Description
Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
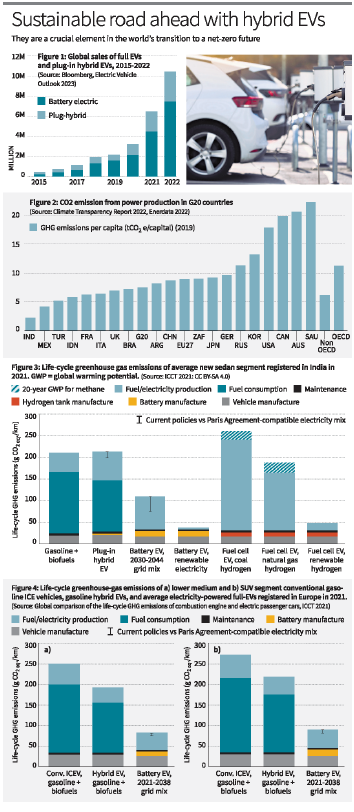
- A crucial element of the world’s transition to becoming net-zero is electric vehicles (EVs).
Details
Introduction
- Electric Vehicles (EVs) play a crucial role in achieving a net-zero emissions future.
- In economically developing countries, hybrid EVs offer an opportunity to kick-start the shift towards sustainable transportation while overcoming challenges associated with full EV adoption.
Types of EVs
- Hybrid EV: Combines an internal combustion engine (ICE) with an electrical generator and a small battery (1-5kWh) as an energy buffer. It cannot be charged from the grid.
- Full EV: Has no ICE and runs solely on electric power. Uses a larger battery (20-120 kWh) and can be charged from the grid.
- Plug-in Hybrid EV: Similar to a hybrid EV but with a larger battery (5-15 kWh) that can be charged from the grid. Can operate in fully electric mode for short commutes.
Fuel Economy and Emissions
- Hybrid EVs have 1.5-2x higher fuel economy than conventional ICE vehicles for city driving and 1-1.5x higher for highway driving.
- Plug-in hybrid EVs offer 3-4x higher fuel economy than conventional vehicles during short commutes.
- Life-cycle emissions analysis shows full EVs can result in 19-34% lower emissions by sedans and 38-49% by SUVs even in fossil-fuel-dominated energy mix regions.
- Hybrid EVs have 20-23% lower life-cycle emissions compared to conventional EVs in Europe.
.jpg)
Challenges in Transitioning to Electric Mobility
- Fast-Charging Infrastructure: Requires power levels of 50-350 kW for cars and up to 1,000 kW for heavy-duty vehicles. Lack of fast-charging discourages full EV adoption.
- Limited Grid Access and Reliability: Many economically developing nations lack reliable access to the grid, hindering EV charging.
- High Vehicle Costs: Mass-market EV price points are lower in developing countries, making EVs with longer range costlier due to higher battery costs.
Role of Hybrid EVs in Decarbonization
- Hybrid EVs, both full and plug-in, offer a practical and cost-effective solution to lower emissions in the interim.
- They drastically reduce fuel costs, emissions, and oil imports with higher fuel economy in electric mode.
- Regenerative braking and engine start-stop mechanisms further improve fuel economy in hybrid EVs.
- Hybrid EVs can match several benefits of full EVs regarding emissions and performance without requiring large batteries.
Conclusion
Hybrid EVs provide an important transition strategy for economically developing countries. They offer fuel economy and emissions benefits while addressing the challenges of limited grid access and high vehicle costs. Full EVs remain the ultimate goal, but in the short term, hybrid EVs present a practical and sustainable solution towards net-zero emissions in the transport sector.
MUST READ ARTICLES:
https://www.iasgyan.in/blogs/electric-vehicles-22
https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/electric-vehicles-28
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Discuss the significance of Hybrid Electric Vehicles (EVs) as a transitional solution in the context of sustainable transportation for economically developing countries. How do they address the challenges associated with full EV adoption, and what are the benefits they offer in terms of fuel economy and emissions reduction? (250 Words)
|

https://epaper.thehindu.com/ccidist-ws/th/th_delhi/issues/45929/OPS/GU2BIAP91.1+G09BIC6TP.1.html






.jpg)










