Description

Copyright infringement is not intended
Context - The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW) proposes to organize Health Melas under National Health Mission.
Details
- As part of the celebration of Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav, the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare proposes to organize ‘Block-Level Health Melas’ between 18th and 22nd April 2022.
- The ‘Block Level Health Mela’ is to be organized in all the blocks of every district across the country.
- At the Health Mela, essential drugs and diagnostic services shall be provided free of cost.
- These block-level Health Melas to be organized with the cooperation of various departments like State Health Authority, Department of Food, Department of Youth Affairs and Sports, Department of AYUSH, Department of School Education, Department of Women and Child Development, Department of Culture, Department of Information and Broadcasting, Department of Panchayati Raj Institution & Urban Development, any other Departments as per the context and local need.
- The planning for the mela should be undertaken by the office of the Chief Medical Officer/District Magistrate.
Objectives of the Health Mela
- Increase health awareness for the prevention of various communicable and non-communicable diseases.
- Encourage People through mass media activities to make positive health behaviour changes.
- Provide screening for early diagnosis, and basic health care services including referrals, specialised services and diagnostic services.
- Make people aware of different health and family welfare programmes and various systems of medicine being undertaken by the Government.
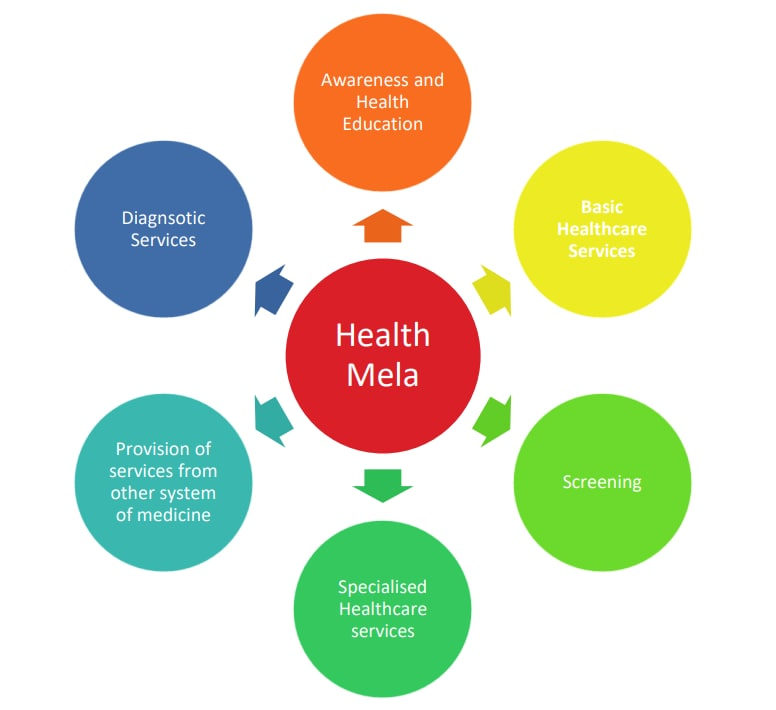
Significance of Health Mela
- Health Melas promote awareness and information about various diseases along with their preventive measures.
- Creating awareness about different schemes and programs of the Government.
- It provides health education, early diagnosis, providing free health care services.
- The Melas will also help in informing people about the different systems of medicine (Allopathy, Homeopathy, Ayurveda and Unani etc).
- Lifestyle information and screening would build awareness of health risks and provide information on how an individual can make changes in their lifestyle to enhance their health.
Healthcare Status in India
- India has the dual burden of both communicable and non-communicable diseases and many of these diseases can be prevented by early diagnosis, providing health education, timely referral and management.
- Nearly 8 lakh cases of cancer are detected each year and around 60-80% of the cases are diagnosed late.
- Lack of awareness and poor health-seeking behaviour have been found to be the major underlying causes of many diseases.
- Inadequate Quality, Accessibility and Affordability of Health Services.
- High out of Pocket expenses.
- Shortage of Infrastructure, Equipment and Skilled Manpower.
- Rigid regulatory Framework Combined with Corrupt enforcement.
- Primary Health Care Centres are not Present in many villages and wherever Present they lack basic facilities.
- Inefficiencies in Procurement Process result in both Shortages and Wastage.
- Nearly 70% of Healthcare delivery is through Private Players which are largely regulated.
- Lack of Sanitation, disease Surveillance, Political will and Public Health response.
- Government spend only 1.5% of GDP on Public Health Care.
- Rising incidence of non-Communicable diseases with income growth, lifestyle Changes and environmental degradation, resulting in a rising total burden of disease.
Steps were taken by the Government
- Promotion of Institutional deliveries through Cash incentive under Janani Suraksha Yojana.
- Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakram: Free ante-natal Check-ups, Post-natal Care and treatment of Sick infants till one year of age.
- Providing Reproductive, Maternal, Newborn, Child and Adolescent Health Services, the establishment of Special Newborn Care Units.
- Mission Indradhnaush: Expanding full immunisation Coverage, the introduction of new vaccines.
- PM Swasthya Suraksha Yojana for strengthening the tertiary health Sector.
- POSHAN Abhiyaan to address Malnutrition.
- Iron and folic acid Supplementation for Prevention of Anaemia, home visits by ASHAs to promote breastfeeding and promote the use of ORS and Zinc for the management of diarrhoea in children.
- Capacity building of Health Care Providers: Training is being conducted under the National Health Mission to build and upgrade the Skills of Health Care Providers.
- Medical Devices Rules, 2017: Transparent regulatory System, Ensure Safety and quality of medical devices, Allowed 100% FDI in medical devices Sector to Promote Make in India.
- National Health Resource Repository: Create a reliable, unified registry of the Country’s healthcare resources showing the distribution pattern of health facilities and Services between Cities and rural areas. ISRO is a technology Partner for providing data Security.
- Allowed 100% FDI in the Medical devices Sector to promote Make in India.
- Kayakalp initiative to Promote Cleanliness, hygiene and infection control practices in public health facilities.
National Health Policy 2017 targets
- Shifts From communicable to non-communicable diseases.
- Collaborating & regulating the private sector.
- A shift from Sick-care to wellness.
- Increase Life Expectancy at birth from 67.5 to 70 by 2025.
- Reduction of TFR to 2.1 at national and Sub-national levels by 2025.
- Reduce under Five Mortality to 23 by 2025 and MMR from current levels to 100 by 2020.
- Reduce infant mortality rate to 28 by 2019.
- Reduce neonatal mortality to 16 and the stillbirth rate to “single-digit” by 2025.
- Reduce premature mortality from cardiovascular diseases, cancer, diabetes or chronic respiratory diseases by 25% by 2025.
Way Forward
- Reduce the Pressure on Secondary and tertiary hospitals by investing in Preventive and Primary Health Care facilities.
- Focus on Early detection and Prevention.
- Provide adequate protection to doctors.
- Increasing the Doctor-Patient ratio.
- Reduce Out of Pocket Expenditure.
- Increase the number of vaccines under Mission Indradhanush.
- Increasing the number of drugs and medical devices under price control.
- The Ministry Should Standardize the Cost of Certain treatments.
- Raising Public Health expenditure to 2.5% of GDP.
- Provide accessible, affordable and quality health care.
- Inform and educate people about the traditional Systems of medicine.
- Ayurveda Doctors and Yoga Teachers for Rural Areas.
- Improve Hospital access, Health worker density, and Access to essential medicine.
- Mobile Medical Units to Provide outreach Services in rural and remote areas.
https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1812383






