





Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
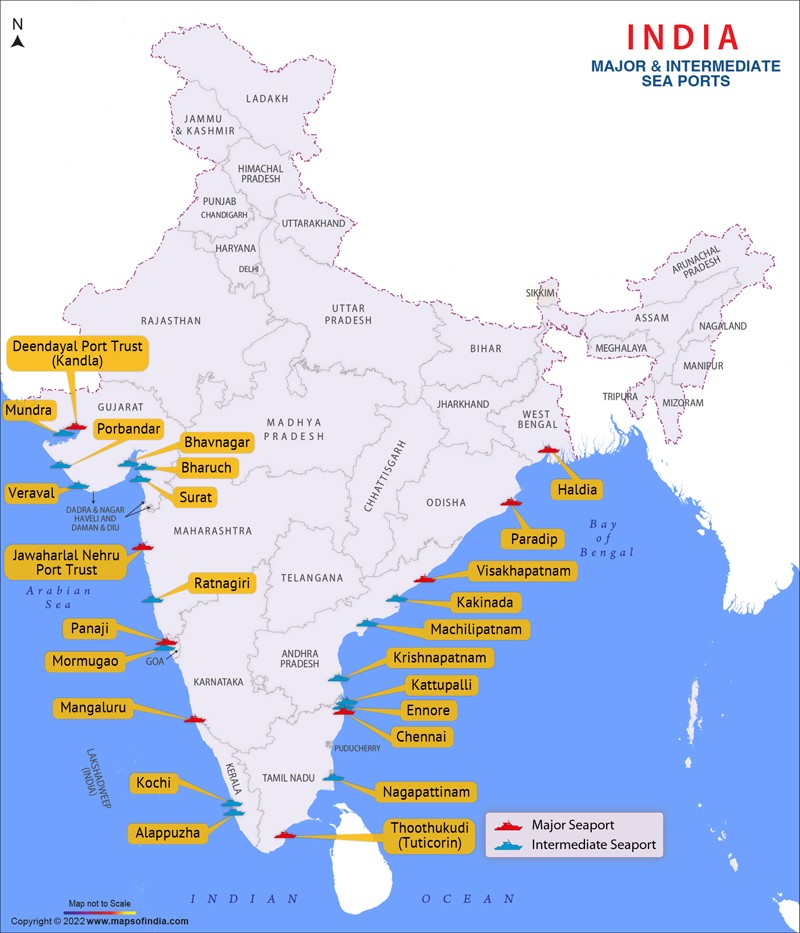
Mundra Port:
History:
MUST READ ARTICLES
NATIONAL LOGISTICS POLICY: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/national-logistics-policy
SAGARMALA PROJECT: https://www.iasgyan.in/daily-current-affairs/sagarmala-project-17#:~:text=Under%20the%20Sagarmala%20Programme%2C%20the,and%20more%20under%20their%20governance.
