Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Several parts of Europe witnessed an unprecedented winter heat wave over New Year’s weekend. Temperatures increased 10 to 20 degrees Celsius above normal. The continent is experiencing an extreme warm spell because of the formation of a heat dome over the region.
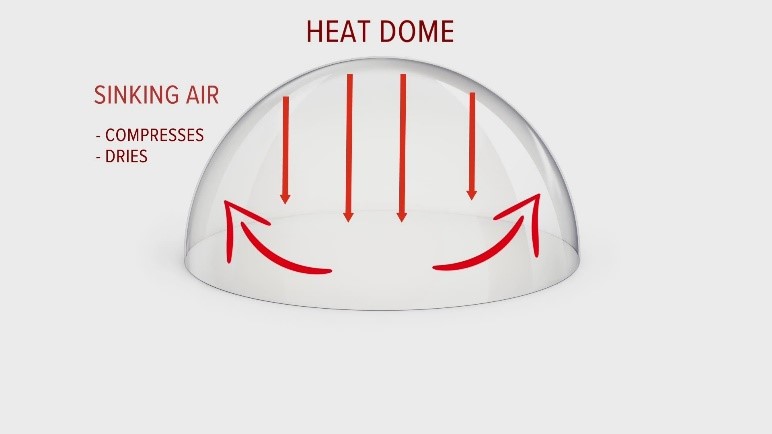
What is a heat dome?
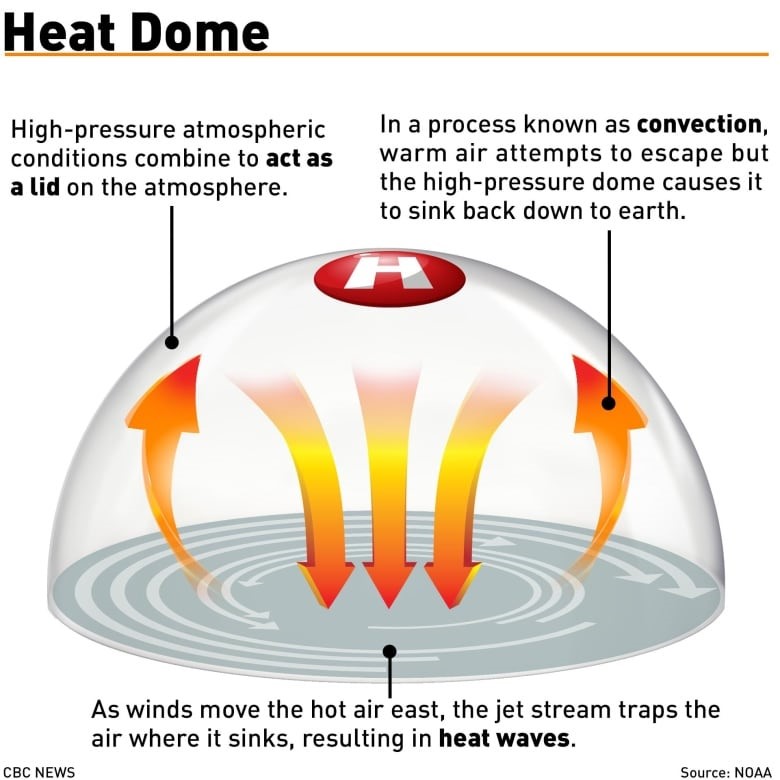
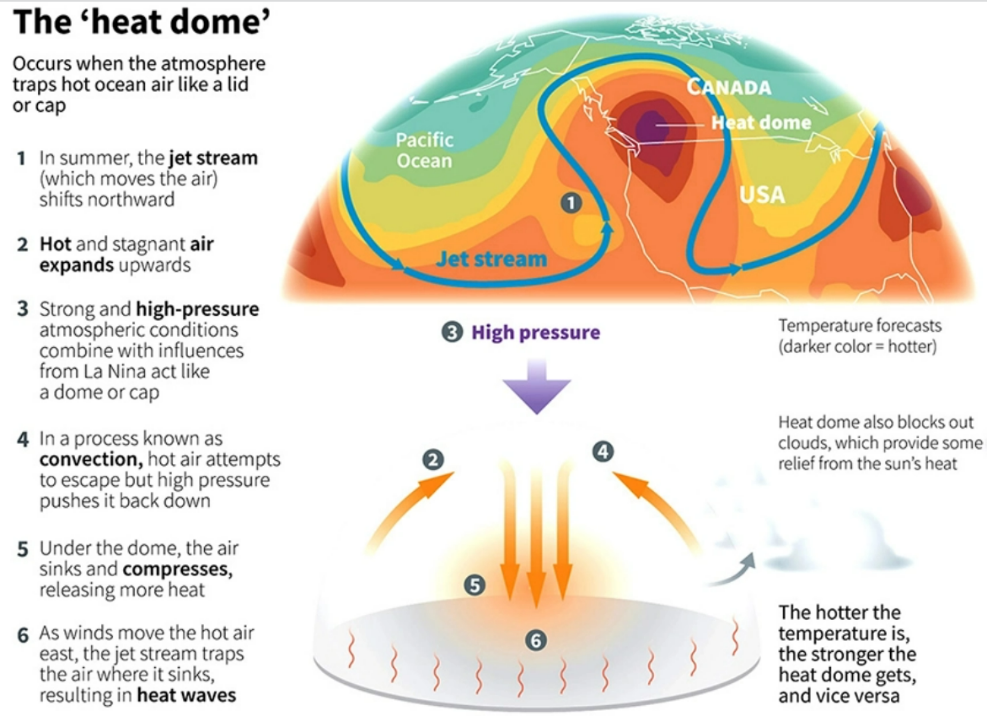
- A heat dome occurs when an area of high-pressure traps warm air over a region, just like a lid on a pot, for an extended period of time.
- The longer that air remains trapped, the more the sun works to heat the air, producing warmer conditions with every passing day.
- Heat domes generally stay for a few days but sometimes they can extend up to weeks, which might cause deadly heat waves.
Relationship between Heat Domes and Jet Streams
- Typically, heat domes are tied to the behavior of the jet stream- — an area of fast-moving air high in the atmosphere, a band of fast winds high in the atmosphere that generally runs west to east.
.jpeg)
|
Jet Streams
Jet streams are relatively narrow bands of strong wind in the upper levels of the atmosphere. The winds blow from west to east in jet streams but the flow often shifts to the north and south. Jet streams follow the boundaries between hot and co ld air.
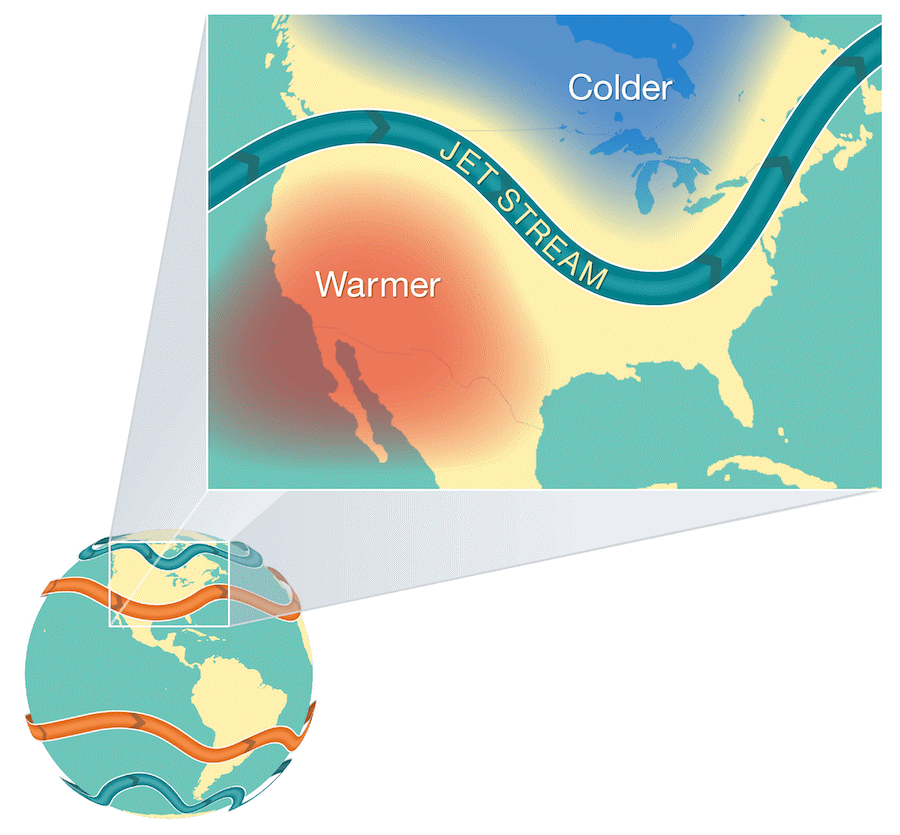
Since these hot and cold air boundaries are most pronounced in winter, jet streams are the strongest for both the northern and southern hemisphere winters. Jet streams form when warm air masses meet cold air masses in the atmosphere.
