Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
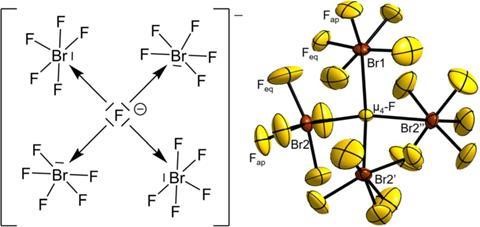
- The recent discovery of a unique interhalogen compound, [NMe4][Br4F21]·BrF5, by chemists represents a significant breakthrough in the field of inorganic chemistry.
Details
- The compound [NMe4][Br4F21]·BrF5 is a novel interhalogen compound, featuring a central fluorine atom coordinated by four BrF5 groups.
- This discovery represents the first example of a central tetracoordinated fluorine atom bridging neither metal nor hydrogen atoms.
About Halogens
- Halogens are a group of chemical elements that belong to Group 17 (formerly Group VIIA) of the periodic table.
- This group includes fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), and astatine (At).
- Halogens are highly reactive nonmetals and exhibit distinct properties due to their unique electronic configurations.
Properties of Halogens:
- Physical Properties:
- Halogens exist in various physical states at room temperature: fluorine and chlorine are gases, bromine is a liquid, and iodine is a solid. Astatine is radioactive and extremely rare.
- They exhibit distinctive colors: fluorine is pale yellow, chlorine is greenish-yellow, bromine is reddish-brown, iodine is violet, and astatine is likely black.
- Chemical Properties:
- Halogens have seven valence electrons, making them highly reactive.
- They readily form compounds with other elements, especially metals, to complete their octet and achieve a stable electron configuration.
- Halogens are strong oxidizing agents, capable of gaining electrons in reactions.
- Reactivity:
- The reactivity of halogens decreases down the group from fluorine to iodine due to increasing atomic size and decreasing electronegativity.
- Toxicity:
- Many halogens, particularly chlorine and fluorine, are toxic in their pure forms. However, they are commonly found in compounds vital to life, such as sodium chloride (table salt).

Uses of Halogens:
- Disinfectants and Bleaches: Chlorine compounds like sodium hypochlorite are widely used as disinfectants and bleaching agents in water treatment and cleaning products.
- Fluorine Compounds: Fluorine compounds, such as fluorides, are essential for dental health (fluoridation of water) and are used in industries like pharmaceuticals and semiconductor manufacturing.
- Organic Synthesis: Bromine compounds are used in organic synthesis, especially in the production of pharmaceuticals, dyes, and flame retardants.
- Iodine: Iodine is essential for human health as a component of thyroid hormones. It's also used in medical disinfectants and dyes.
- Fluorocarbons: Fluorine compounds like Teflon (polytetrafluoroethylene) are used as non-stick coatings and in refrigerants.
Reactions of Halogens:
- Halogen Displacement Reactions: Halogens can displace less reactive halogens from their salts in solution. For example, chlorine water can displace iodine from potassium iodide solution.
- Redox Reactions: Halogens readily undergo redox reactions, gaining electrons to form halide ions (e.g., F⁻, Cl⁻, Br⁻, I⁻) or being reduced to halides in various chemical reactions.
- Combustion: Halogens can support combustion, reacting with many substances, particularly metals, to form halides.
Significance of Halogens:
- Biological Importance: Halogens play crucial roles in biological systems, such as in the function of thyroid hormones (iodine) and enzymes.
- Industrial Applications: Many industrial processes rely on halogens and their compounds, from water purification to the production of pharmaceuticals, plastics, and textiles.
- Environmental Impact: Halogen compounds can have significant environmental impacts, such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) contributing to ozone depletion and polyhalogenated compounds causing bioaccumulation in ecosystems.

Conclusion
The synthesis and structural analysis of [NMe4][Br4F21]·BrF5 represent a remarkable achievement in inorganic chemistry, shedding light on novel bonding arrangements and pushing the boundaries of our understanding of interhalogen compounds.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Halogens are a diverse group of elements with unique properties and versatile applications across various industries. Comment. (15 marks)
|
















