Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
The potential collapse of the Gulf Stream system, known as the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (Amoc).
Details
- The Gulf Stream system faces a threat of collapse, known as the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (Amoc).
- Scientists have observed warning signs of a tipping point in 2021, and a new study suggests a potential timescale for the collapse.
- The consequences of Amoc collapse would be catastrophic, with severe climate impacts around the world.
The Weakening of Amoc
- Amoc is already at its weakest in 1,600 years due to global heating.
- Researchers have identified an influx of fresh water from melting ice caps as a key factor smothering the currents.
- Past collapses during ice ages indicate temperature changes of 10 degrees Centigrade in just a few decades.
Estimates and Uncertainties
- The new analysis estimates a timescale for the collapse between 2025 and 2095, with a central estimate of 2050, if global carbon emissions are not reduced.
- Uncertainties in assumptions and data make it challenging to provide a reliable estimate of the tipping point's timing.
- However, scientists agree that the prospect of Amoc collapse is extremely concerning and calls for immediate cuts in carbon emissions.
Impact of Amoc Collapse
- Disrupts rains in regions like India, South America, and West Africa, impacting food supply for billions of people.
- Increases storms and lowers temperatures in Europe.
- Leads to a rising sea level on the eastern coast of North America.
- Endangers the Amazon rainforest and Antarctic ice sheets.
Significance of the Study
- Led by Prof Peter Ditlevsen from the University of Copenhagen, the study sheds light on the unprecedented nature of Amoc collapse.
- Amoc has not been shut off for 12,000 years, making the potential impact unprecedented.
- The study adds to the growing body of evidence regarding climate tipping points.
Debate and Further Research
- The potential collapse of Amoc is intensely debated among scientists.
- Some suggest that the uncertainties and limitations of the study may affect the accuracy of the tipping point's timing.
- Scientists call for further research and improved models to gain a better understanding of Amoc behavior.

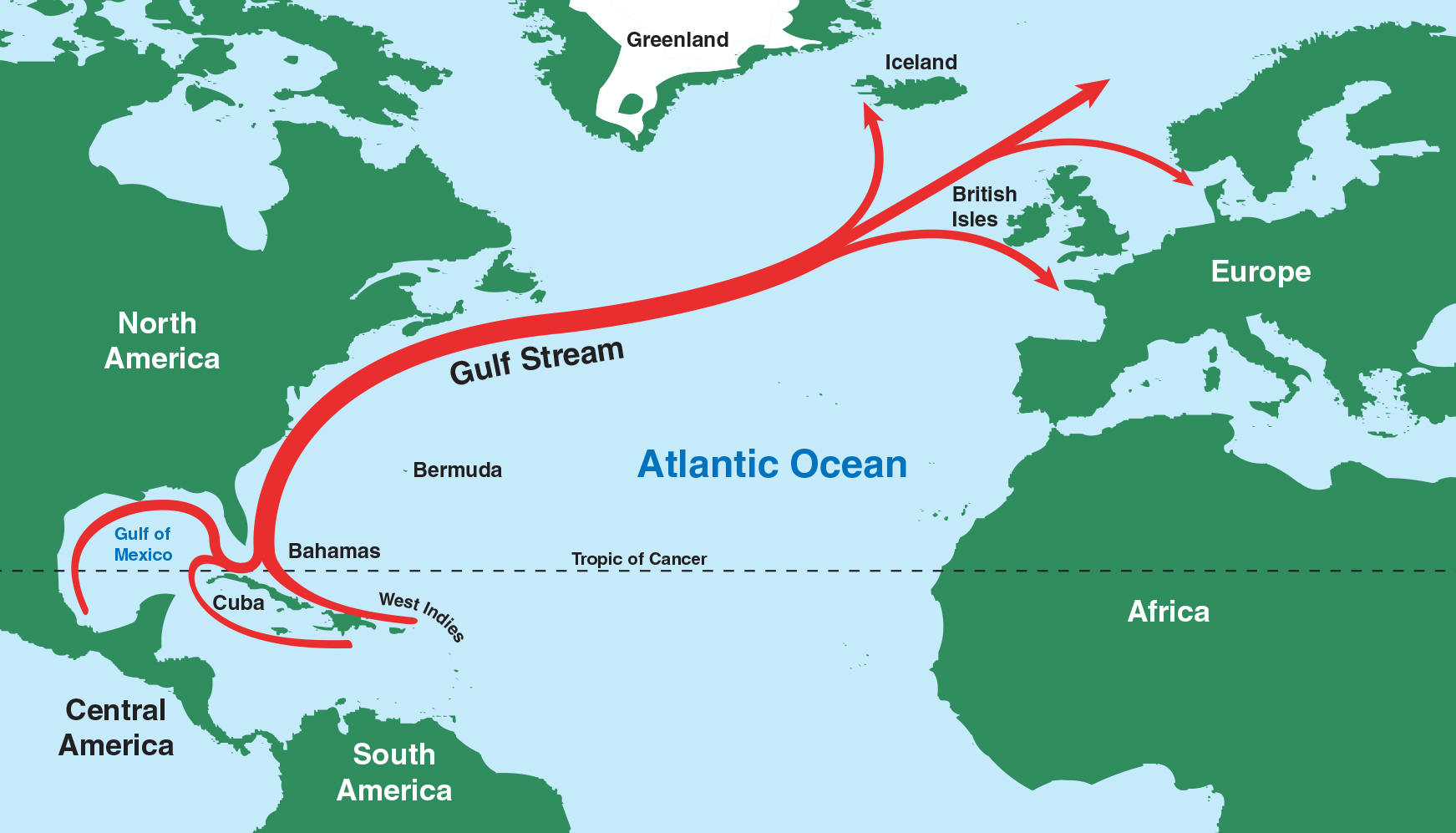
About Gulf Stream
- The Gulf Stream is a powerful ocean current in the Atlantic Ocean, known for its significant role in influencing regional and global climates.
- Originating in the Gulf of Mexico, the Gulf Stream flows northward along the eastern coast of North America before crossing the Atlantic towards Europe.
- It is one of the major components of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (Amoc).
Formation and Pathway
- The Gulf Stream is formed by the convergence of warm waters from the equator and the Caribbean Sea in the Gulf of Mexico.
- It follows a distinct pathway along the eastern coast of the United States, extending northward towards the Canadian Maritimes.
- The current then veers eastward across the Atlantic Ocean, eventually reaching Europe.
Warmth and Climate Influence
- The Gulf Stream is characterized by its warm waters, which are significantly warmer than the surrounding ocean currents.
- As it moves along the eastern coast of North America, it has a moderating effect on the climate, leading to milder temperatures in the region.
- The warm waters of the Gulf Stream also contribute to the formation of hurricanes and tropical storms in the Atlantic.
Influence on European Climate
- The Gulf Stream plays a crucial role in maintaining the relatively mild climate of Northwestern Europe, particularly in regions like the UK, Ireland, and Scandinavia.
- It transfers large amounts of heat from the tropics to the higher latitudes, which keeps the coastal areas warmer during winters.
Impact on Marine Life
- The Gulf Stream supports a diverse array of marine life due to its warm waters and rich nutrient content.
- It serves as a migratory pathway for various marine species, including fish, sea turtles, and marine mammals.
- The abundance of food resources along the Gulf Stream sustains numerous fisheries.
Trans-Atlantic Shipping and Trade
- The Gulf Stream has historically been essential for trans-Atlantic shipping and trade routes.
- Sailors and navigators have utilized the current to facilitate faster voyages between the Americas and Europe.
Vulnerability to Climate Change
- The Gulf Stream is vulnerable to disruptions and shifts due to climate change and melting ice in the Arctic.
- Changes in temperature and salinity can affect the strength and stability of the current, potentially leading to alterations in weather patterns and regional climates.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q) Consider the following statements regarding Gulf Stream
- The Gulf Stream is a warm ocean current that originates in the Gulf of Mexico.
- It has a moderating effect on the climate, leading to colder temperatures along the eastern coast of North America.
Select the correct statements using the codes below
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: C
|

https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2023/jul/25/gulf-stream-could-collapse-as-early-as-2025-study-suggests