MAJOR PORTS IN INDIA: https://www.iasgyan.in/blogs/major-sea-ports-in-india
India’s Maritime Sector and Shipping Industry
Challenges in the Functioning of Major Ports in India
|
Challenge |
Details |
|
Inadequate Depths |
Major ports in India faced limitations in their available depths, making them unsuitable for various international vessels. |
|
Dredging Challenges |
Dredging efforts by these ports proved ineffective, resulting in substantial discrepancies between the drafts in access channels and berths. |
|
Extended Ship Turnaround |
India’s ports encountered extended ship turnaround times, contrasting with Singapore where this process takes less than a day. |
|
Inefficient Cargo Handling |
Cargo handling services at ports were inefficient, with many berths lacking dedicated facilities necessary for swift processing of key cargo types. |
|
Obsolete Equipment |
Over half of the port equipment exceeded their economic lifespans, leading to low utilization, as users preferred modern privately-owned equipment. |
|
Storage Shortages |
Ports experienced issues related to storage space and connectivity, crucial for seamless accumulation and distribution of cargo. |
|
Connectivity Challenges |
Connectivity infrastructure deficiencies hindered efficient cargo evacuation, including narrow last-mile links, daytime truck movement restrictions, and lack of dedicated port roads connecting to highways. |
|
Lengthy Inspections and Scrutiny |
Despite advancements in digitization and paperless customs procedures, maritime operations and cargo remained subject to prolonged inspections and scrutiny. |
|
Environmental Non-Compliance |
Port operations often resulted in spills, leaks during cargo operations, and oil spills, as they failed to adhere to environmental regulations and standards. |
|
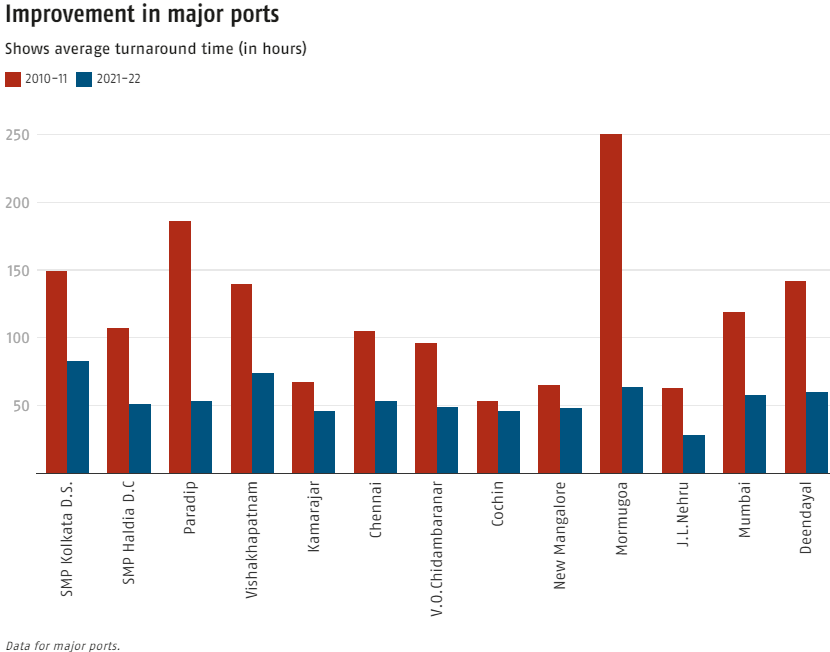
High Turnaround Times |
Ports in India suffer from high turnaround times for ships. For example, in Singapore, the average ship turnaround time is less than a day, whereas in India, it is over two days. |
|
Port Congestion |
Port congestion due to container volume, shortage of handling equipment, and inefficient operations is a major concern. Example: In Nhava Sheva port. |
|
Sub-optimal Transport Modal Mix |
Lack of requisite infrastructure for evacuation from major and non-major ports leads to sub-optimal transport modal mix. |
|
Limited Hinterland Linkages |
Poor hinterland connectivity through rail, road, highways, coastal shipping, and inland waterways increases the cost of transportation and cargo movement. |
|
Lengthy Inspection and Scrutiny |
Despite the shift to digital customs operations, inspections and scrutiny continue to be lengthy for cargo and other shipping operations. |
|
Inadequate Infrastructure and Technology Issues |
Lack of adequate berthing facilities, material handling equipment, navigational aids, and IT systems pose operational challenges at non-major ports. |
|
Issues with Regulations |
Regulatory disparities between major and non-major ports, rigid frameworks, and restrictions on foreign-flagged vessels contribute to regulatory challenges. |
|
Issues with PPP Model |
Port PPPs impose restrictions on private operators, tariff regulation issues, and the absence of dispute resolution mechanisms, hampering operational flexibility. |
|
Environmental Impact |
Poor adherence to environmental laws leads to spillage, pollution, and dredging-related environmental problems, threatening marine ecosystems. |
|
Social Impacts of Port Development |
Port projects often result in community displacement, restrictions on fishing grounds, and other social concerns among affected populations. |
|
Manpower and Labour Issues |
Lack of training, declining manpower quality, and resistance to reform pose challenges to port labor management. |
|
Unhealthy Competition |
Development of multiple ports handling similar cargo in close vicinity may lead to unhealthy competition for cargo arrivals. |
In a nutshell, Existing ports face numerous shortcomings, such as outdated designs unfit for modern demands, inadequate infrastructure, poor connectivity, insufficient dredging capacity, and a lack of technical expertise and equipment.
Silver Lining: Industry Scenario
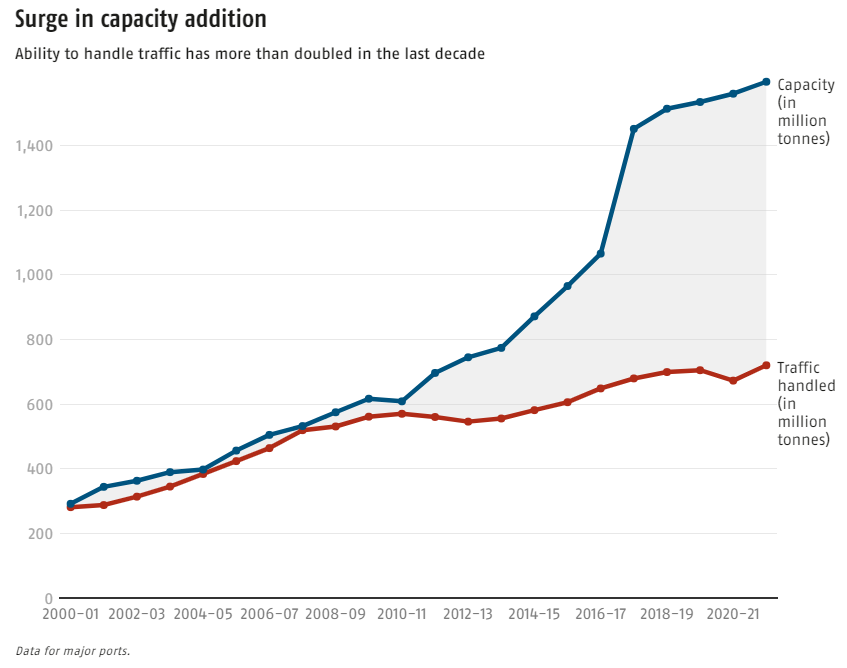
Cargo Traffic on the rise
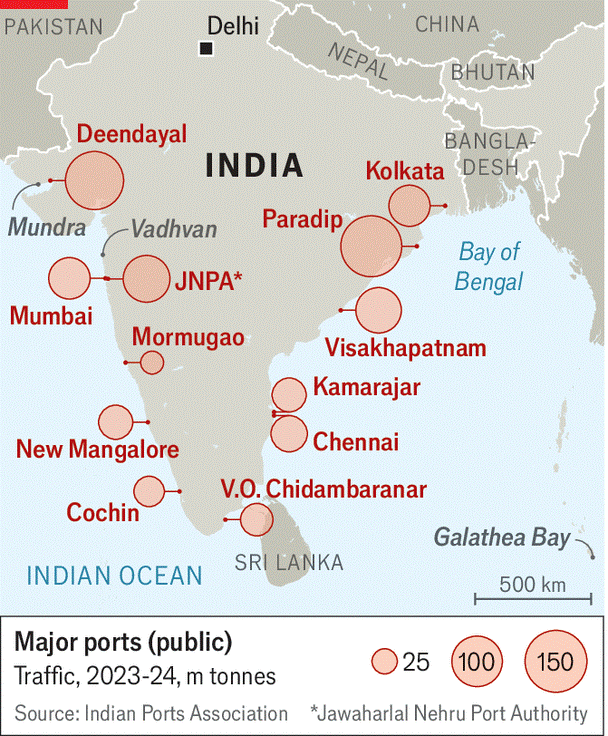
Performance
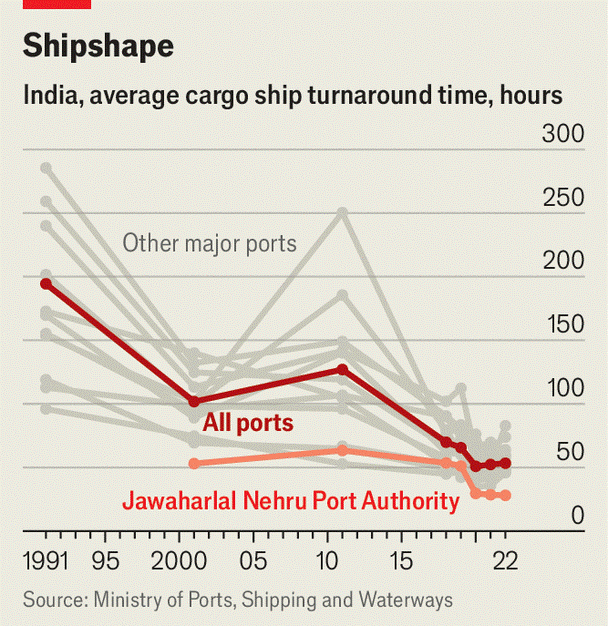
Turnaround Time
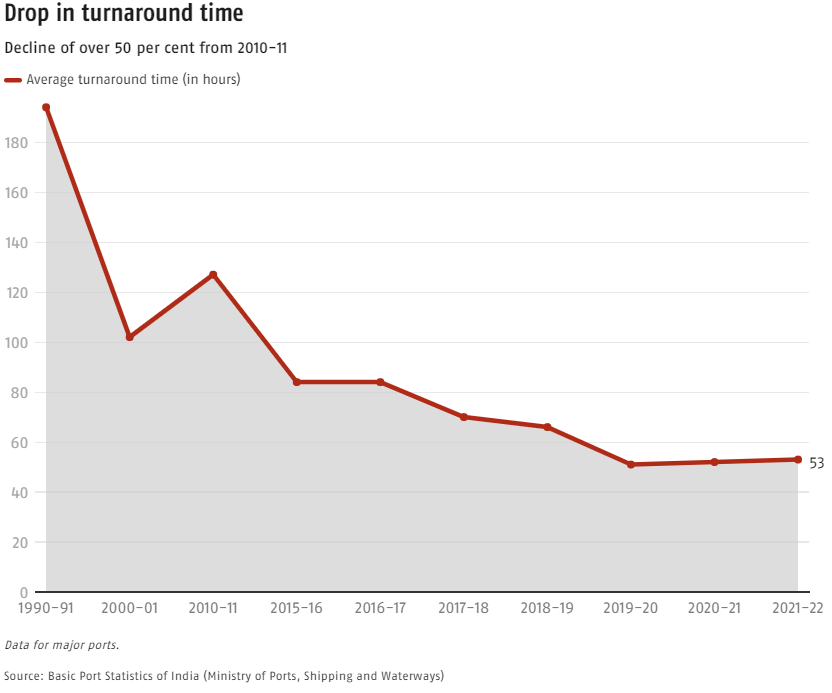
Port Traffic
Government Initiatives and Policies

Roadmap for Improving Efficiency of Major Ports in India
Draft Facility Maintenance
Dredging Policy
Connectivity Enhancement
Operational Efficiency Improvement
Technology Integration
Simplification of Regulatory Regime
Review of Tariff Authority and Regulatory Bodies
Leverage Sagarmala Project
Recommendations by Niti Aayog
Easing Cabotage Restrictions
Eliminating Discriminatory Provisions
Exploring Deep-water Ports and Barges
Facilitating Connectivity with Hinterland Areas
Closing Remarks
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q. Evaluate the current status, challenges, and future prospects of India's ports and shipping industry. Discuss key policy reforms needed to enhance efficiency and competitiveness. Assess the impact of initiatives like the Sagarmala project and public-private partnerships on the sector's development goals. |









© 2025 iasgyan. All right reserved