Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- The Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) for setting up of campus of IIT Madras in Zanzibar- Tanzania was signed between India and Zanzibar- Tanzania.
Details
- This is the first ever IIT campus to be set up outside India.
- IIT campus in Zanzibar- Tanzania is envisioned as a world-class higher education and research institution with a broader mission to develop competencies in response to emerging global requirements, deepen ties between the nations, and support research and innovation in the region. It will serve as an example to the world, of the aspirational qualities of Indian higher education and innovation.
- It is reflective of the longstanding friendship between India and Tanzania and a reminder of the focus India places on building people-to-people ties across Africa and the Global South.
- Recognizing the strategic partnership between the Tanzania and India, the relationship of educational partnership has been formalized by signing the document.
- The setting up of IIT Campus shall also enhance India’s reputation globally and its diplomatic relationships and expand the international footprint of IIT.
- It will further serve to deepen research collaborations with other top-ranked academic institutions worldwide.
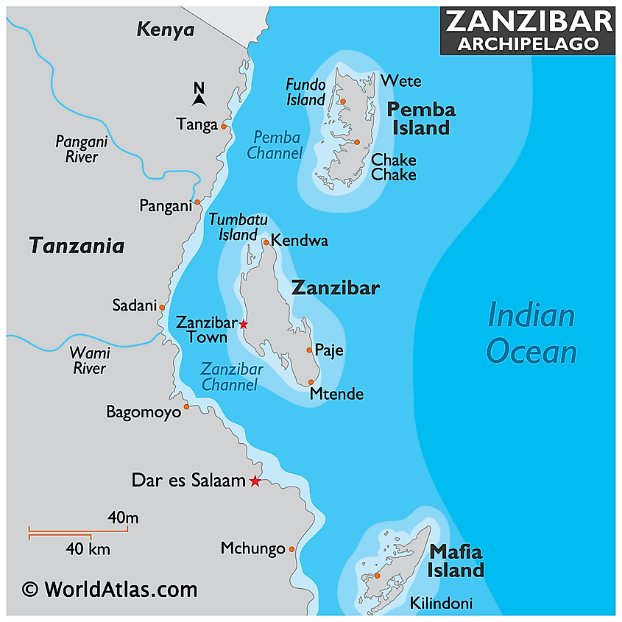
Zanzibar
- Zanzibar is an archipelago off the coast of east Africa that united with Tanganyika in 1964 to form the United Republic of Tanzania.
- It is a semi-autonomous region of Tanzania.
Tanzania
History
- After Tanganyika and Zanzibar became independent countries, they merged in 1964 to form the nation of Tanzania.
Size and Islands
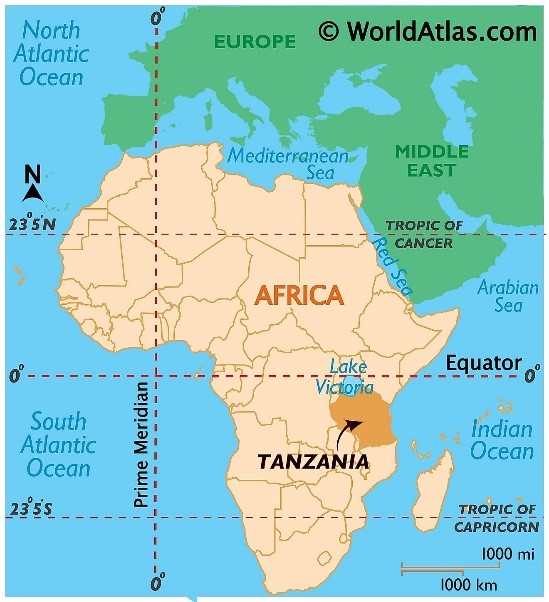
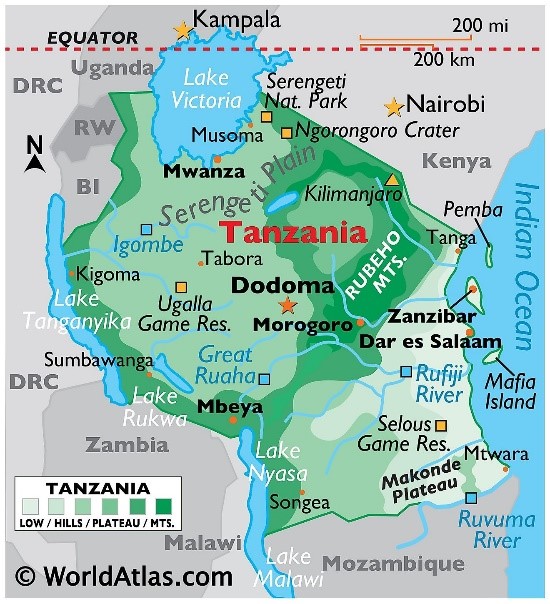
- Tanzania is the largest country in East Africa and includes the islands of Zanzibar, Pemba, and Mafia.
