Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- The Indian Navy has completed its second anti-piracy patrol in the Gulf of Guinea (GoG) in the Atlantic Ocean.
- The offshore patrol vessel INS Sumedha, which is on an extended range operational deployment and is currently operating in the Atlantic Ocean along the west coast of Africa, undertook a 31-day anti-piracy patrol, the Navy said on Thursday.
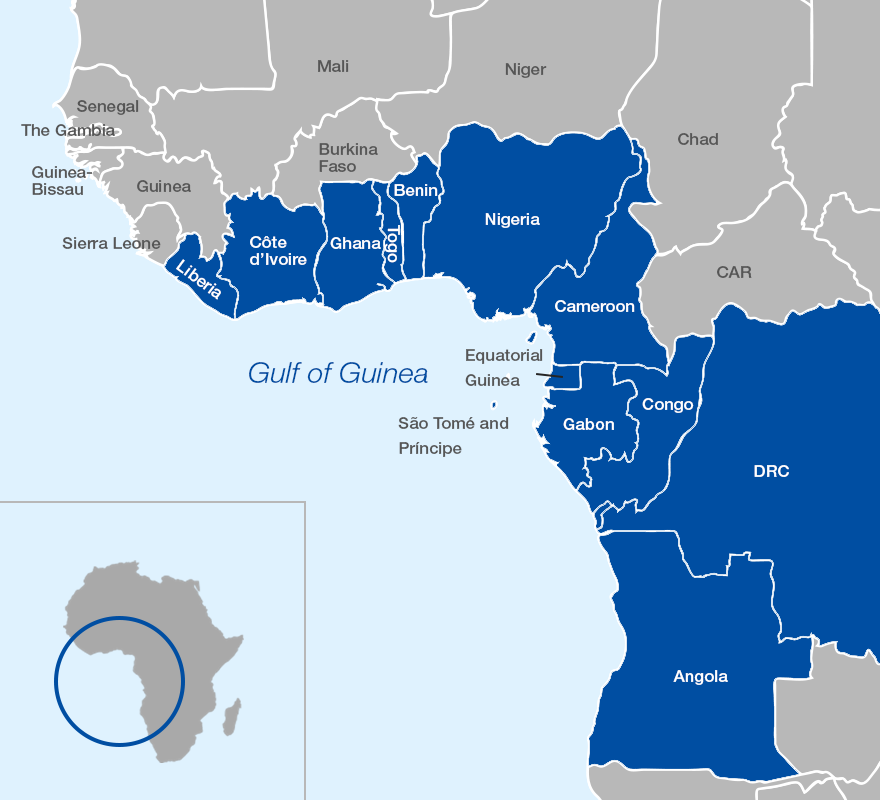
About the Gulf of Guinea
- It is the most northeastern part of the tropical Atlantic Ocean, located off the western coast of Africa.
- It is located at 0°0'N and 0°0'E, at the intersection of the Prime Meridian and the Equator.
- The region is 2.3 million square kilometres, with 6,000 kilometres of coastline.
- It has a relatively narrow continental shelf.
- Because of the rivers that pour into it and the region's heavy rainfall, it has warm tropical waters with relatively low salinity.
- The Volta and Niger Rivers are two of its primary tributaries.

Coastline:
- Angola, Benin, Cameroon, Cote d'Ivoire, Democratic Republic of Congo, Republic of Congo, Guinea, Equatorial Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Gabon, Nigeria, Ghana, So Tomé and Principe, Togo, and Sierra Leone are the 16 coastal countries around the Gulf of Guinea.
- The Gulf's coastline section is largely low-lying, with mangrove swamps, marshes, and lagoons intermingled.
- The shoreline of the Gulf of Guinea is strikingly comparable to South America's continental margin (which spans from Brazil to the Guianas), providing strong support for the notion of continental drift.
- The Gulf of Guinea region accounts for more than 35% of the world’s total petroleum
- It is one of the world’s most dangerous gulfs because of the widespread piracy that has severely affected many countries in West Africa, along with other international countries.
What is the significance of the Gulf?
- It is believed that the Gulf of Guinea today accounts for 7% and 4.5% of the world's gas and oil reserves, respectively.
- It has been a hotspot for piracy and armed robbery at sea.
- It is vital to the major imports and exports of landlocked countries like as Burkina Faso, Central African Republic, Chad, and Mali.
About INS Sumedha
- It is the third ship in the Saryu-class Naval Offshore Patrol Vessels (NOPV) produced in Japan.
- Goa Shipyard Limited designed and built it in-house.
- On March 7, 2014, it was commissioned into the Indian Navy.
- It is part of the Indian Navy's Eastern Fleet, which is headquartered in Visakhapatnam.
- Primary responsibilities include EEZ surveillance, anti-piracy patrols, fleet support operations, maritime security for offshore assets, and escort operations for high-value assets.
Features
- It has a displacement of 2,230 tonnes, a length of 105 meters, and a beam of 12.9 meters.
- It is outfitted with a cutting-edge weapon and sensor suite.
- It is capable of transporting an Advanced Light Combat Helicopter.
- The ship is propelled by two diesel engines, the largest of their sort ever deployed in the Indian Navy, and can attain speeds of up to 25 knots.
- The offshore patrol vessel has a range of 6,000 nautical miles (11,000 km) at 16 knots (30 km/h), making it suited for extended missions and operations.

India’s role in Piracy control and Maritime security
- In order to curb, contain, and eliminate the threat of maritime piracy and armed robbery prevailing in the Gulf of Guinea, the Government of India has sent Indian Navy Ships for patrolling purposes and has sent a fleet to develop anti-piracy capacities of other nations in the vicinity of the Guinean Gulf who are eager to help in fighting for the cause.
- Piracy in the region can be defeated through effective cooperation and implementation of legal frameworks.
- The legal framework is none other than the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea.
- The issue is important in the sense that Piracy is not only a threat to the freedom of navigation but also causes destabilizing effects on global and regional trade and security.
- The negative humanitarian impact of this threat on sea, piracy, and the lifeline of international shipping cannot be compromised any longer.
- The rapid growth of international trade through maritime navigation and the growth of piracy in the past two decades has been unprecedented.
- Another area that is crucial for both India and the Gulf of Guinea is maritime security.
- According to a report from the UN Secretary-General, the number of piracy issues has been reduced in the Gulf by the deterrent effects of the Nigerian Navy naval patrols.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Discuss India's strategic and operational contributions in countering anti-piracy efforts along Africa's western coast. Examine the challenges faced by India in this endeavor and suggest measures for further strengthening its role in ensuring maritime security in the region. (250 words)
|











