- Right to be protected against the marketing of goods and services which are hazardous to life and property.
- Right to be informed about the quality, quantity, potency, purity, standard and price of goods or services.
- Right to Choice among a variety of goods or services at competitive prices.
- Right to be heard
- Right to seek Redressal against unfair or restrictive trade practices.
- Right to Consumer Awareness
- Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA) to promote, protect and enforce the rights of consumers.
- It functions under the guidelines of The Minister of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution
- It regulates matters linked to the violation of consumer rights, unfair trade practices, and misleading advertisements.
- The CCPA has an investigation wing; they may conduct an inquiry or investigation into the case of violations of rules.
- Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA) functions;
- Inquiring into violations of consumer rights, investigating and taking appropriate action.
- It could pass orders to recall goods or withdraw hazardous services, and refund the price paid.
- It Issues directions to the concerned trader/ manufacturer/ endorser/ advertiser/ publisher to either discontinue a false or misleading advertisement.
- It imposes penalties on a manufacturer or an endorser of up to Rs 10 lakh and imprisonment for up to two years for a false or misleading advertisement. In case of a subsequent offence, the fine may extend to Rs 50 lakh and imprisonment of up to five years.
- It Issues safety notices to consumers against unsafe goods and services.
- Consumer Disputes Redressal Commissions (CDRCs) at the District, State, and national levels.
- Appeals from the State CDRC will be heard by the National CDRC.
- The final appeal to the Supreme Court.
- The District CDRC will entertain complaints where the value of goods and services does not exceed Rs 1 crore.
- The State CDRC will entertain complaints when the value is more than Rs 1 crore but does not exceed Rs 10 crore.
- Complaints with a value of goods and services over Rs 10 crore will be entertained by the National CDRC.
Copyright infringement not intended
https://www.pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1832906
1.png)
https://t.me/+hJqMV1O0se03Njk9














