Description
Copyright infringement not intended
Picture Courtesy: https://www.everydayhealth.com/tuberculosis/guide/risk-factors-causes-prevention/
Context: The India TB Report 2024, released by the Union Health Ministry, provides significant information about the country's current tuberculosis (TB) control activities.
Key Highlights of the Report
Missing Cases on the Decline
- The report highlights a significant decrease in "missing cases." These are individuals with TB who haven't been diagnosed and can unknowingly spread the infection. In 2023, the number dropped to 2.3 lakh, compared to 3.2 lakh the previous year.
- This reduction is credited to the Ni-kshay portal, a government initiative that effectively tracks TB patients. The portal ensures they receive proper care, healthcare providers can monitor their progress, and potential issues are identified early on. This comprehensive approach helps find and treat missing cases before they can spread the disease.
|
Tuberculosis
●Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB).
●It primarily affects the lungs, but it can spread through the bloodstream to other parts of the body, such as the brain, spine, kidneys, and even the bones.
|
Closing Gap between Estimated and Actual Cases
- Narrowing the gap between the estimated number of TB cases and the actual number diagnosed. This is important because "missing cases" are assumed not to have received treatment, and can continue to transmit TB.
- With better detection methods and improved surveillance, the gap is closing, signifying a more accurate picture of the TB burden in India.
Private Sector Stepping Up
- While government health centres still report the majority of TB cases, the private sector is playing a more prominent role.
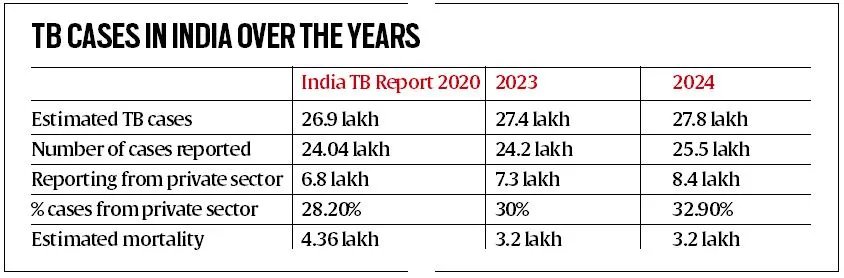
- In 2023, a significant portion (33% or 8.4 lakh) of reported cases came from private facilities, compared to just 1.9 lakh in 2015.
- This trend indicates a positive shift. Broader participation from private healthcare strengthens India's fight against TB by expanding access to diagnosis and treatment across the healthcare system.
TB Burden and Mortality
- Despite the positive trends, the estimated number of TB cases remains high, with 27.8 lakh cases in 2023. The number of TB-related deaths remained unchanged at 3.2 lakh.
- These figures highlight the substantial TB burden in India and the need for continued efforts to reduce both incidence and mortality.

Reaching Treatment Targets
- India achieved a commendable goal in 2023: initiating treatment for 95% of diagnosed TB patients. This signifies a well-functioning healthcare system with efficient treatment initiation processes.
- More patients (58% in 2023 compared to 25% in 2015) are being tested for drug resistance, a crucial step in ensuring they receive the most effective therapies.
Prioritising Drug Susceptibility Testing
- The report emphasises the importance of drug susceptibility testing (DST) to identify drug-resistant TB early.
- Early detection allows for prompt initiation of appropriate treatment, minimising the risk of treatment failure and further transmission of drug-resistant strains.
Conclusion
- The India TB Report 2024 demonstrates significant progress in TB control. However, the fight is far from over. Continued investment in surveillance, diagnostic tools, and treatment services is crucial to address the remaining challenges. Collaboration between public and private healthcare sectors, coupled with innovative strategies, will move India further towards its goal of eliminating TB as a public health threat.
Must Read Articles:
TUBERCULOSIS: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/tuberculosis
WORLD TB DAY: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/world-tb-day-47
|
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. Which drug is commonly used as a first-line treatment for tuberculosis (TB)?
A) Penicillin
B) Rifampicin
C) Ciprofloxacin
D) Acyclovir
Answer: B
|