Borders
- It is bordered by the Indian Ocean and eight countries: Kenya, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Democratic Republic of Congo, Zambia, Malawi, and Mozambique.
Physical Features
- It is home to Mount Kilimanjaro, the tallest mountain in Africa. Three of the largest lakes on the continent are also found in Tanzania – Lake Victoria in the north, Lake Tanganyika in the west and Lake Nysa in the southwest. These lakes border the Mount Kilimanjaro.
- It also incorporates Africa's lowest point: the floor of Lake Tanganyika, at 1,471 metres (4,826 ft) below sea level.
- Kalambo Falls in the southwestern region of Rukwa is the second highest uninterrupted waterfall in Africa, and is located near the southeastern shore of Lake Tanganyika on the border with Zambia.
Human Settlements
- Some of the world’s oldest human settlements have been found in Tanzania, at a site called Olduvai Gorge. The hundreds of fossilised bones and stone tools excavated here, are over two millions years old.
- The genus Australopithecus ranged across Africa between 4 and 2 million years ago, and the oldest remains of the genus Homo are found near Lake Olduvai.
Biodiversity
- Tanzania is highly biodiverse and contains a wide variety of animal habitats.
- On Tanzania's Serengeti plain, white-bearded wildebeest (Connochaetes taurinus mearnsi), other bovids and zebra participate in a large-scale annual migration.
- Tanzania is home to about 130 amphibian and over 275 reptile species, many of them strictly endemic and included in the International Union for Conservation of Nature's Red Lists of countries.
- Tanzania has the largest lion population in the world.
- Tanzania is the world’s largest producer of cloves.
Conservation
- Tanzania has a number of important national parks and nature reserves – such as the Selous Game Reserve, where one of the largest populations of elephants live, and The Gombe Stream National Park, where animal expert Dr Jane Goodall carried out her famous research on chimps in their natural habitat.
- The Serengeti National Park, Tanzania’s oldest and most popular park for tourists, is home to over 1.7 million wildebeest and about a million other animals.

India-Tanzania Relations: Overview
- Tanzania and India have traditionally enjoyed close, friendly, and cooperative relations.
- From the 1960s to the 1980s the political relationship was driven largely by shared ideological commitments to anti-colonialism and socialism in various.
- Traditional ties and the spirit of mutual cooperation between Tanzania and India have been consistently reinforced through various international co-operations such as the Non-Aligned Movement (NAM) and later through the various initiatives of South-South Cooperation. The most recent example of such South-South solidarity was the 2008 India – Africa summit hosted by India to advance and strengthen the ties between India and Sub-Saharan Africa.
- The traditional ties between India and Tanzania have their historical roots in the migration of Indian traders to East Africa. The colonial dimension played a significant role in migratory patterns. It should be noted that Indian traders, mostly settled in the other British colonies of Kenya and Uganda and the British protectorate of Zanzibar.
- India is the second largest trading partner of Tanzania with bilateral trade of USD 2.37 billion in 2020-21.