Mechanism
The Sun doesn’t heat the whole Earth evenly. That’s why areas near the equator are hot and areas near the poles are cold.
So, when Earth’s warmer air masses meet cooler air masses, the warmer air rises up higher in the atmosphere while cooler air sinks down to replace the warm air. This movement creates an air current, or wind. A jet stream is a type of air current that forms high in the atmosphere.
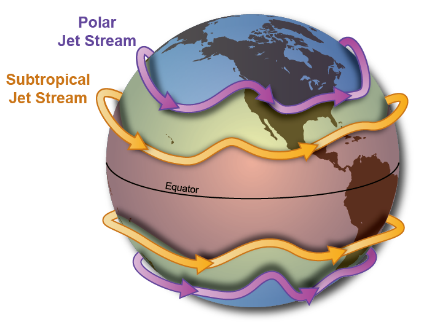
The fast-moving air currents in a jet stream can transport weather systems across the Earth. Jet streams are located about five to nine miles above Earth’s surface in the mid to upper troposphere — the layer of Earth’s atmosphere where we live and breathe.
Airplanes also fly in the mid to upper troposphere. So, if an airplane flies in a powerful jet stream and they are traveling in the same direction, the airplane can get a boost. That’s why an airplane flying a route from west to east can generally make the trip faster than an airplane traveling the same route east to west.
|
- When the waves in a Jet Stream get bigger and elongated, they move slowly and sometimes can become stationary. This is when a high-pressure system gets stuck and leads to the occurrence of a heat dome
Climate Change and Heat Domes
- Researchers say that climate change may be making Heat Domes more intense and longer.
- They suggest with the rising temperatures, it is expected that the jet stream will become wavier and will have larger deviations, causing more frequent extreme heat events.
Heat Domes and their impact on Human Beings
- A heat dome can have serious impacts on people, because the stagnant weather pattern that allows it to exist usually results in weak winds and an increase in humidity. Both factors make the heat feel worse – and become more dangerous – because the human body is not cooled as much by sweating.
- The heat index, a combination of heat and humidity, is often used to convey this danger by indicating what the temperature will feel like to most people. The high humidity also reduces the amount of cooling at night.
- All these, increases the risk of heat illnesses and deaths. With global warming, temperatures are already higher, too.
- One of the worst recent examples of the impacts from a heat dome with high temperatures and humidity in the U.S. occurred in the summer of 1995, when an estimated 739 people died in the Chicago area over five days.
Closing Thoughts
- A 2022 study found that this heat dome was amplified by climate change and it could become a once-in-10-year event if global temperatures aren’t kept under two degree Celsius above pre-industrialization levels.
.jpeg)
Read about Heat Waves and Climate Change: https://www.iasgyan.in/rstv/heat-waves-and-climate-change
https://indianexpress.com/article/explained/explained-climate/what-is-causing-the-winter-heat-wave-in-europe-8359403/













