Description
Context
- India is expected to have the highest ever horticulture production of 329.86 million tonnnes in 2020-21, up by 2.93% over previous year.
India's position in production of horticulture crops
- It ranks second in fruits and vegetables production in the world, after China.
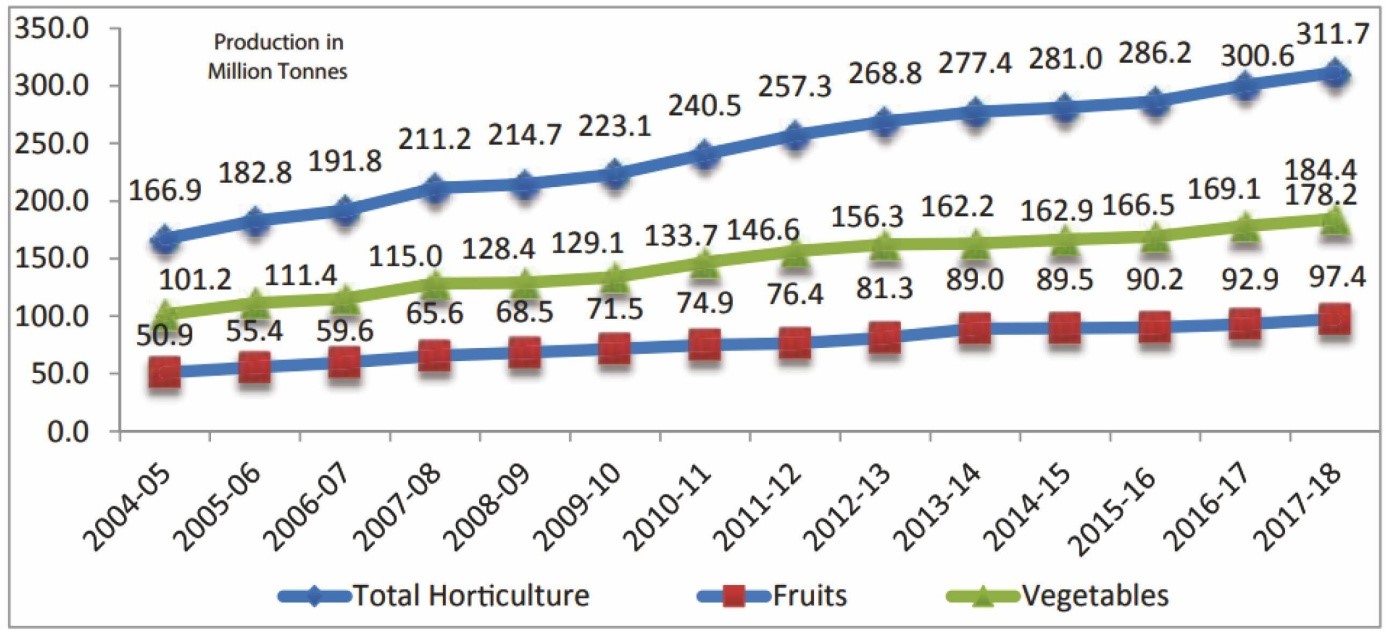
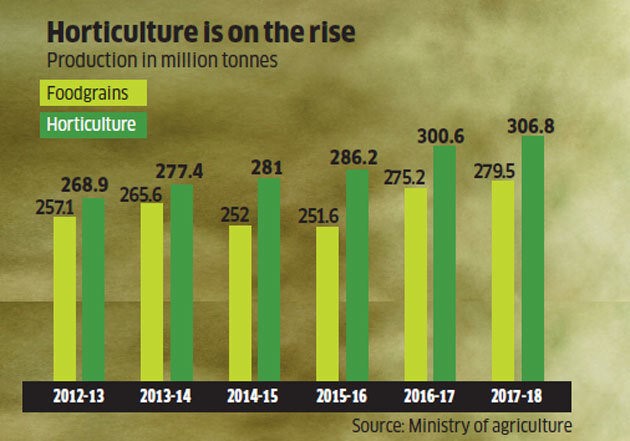
- Its horticulture production has increased by 30 per cent in the last five years.
- India is the second largest producer of fruits and vegetables in the world with first rank in the production of Banana, Mango, Lime & Lemon, Papaya and Okra.
Top State and their percent(%) Share in Production
|
Fruit
|
|
State
|
Share
|
|
Andhra Pradesh
|
15.63%
|
|
Maharashtra
|
12.05%
|
|
Uttar Pradesh
|
10.82%
|
|
Vegetable
|
|
Uttar Pradesh
|
15.40%
|
|
West Bengal
|
15.03%
|
|
Madhya Pradesh
|
9.52%
|
|
Plantation Crops
|
|
Kerala
|
33.48%
|
|
Karnataka
|
27.30%
|
|
Tamil Nadu
|
23.42%
|
|
Flower
|
|
Tamil Nadu
|
17.33%
|
|
Andhra Pradesh
|
15.40%
|
|
Karnataka
|
11.63%
|
|
Spices
|
|
Madhya Pradesh
|
14.67%
|
|
Rajasthan
|
14.09%
|
|
Andhra Pradesh
|
13.54%
|
Challenges in the Horticulture Sector
- Minimum Support Price (MSP) is not applicable to this sector.
- Lack of machinery and equipment.
- High price fluctuations.
- Lack of good cold chain storage and transport networks.
Way Ahead
- Science and technology-led advancement
- Improvement in quality seeds & plants and bringing newly introduced cultivators that ensures quick and efficient cultivation process.
- Imparting the meaningful education related to Horticulture to upscale youth knowledge regarding various government schemes and modern equipment and machinery.
- Adopt post-harvest management exercises to enhance the value of fruits in the long run.
- Value addition is the process that meets the requirements of nutritional security. It boosts the economic value of Horticulture crops.
- Organizing Research & Development Programmes at National level.
- Establishing a better long-distance transportation network should be a task of utmost importance to ensure smooth and hindrance-free transportation of fresh Horticultural produce.
- Preserved cultivation, hydroponic & aeroponic should get enfolded for polishing up productivity along with the quality of produce.
Initiatives taken
- Horticulture Area Production Information System (HAPIS) - a web enabled information system by which data from the states/districts is reported. This minimizes the time-lag and maximizes the coverage area.
- Coordinated programme on Horticulture Assessment and MANagement using geoinformatics (CHAMAN) - to develop scientific methodology for estimation of area & production under horticulture crops. Method used: Remote Sensing and Sample Survey Techniques.
- Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH) is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme for the holistic growth of the horticulture sector.Under MIDH, Government of India (GOI) contributes 60%, of total outlay for developmental programmes in all the states except states in North East and Himalayas, 40% share is contributed by State Governments. In the case of North Eastern States and Himalayan States, GOI contributes 90%. Schemes under it are: National Horticulture Mission (NHM); Horticulture Mission for North East and Himalayan States (HMNEH); National Horticulture Board (NHB); Coconut Development Board (CDB) & Central Institute of Horticulture (CIH), Nagaland
https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/economy/agriculture/horticulture-production-to-high-record-high-at-329-86-million-tonnes-says-agriculture-ministry/articleshow/84446709.cms












