Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
A U.S. Navy warship responded to a distress call from a commercial tanker in the Gulf of Aden that had been seized by armed individuals and the vessel is now safe.
Details
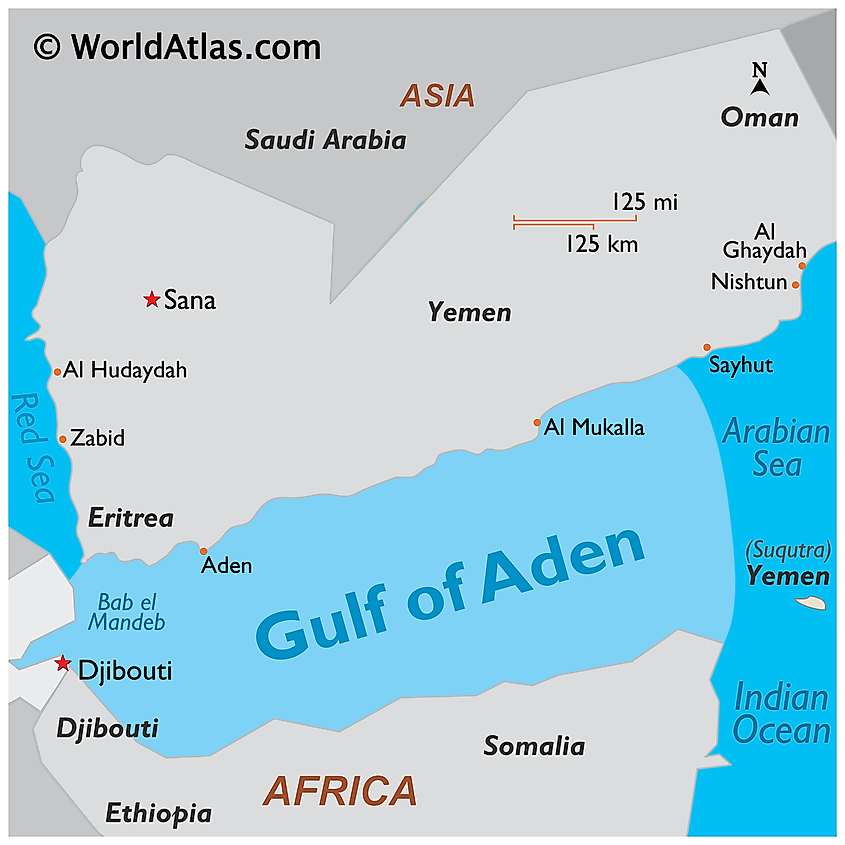
- The Gulf of Aden is a significant water body located in the Arabian Sea between Yemen to the north and Somalia to the south.
- It connects the Arabian Sea to the Red Sea through the Bab-el-Mandeb strait.
Geographic Location and Physical Features
- Location: Situated in the Western Arabian Sea, the Gulf of Aden extends approximately 1,000 kilometers (600 miles) in length and varies in width, narrowing towards the Bab-el-Mandeb strait.
- Surrounding Countries: It is bordered by Yemen on the north, Somalia on the south, Djibouti and Eritrea on the west, and the Arabian Peninsula on the east.
- Physical Features: The gulf is characterized by its strategic location, deep waters, and diverse marine life. It contains several islands, including the volcanic Socotra archipelago, known for its unique flora and fauna
Strategic Importance
- Trade Route: The Gulf of Aden serves as a crucial maritime route, connecting the Indian Ocean with the Red Sea and beyond, making it a significant international shipping passage.
- Bab-el-Mandeb Strait: The strait at the gulf's southwestern tip is one of the world's busiest chokepoints, through which a substantial volume of global trade, including oil shipments from the Middle East, passes

Socio-Political Significance
- Piracy Concerns: The Gulf of Aden gained global attention due to piracy incidents affecting international shipping lanes in the late 2000s. Pirates, primarily from Somalia, targeted vessels for ransom, prompting international naval patrols and security measures.
- Geopolitical Dynamics: The region's strategic location has led to geopolitical interests and tensions among countries vying for control, influence, and access to maritime trade routes.
Environmental and Ecological Aspects
- Marine Biodiversity: The gulf hosts diverse marine ecosystems, including coral reefs, seagrasses, and various fish species. Conservation efforts aim to protect this biodiversity.
- Environmental Challenges: Pollution, overfishing, and illegal fishing practices pose threats to the gulf's marine environment, affecting its ecosystems and the livelihoods of local communities.
Economic Activities
- Fishing and Maritime Industries: Fishing is a significant economic activity for coastal communities around the gulf, supporting livelihoods. Additionally, the region's ports facilitate trade and commerce.
- Oil and Gas Resources: The surrounding areas, including Yemen and Somalia, possess potential oil and gas reserves, attracting exploration activities.

Conclusion
The Gulf of Aden, with its strategic location, economic significance, environmental diversity, and geopolitical complexities, remains a crucial maritime region connecting the Indian Ocean with the Red Sea. Its multifaceted nature presents both opportunities and challenges, requiring international cooperation for sustainable management, security, and conservation efforts.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Which of the following countries borders the Gulf of Aden?
A) Oman
B) Yemen
C) Iran
D) Qatar
Answer: B)
|
















