





Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://www.governing.com/archive/gov-hydropower-renewable-energy.html
Context: Droughts have highlighted the vulnerability of hydropower to climate change, as reduced reservoir water levels have severely impacted electricity generation in many countries.
Details
Vulnerability to Climate Change
|
Recent Examples ●Recent droughts in Colombia and Ecuador have significantly reduced reservoir water levels, leading to energy shortages and the need for power cuts. This demonstrates the immediate impact of climate-related water scarcity on hydropower-dependent regions. ●The global drop in hydropower generation in 2023, mainly due to drought conditions intensified by climate change, highlights the greater risks connected with over-reliance on this energy source. |
Mitigation Strategies and Adaptations
|
Despite its limitations, hydropower is regarded as critical for decarbonising the global economy because of its scalability and cost-effectiveness. To reach climate targets, significant investment in hydroelectric capacity is required. This includes updating existing infrastructure and creating new initiatives with an emphasis on sustainability. |
About Hydropower
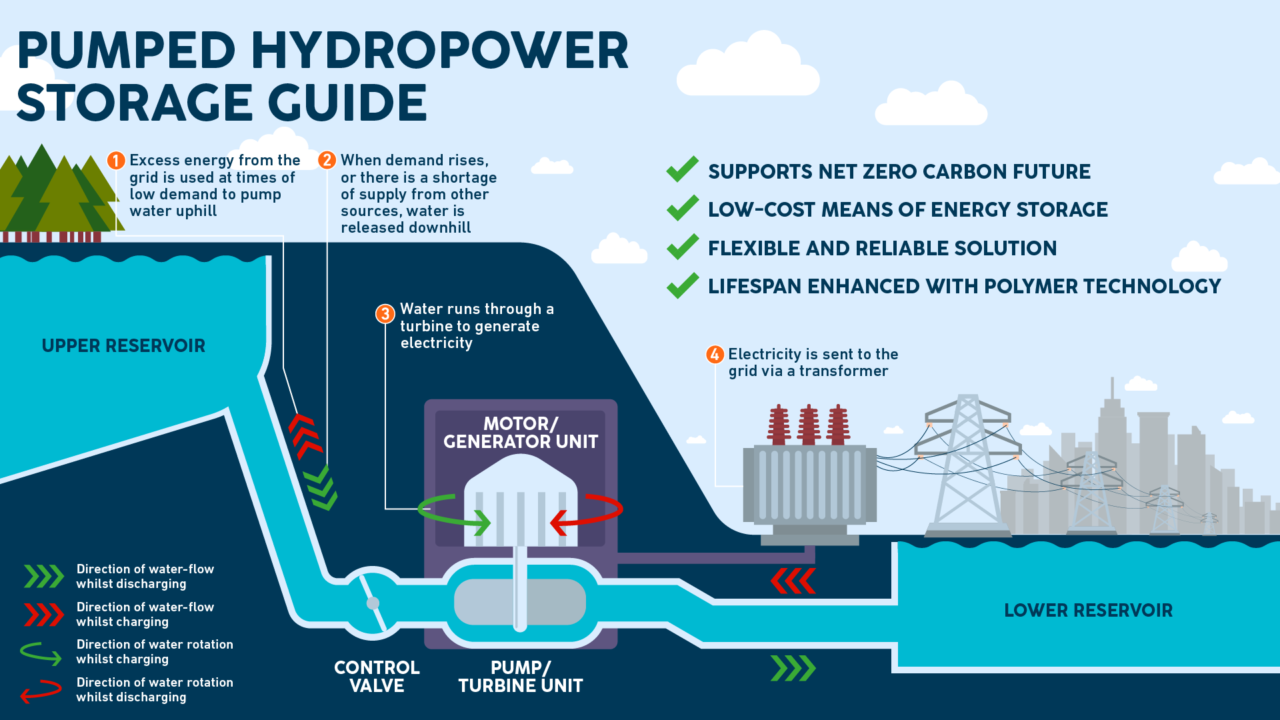
Advantages of Hydropower
Considerations and Downsides
Role in Sustainable Development
|
Reuters analysis of Indian government data on Hydropower output ●India is 5th globally for installed hydroelectric power capacity. ●Hydropower's share in India's total power output dropped to a record low of 8.3% during the fiscal year ended March 31, 2024. ●The share of renewables in India's power output also decreased for the first time since the Prime Minister made commitments to boost solar and wind capacity at the United Nations climate talks in Paris in 2015. Renewables accounted for 11.7% of India's power output, down from 11.8% in the previous year. ●With hydroelectricity output decreasing, there is a higher dependence on coal-fired power generation, especially during periods of high demand. India, being the world's third-largest greenhouse gas emitter, faces challenges in reducing its reliance on coal. ●Low reservoir levels due to light rainfall suggest that hydro output will likely remain low during the upcoming hot months of April to June. Any potential increase in hydro generation due to the monsoon season may not be evident until July. ●Erratic rainfall patterns raise concerns about the long-term reliability of hydropower as a consistent energy source. Experts caution against relying too heavily on hydroelectricity given the unpredictability of future rainfall patterns. ●While hydropower output globally experienced a decline, India's decline was notably faster than the global average. Factors such as lower rainfall and warmer temperatures due to the El Nino weather pattern contributed to this trend. |
Conclusion
Source:
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. India has immense hydropower potential, but many projects face resistance due to concerns about displacing communities and disrupting ecosystems. Critically analyze the challenges of finding a balance between hydroelectric development and sustainable environmental and social practices in India. Propose specific strategies that could be implemented to mitigate these challenges. |










© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved