Description
Copyright infringement not intended
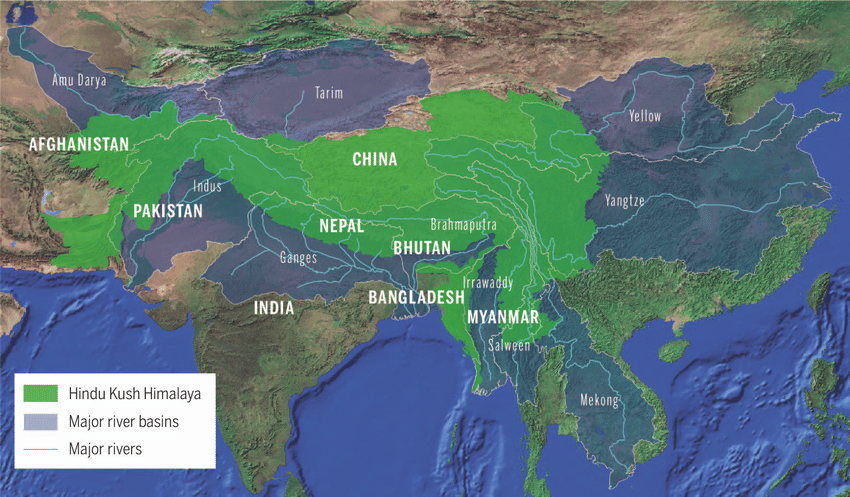
Picture Courtesy: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/The-Hindu-Kush-Himalaya-region-and-10-major-river-basins-Map-by-ICIMOD_fig1_343908172
Context: The Hindu Kush Himalaya (HKH) region faces a critical situation, emphasizing the urgency for action and financial support by the International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) to prevent the collapse of natural ecosystems in High Mountain Asia.
Key points of the ICIMOD's Report
- ICIMOD characterizes the HKH region as a 'biosphere on the brink,' indicating a state of imminent ecological crisis.
- The organization is hosting the Third Lead Authors meeting of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) in Kathmandu.
Losses in Nature and Habitat
- Experts from ICIMOD express deep concern about the rapid and extensive losses in both nature and habitat within the HKH region, describing them as 'catastrophic.'
- Deputy Director General conveys a sense of urgency, suggesting that it may be nearly too late to address the crisis effectively.
Biodiversity Hotspots and Protected Areas
- The HKH region stands out globally, hosting four of the world’s 36 recognized biodiversity hotspots.
- Additionally, the region boasts 575 Protected Areas and 335 important bird areas, signifying its ecological significance.
Impact on Mountain Communities
- Despite concerted conservation efforts, a significant portion (70%) of the original biodiversity in the HKH region has been lost over the last century.
- The dependence of mountain communities, constituting 85% of the region's population, on this biodiversity for fundamental needs like food, water, flood control, and cultural identity is stressed.

High Mountain Asia - 'Water Tower’
- High Mountain Asia, encompassing the Tian Shan, Kunlun Shan, Pamir, Karakoram, Hindu Kush, Tibetan Plateau, and the Himalayas, is termed the 'Water Tower of Asia.'
- This region, spanning 3,500 kilometres and eight countries, plays a critical role in providing essential ecosystem services, including clean water for a third of the world’s population.
Population and Food Security
- The HKH region has a population of 241 million people, with 31% categorized as 'food-insecure,' and half facing some form of malnutrition.
- Urgent prioritization of investment is advocated to fund efforts against nature loss and species extinction.
Call for Urgent Investment
- It emphasizes the immediate need to prioritize investment in the HKH region to combat nature loss and prevent the collapse of crucial ecosystems.
- The call includes a plea for accelerated policy, institutional, and market reforms, along with a rapid increase in integrated global finance, particularly for vulnerable regions like the HKH.
|
Global Mountains Assessment
●Given the acute vulnerability of mountains to climate change, ICIMOD researchers propose a dedicated Global Mountains assessment by IPBES.
●Mountains cover 22% of Earth’s land surface but hold 50% of the world’s global biodiversity hotspots, making them a critical focus for global biodiversity efforts.
|
ICIMOD (International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development)
- ICIMOD is a regional knowledge and learning centre serving the eight regional member countries of the Hindu Kush Himalayan (HKH) region: Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, China, India, Myanmar, Nepal, and Pakistan.
- Established in 1983, ICIMOD works to promote sustainable mountain development through knowledge generation, capacity building, and regional cooperation.
- The Hindu Kush Himalaya (HKH) is a vast mountain range stretching across eight countries, home to some of the highest peaks in the world, including Mount Everest. The region is vital for the well-being of over 2 billion people downstream, providing water, food, and energy. However, it is also facing immense challenges, such as climate change, poverty, and natural disasters.
ICIMOD focuses on several key areas in the HKH
- Studying glaciers, snow cover, and river systems to understand the impacts of climate change on water resources and develop adaptation strategies.
- Assessing the impacts of climate change on the HKH region and supporting countries in developing adaptation and mitigation strategies.
- Conserving biodiversity and restoring degraded ecosystems in the HKH.
- Improving the livelihoods of mountain communities through sustainable agriculture, disaster risk reduction, and other initiatives.
- Fostering cooperation among HKH countries on issues of common concern.
Key ICIMOD Initiatives
- Hindu Kush Himalayan Assessment (HKHA): A comprehensive assessment of the HKH region published in 2019, highlighting the region's importance and vulnerability in the face of climate change.
- HI-WISE (Water, Ice, Society, and Ecosystems in the Hindu Kush Himalaya): A follow-up to the HKHA, focusing on the ecological and human impacts of changes in the cryosphere.
- Hindu Kush Himalayan Monitoring and Assessment Programme (HIMAP): A long-term program that monitors and assesses the state of the HKH region and provides data and information for decision-making.
- Regional Information System (RIS): A platform that provides access to data and information on the HKH region.
- Knowledge Management and Capacity Building: ICIMOD provides training, workshops, and other capacity-building programs to stakeholders in the HKH region.
The HKH region faces many challenges, including:
- Climate change: The HKH is warming at twice the global rate, leading to glacier retreat, floods, and other impacts.
- Poverty: Many mountain communities in the HKH are among the poorest in the world.
- Natural disasters: The HKH is prone to earthquakes, landslides, and other natural disasters.
Way forward for sustainable development in the HKH
- Climate Resilience Programs: Implementing initiatives to enhance climate resilience in communities, focusing on sustainable agricultural practices and water management.
- Poverty Alleviation Measures: Introducing poverty alleviation programs that empower communities economically and socially, improving their adaptive capacity.
- Disaster Preparedness: Strengthening infrastructure, early warning systems, and community-based disaster preparedness to reduce the impact of natural disasters.
- International Cooperation: Collaboration between nations, organizations, and communities to develop and implement sustainable strategies for climate resilience, poverty reduction, and disaster management in the HKH region.
- Research and Innovation: Investing in research and innovation to better understand the complex interplay of climate change, poverty, and natural disasters, leading to informed decision-making and effective solutions.

Conclusion
- ICIMOD plays a vital role in promoting sustainable development in the Hindu Kush Himalaya region. By focusing on key areas such as water, climate change, and livelihoods, ICIMOD is helping to build a brighter future for the mountains and their people.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. The HKH region is often referred to as the "water towers of Asia," feeding major rivers like the Indus, Ganges, and Brahmaputra. However, climate change and human activities pose significant threats to these crucial water sources. Discuss the complex interplay between glacial retreat, changing precipitation patterns, and growing water demands in the region. What are some potential solutions and challenges to ensuring sustainable water management in the HKH?
|












