





Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
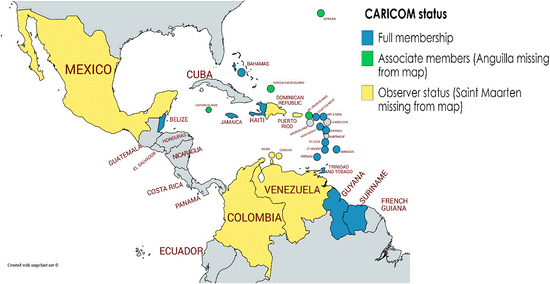
About CARICOM
Pillars of Integration
History
Members
Organisational strcture
India – CARICOM: a brief
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q) Which of the following statements with reference to CARICOM is/are incorrect? a. It is a political and economic union of 15 nation states. b. CARICOM came into being in 1973 with the signing of the Treaty of Chaguaramas.
Correct Answer: 1 |








© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved