Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- UNESCO's World Heritage Centre has agreed to publish Hindi descriptions of India's UNESCO World Heritage Sites on its website.
Official Languages
- There is no national language in India.
- However, article 343(1) of the Indian constitution specifically mentions that, "The official language of the Union shall be Hindi in Devanagari script.”
- The form of numerals to be used for the official purposes of the Union shall be the international form of Indian numerals.
- The business in Indian parliament can only be transacted in Hindi or in English.
- English is allowed to be used in official purposes such as parliamentary proceedings, judiciary, communications between the Central Government and a State Government.
- There are various official languages in India at the state/territory level.
- States within India have the liberty and powers to specify their own official language(s) through legislation.
Constitutional Provision about Official Language
|
Constitutional Provision for Union
|
● Article 348 states that Parliament official language: Hindi or English
● Speaker or Chairman can permit other members to speak in his mother tongue if he is not confident to speak in English or Hindi.
● Under Article 343: Official language of Union is in Devnagari script.
● Numerals would be International numerals.
|
|
Constitutional Provision for States
|
● Under article 210, Official language of State legislature : Hindi, English , Any other official language.
● President can allow any language spoken by majority of people to be used as official language of state.
|
|
Language for communication between two states
|
● Official language of Union will be the official language of communication between two state and states and union.
● If two states agree, then they can choose Hindi to be official language.
|
|
Provision for Judiciary (Supreme Court )
|
● Parliament can provide for Hindi language in Supreme court.
● Since, Parliament has not made any law for it, English is the sole language of Supreme Court.
|
|
High Court
|
● Governor with assent of the president can provide for Hindi or any other language to be the official language of High court.
● Otherwise, language of transaction will be English.
|
|
Language for Bills,Acts
|
● Parliament can provide for Hindi language in Supreme court.
● Since, Parliament has not made any law for it, English is the sole language of bills and acts in parliament.
|
About Hindi Diwas
- Hindi Day/Hindī Diwas is celebrated every year on 14 September marking the declaration of Hindi language as one of the official languages of Union government of India.
- On 14 September 1949, Hindi was adapted as one of the official languages in India.
- As such, on the 50th birthday of Beohar Rajendra Simha on the 14th of September 1949, the efforts resulted in the adoption of Hindi as an official language.
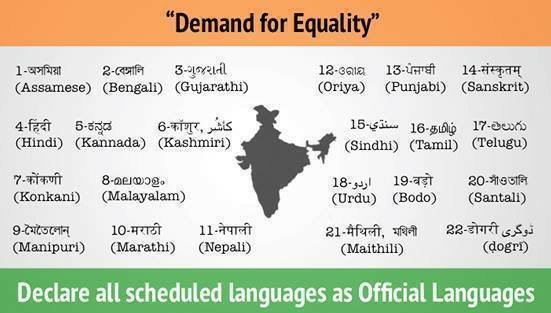
- In all, there are 22 Scheduled languages of India.
UNCESCO World Heritage Centre
- Established in 1992, the World Heritage Centre is the focal point and coordinator within UNESCO for all matters related to World Heritage.
Functions
- Ensuring the day-to-day management of the Convention.
- The Centre organizes the annual sessions of the World Heritage Committee and its Bureau.
- It provides advice to States Parties in the preparation of site nominations.
- It organizes international assistance from the World Heritage Fund upon request.
- It coordinates both the reporting on the condition of sites and the emergency action undertaken when a site is threatened.
- The Centre also organizes technical seminars and workshops, updates the World Heritage List and database, develops teaching materials to raise awareness among young people of the need for heritage preservation, and keeps the public informed of World Heritage issues.
World Heritage Sites in India
- A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO).
- World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, scientific or other form of significance.
- India has 40 world heritage sites that include 32 Cultural properties, 7 Natural properties and 1 mixed site.
- India has the sixth largest number of sites in the world.
Cultural (32)
- Agra Fort (1983)
- Ajanta Caves (1983)
- Archaeological Site of Nalanda Mahavihara at Nalanda, Bihar (2016)
- Buddhist Monuments at Sanchi (1989)
- Champaner-Pavagadh Archaeological Park (2004)
- Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus (formerly Victoria Terminus) (2004)
- Churches and Convents of Goa (1986)
- Elephanta Caves (1987)
- Ellora Caves (1983)
- Fatehpur Sikri (1986)
- Great Living Chola Temples (1987,2004)
- Group of Monuments at Hampi (1986)
- Group of Monuments at Mahabalipuram (1984)
- Group of Monuments at Pattadakal (1987)
- Hill Forts of Rajasthan (2013)
- Historic City of Ahmadabad (2017)
- Humayun's Tomb, Delhi (1993)
- Jaipur City, Rajasthan (2019)
- Khajuraho Group of Monuments (1986)
- Mahabodhi Temple Complex at Bodh Gaya (2002)
- Mountain Railways of India (1999,2005,2008)
- Qutb Minar and its Monuments, Delhi (1993)
- Rani-ki-Vav (the Queen’s Stepwell) at Patan, Gujarat (2014)
- Red Fort Complex (2007)
- Rock Shelters of Bhimbetka (2003)
- Sun Temple, Konârak (1984)
- Taj Mahal (1983)
- The Architectural Work of Le Corbusier, an Outstanding Contribution to the Modern Movement (2016)
- The Jantar Mantar, Jaipur (2010)
- Victorian Gothic and Art Deco Ensembles of Mumbai (2018)
- Rudreswara Temple of Telangana (2021)
- Dholavira in Gujarat (2021)
Natural (7)
- Great Himalayan National Park Conservation Area (2014)
- Kaziranga National Park (1985)
- Keoladeo National Park (1985)
- Manas Wildlife Sanctuary (1985)
- Nanda Devi and Valley of Flowers National Parks (1988,2005)
- Sundarbans National Park (1987)
- Western Ghats (2012)
Mixed (1)
- Khangchendzonga National Park (2016)
World Heritage Sites across the world
- The World Heritage List comprises 1121 properties of Outstanding Universal Value.
- Natural sites represent about 23% of this list, including 39 mixed (both cultural and natural) sites and 213 natural sites.
- Apart from India, countries like Italy, Spain, Germany, China and France also have 40 such sites each.
- China is home to largest number of UNESCO world heritage sites in the world. It has 55 world heritage sites.
Benefits of a World Heritage Site designation
- It brings international attention to the need for the preservation and conservation of the site.
- It brings tourism to the site, with its accompanying economic benefits to the host country and local area.
- It can provide funds for restoration, preservation, and training. For example, in 2001, the Taliban destroyed two 6th century, 150-ft. statues of Buddha carved into the mountainside in the Bamiyan Valley in Afghanistan. The site has received more than $4 million from UNESCO to help with reconstruction and to hire a sculptor to re-carve some of the damaged stone.
- It promotes national and local pride in the natural and man-made wonders of the country.
- It promotes close ties with the United Nations system and the prestige and support it provides.
- It provides access to global project management resources.
- It facilitates creating partnerships between government, the private sector, and NGOs to achieve conservation goals.
- Once declared, the site becomes protected under Geneva convention against destruction during a war.
https://newsonair.gov.in/News?title=UNESCO-agrees-to-publish-Hindi-descriptions-of-India%26%2339%3bs-World-Heritage-Sites-on-its-website&id=433286















