Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- Earlier in August, Iran recorded a scorching heat index of 70 degrees Celsius (°C) in the coastal part of the country, a metric at which survival of life is unfathomable, if not impossible.
- The country had also declared public holidays on August 2 and 3 on account of "unprecedented heat".
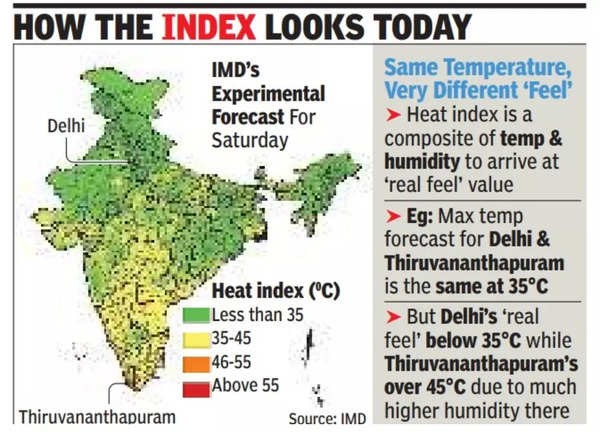
Heat Index
- The heat index, also known as apparent temperature, is a measure of how the temperature feels to humans.
- Relative humidity is an important factor that determines heat index, along with air temperature.
How is the heat index calculated?
- The dew point, which is the temperature at which gas is transformed into a liquid state, is an important factor in the calculation of heat index.
- In terms of atmospheric moisture, it's the temperature at which air cannot hold any more water vapour, and droplets of water begin to form.
- Some countries have developed their corresponding indices to measure heat index.
Importance of the measurement of Heat Index
- It will aid people in comprehending the effect of humidity on high temperatures.
- This index's data could be used to detect the heat implications for humans and to comprehend temperature ranges that cause discomfort.
- It will also aid in directing folks to take extra precautions to alleviate discomfort.
- It will display the minimum and maximum temperatures for the day, as well as how the current temperature feels.
- It will make use of data on air temperature and relative humidity.
- However, it is experimental, and there is a need to modify and validate it for Indian conditions.

Impact of Humidity on the Human Body
- High humidity can lead to heat stress; meaning the body is unable to get rid of excess heat. Humans usually maintain a core temperature in the range of 36.1 to 37.2 °C.
- When the body is unable to get rid of excess heat, the heart rate increases due to a rise in core temperature, leading to heat-related exhaustion and rashes, among other symptoms. It can also be fatal if not addressed promptly.
- At high temperatures, the human body can lose excess heat through perspiration and cool itself. But when humidity is high as well, it is difficult to sweat and then for that sweat to evaporate because the air around is already saturated with moisture. This makes it difficult for the body to lose heat.
- On the other hand, if the humidity is low, evaporation of sweat is easier, thus making the apparent temperature feel close to the actual air temperature.
- This is why a measure of heat index is more useful than just the temperature to gauge the impact of heat on humans.
Measures to adopt
- A heat index value of 67°C or above can be extremely dangerous for people and animals who have direct and prolonged exposure.
- With climate change, we will likely continue to witness record-breaking heat index values across the world.
- We will need to prepare and adapt to such extreme conditions by investing in early warning, making changes to work timings, and finding.
Studies of IMD on Heatwave
- The IMD conducted a study on the impact of meteorological conditions on heatwaves and the country's "heat wave hazard zonation."
- According to the IMD report "Hot Weather Analysis over India," the mechanism by which heat affects humans is complex; it is the result of interactions between temperature, radiation, wind, and humidity.
- There is significant experimental evidence that physiologic stress caused by high temperatures is increased when humidity levels are high.
IMD's Initiatives and Tools to Combat Heat Waves
- Heatwave forecasts must be issued on time to keep the people informed.
- Warnings were issued to disaster management authorities for them to be prepared.
- IMD provides Seasonal outlook and long-term prediction providing more insight into temperature trends.
- Forecasts for the next five days, are updated in real-time.
- Color-coded extreme weather alerts, including heat waves.
- Heat action plans will be developed in collaboration with the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) and local health agencies.
- Plan implementation in susceptible areas to reduce heat-related dangers.
Effects of Heat Stress
- Thermal discomfort affects a variety of activities and jobs.
- Workers have to deal with extreme heat stress, which can hurt their work and productivity and even put their lives at risk.
- Occupational health risks ultimately affect the nation’s income and economy.
- In India, about 75 percent of workers, which is around 380 million people, experience heat-related stress. The increasing heat intensity poses a substantial risk to human health and life.
- This extreme heat is a health hazard and has continued to grow as a disease burden over the past few years.
- Human health can be severely affected. It can cause dehydration, acute cerebrovascular accidents, and blood clots, which result in cramps, exhaustion, stress, heat stroke and even death in extreme cases.
- The elderly, children, people with psychiatric disorders and other diseases are particularly impacted.
- A significant number of deaths have been reported in different parts of the world due to heat vulnerability.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Analyze the reasons for heat island creation in the world's urban habitat.
|

https://epaper.thehindu.com/ccidist-ws/th/th_delhi/issues/50970/OPS/G63BNKJJH.1.png?cropFromPage=true
https://www.downtoearth.org.in/blog/climate-change/heat-index-is-a-critical-tool-to-help-beat-heat-stress-90357
