- India is also among the top five investment sources in Tanzania with investments in Tanzania reaching USD 3.65 billion in 2022. The exports of India to Tanzania have increased at an annualized rate of 10.5%, from USD 115M in 1995 to USD 1.41B in 2020. The main products that India exported to Tanzania in 2020 were Refined Petroleum (USD 481M), Packaged Medicaments (USD 215M), and Raw Sugar (USD 30.7M).
- The exports of Tanzania to India have increased at an annualized rate of 9.51%, from USD 92M in 1995 to USD 891M in 2020.
- In 2020, Tanzania exported USD 891M to India.
- The main products that Tanzania exported to India were Raw Copper (USD 260M), Coconuts, Brazil Nuts, and Cashews (USD 221M), and Gold (USD 159M).
Recent high-level visits
- Prime Minister Narendra Modi paid a State Visit to Tanzania from 9-10 July 2016.
- During the visit, the following MOU/agreements were signed:
-
- MOU on Cooperation in the field of water resource management and development;
- Agreement on Joint Action Plan between National Small Industries Corporation of India and Small Industries Development Organization of Tanzania;
- Visa waiver agreement for Diplomatic/Official passport holders (entered into force in December 2016);
- MOU for the Establishment of Vocational Training Centre at Zanzibar;
- Line of Credit of USD 92 million for rehabilitation and improvement of the water supply system in Zanzibar.
-
Commercial and Economic Relations
- India and Tanzania share vibrant economic, commercial and business ties.
- India is the third largest trading partner of Tanzania with bilateral trade of USD 4.58 billion in 2021-22 (as per DGCI&S data). India is also among the top five investment sources in Tanzania and as per Tanzania Investment Centre, Indian investments in Tanzania add up to USD 3.68 billion.
- At present major Indian companies in Tanzania are Airtel (telecom); Tata Africa Holdings Ltd, Mahindra & Mahindra (tractors), Kamal Group (Steel), Kalpataru (power transmission), Tanzindia (insurance with significant share of Indian PSEs), Larsen & Toubro, Afcons, Hester Biosciences (animal vaccines), Mahashree Agro, Purandare Industries (sugar factory) etc.
- Hester Biosciences Africa Limited is constructing a USD 18 million veterinary Vaccines manufacturing factory in Kibaha, Coast Region.
- Purandare Industries (Tanzania) Limited is setting up a sugar factory in Chamvino District of Tanzania near Dodoma.
- Mahashree Agro has invested in Tanzania for pulses processing.
- A large number of Escorts manufactured tractors and farm equipment, TATA, Ashok Leyland and Eicher commercial vehicles can be seen in Tanzania.
- 3 Indian banks that are operating in Tanzania are Bank of Baroda, Bank of India, and Canara Bank.
- Two Indian companies – M/s Pacco Gems Limited and M/s Nazareth Investment Company Limited have obtained licenses for Graphite extraction in Tanzania.
- India’s major exports to Tanzania include petroleum products, pharmaceuticals & chemicals, motor vehicles, electrical goods, articles of iron & steel, sugar, machinery, etc. Tanzania’s major exports to India include gold dore, cashew nuts, pulses, timber, spices (mainly cloves), ores and metal scrap, gemstones, etc.
Bilateral Treaties & Agreements
India and Tanzania have signed a number of bilateral Treaties/MOUs/Agreements. They are:
- Agreement on Friendship & Technical, Economic and Scientific Cooperation (1966)
- Trade Agreements (1972)
- MOU on Technical Cooperation in the field of Posts and Telecommunications (1996)
- Agreement on the establishment of Joint Business Council (1997)
- Agreement on establishment of a Joint Trade Committee (2000)
- MOU for Co-operation in the field of Agriculture and Allied Sectors (2002)
- Agreement in the field of Health & Medicine (2002)
- MoU on Exchange Programme on Co-operation in the field of Education (2003)
- MOU on Defence Cooperation (2003)
- Agreement on Waiving Tanzania’s Outstanding Loans (2004)
- Agreement on Cooperation in Information Technology and Services (2004)
- Letter of Intent on PTA/FTA (2008)
- MOU on JV between National Social Security Fund, Tanzania, Ministry of Health and Social Welfare and Apollo Hospitals Ltd. (2011)
- Agreement on Double Taxation and Prevention of Fiscal Evasion (2011). Earlier DTAA was signed in 1979.
- Joint Action Plan between National Small Industries Corporation Ltd and Small Industries Development Organisation (2011).
- Letter of Intent between Ministry of Steel and Ministry of Energy & Minerals.
Defence & Security Cooperation
- India and Tanzania signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) on Defence Co-operation in Oct 2003. The MoU provides an over-arching framework for progressing various defence co-operation initiatives between the two countries.
- In recent years, India and Tanzania have been cooperating in the field of defence training in Indian institutions. Over 550 Tanzanian defence personnel have been trained in India.
- Hydrography is another advancing area of cooperation between the two countries. Indian naval survey ships have conducted hydrographic surveys of Tanzanian ports and prepared navigational charts
- High Commission of India organised a DefExpo on 30th May 2022 in Dar es Salaam in association with Department of Defence Production, Ministry of Defence & Society of Indian Defence Manufacturers (SIDM).
- In 2022, IN Ship Tarkash participated in bilateral Maritime Partnership Exercise with Tanzania and 1st trilateral exercise involving India-Tanzania-Mozambique.
Culture
- Swami Vivekananda Cultural Centre (SVCC), Dar es Salaam under the Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR), coordinates cultural outreach since its establishment in December 2010. SVCC offers classes in Yoga, vocal music, tabla and Hindi language by Indian teachers.
- In 2021, ICCR sponsored Baba Gorekhnath Gotipua Dance Association from Odisha to perform at prestigious 40th Bagamoyo International Festival in Bagamoyo, Tanzania.
- An MoU for establishment of ICCR chair at University of Dar es Salaam (UDSM) was signed between ICCR and UDSM in 2021. Tanzanian siblings Kili and Neema Paul who lip sync Indian songs, have a huge following in India.
- Famous Nyati Mchoya group from Tanzania were sponsored by Government of India to perform at International Suraj Kund Mela in Faridabad from in 2022.
- 8th International Day of Yoga (IDY 2022) was celebrated on 19 June 2022 at Uhuru Stadium in Dar es salaam.
- High Commission in collaboration with Institute of Social and Cultural Studies (ISCS) Kolkata and National Museum of Tanzania organized a 2-day International Conference on “India-Tanzania Relations: An Overview” in 2022.
Indian Diaspora
- Tanzania is home to about 40,000 people of Indian origin which are concentrated in the major urban centres of Dar es Salaam, Arusha, Mwanza, Dodoma, Morogoro, Zanzibar, and Mbeya.
- The Indian origin community is active in the field of trade and industry in Tanzania.
- Indian/Asian community organizations active in Tanzania regularly organize Indian festivals and social events mostly with local participation and occasionally by inviting performing artistes from India.
- Indian community have managed to retain their cultural identity and celebrate all Indian festivals.
- The real core of India’s relation with Tanzania lies in its people-to-people relations. The role of People of Indian Origin (PIO) and other Indian settlers is crucial in strengthening the historical bond shared by these countries across the Indian Ocean.

Closing Remarks
- In addition to the booming trade, India and Tanzania have also strengthened their relations through cooperation in human resources, health, education and infrastructure, among other areas.
- The years to come will require increased movement of trade, capital and human resources from both India to Tanzania as well as vice versa.
- The flow of human capital and trade has laid the foundation for a relationship which continues to have a great scope for growth.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Indians in Tanzania played a crucial role, not only in its economy but also in its politics and became a distinctive part of the country’s social fabric. The flow of human capital and trade has laid the foundation for a relationship that continues to have a great scope for growth. Comment.
|
https://pib.gov.in/PressReleasePage.aspx?PRID=1937687
















