Description

Disclaimer: Copyright infringement not intended.
Context
- INDUSTRIAL OUTPUT, as measured by the Index of Industrial Production (IIP), slumped to a 26-month low of (-) 4 per cent in October on the back of a contraction in manufacturing and consumer goods, data released by the National Statistical Office (NSO) showed.
- It indicates weak exports and sluggish consumer demand, alongside the continuing weakness of small and medium enterprises.
Findings
- Manufacturing output, which accounts for 77.6 per cent of the weight of the IIP, contracted 5.6 per cent in October as against 3.3 per cent growth in the previous year.
- The maximum decline in output was seen for clothing, electrical equipment, textiles, pharmaceuticals, and leather and related products, with most of these sectors having a large export share and production concentrated in the small and medium enterprises (SMEs) segment.
- The IIP data indicates that the global manufacturing slowdown is also being felt in India, as negative spillovers from a slowing global economy take their toll through both the trade and financial channels.
- A contraction was recorded for capital goods output — a proxy for investment sentiment — after a gap of nine months at (-) 2.3 per cent, indicating weak investment.
- Consumer durables and consumer non-durables output — an indicator of fast-moving consumer goods — also continued to be in negative territory at (-) 15.3 per cent and (-) 13.4 per cent, respectively, reflecting weak consumption demand, especially in rural areas.
Index of Industrial Production
- The Index of Industrial Production (IIP) is an index which shows the growth rates in different industry groups of the economy in a stipulated period of time.
- More formally, it chooses a basket of industrial products — ranging from the manufacturing sector to mining to energy, creates an index by giving different weight to each sector and then tracks the production every month.
- Finally, the index value is compared to the value it had in the same month last yearto figure out the economy’s industrial health.
- The IIP number measures the industrial production for the period under review, usually a month, as against the reference period.
.jpg)
Who releases Index of Industrial Production or IIP data?
- The IIP is estimated and published on a monthly basis by the Central Statistical Organisation (CSO).
- As an all India index, it gives general level of industrial activity in the economy.
IIP base year/ Reference Period
- The IIP base year was changed to 2011-12 from 2004-05 in the year 2017.
- The earlier base years were 1937, 1946, 1951, 1956, 1960, 1970, 1980-81, 1993-94 and 2004-05.
Where is IIP data sourced from?
- The CSO uses secondary data to reach the monthly IIP number.
- The data is sourced from various agencies in different ministries or departments of the government.
- The Department of Industrial Policy and Promotion (DIPP)is the source for the major chunk of data for the calculation.
Who uses IIP data?
- The factory production data (IIP) is used by various government agencies such as the Ministry of Finance, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), private firms and analysts, among others for analytical purposes.
- The data is also used to compile the Gross Value Added (GVA) of the manufacturing sector in the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) on a quarterly basis.
Calculation of IIP:
IIP is a composite indicator that measures the growth rate of industry groups classified under,
- Broad sectors,namely, Mining, Manufacturing and Electricity
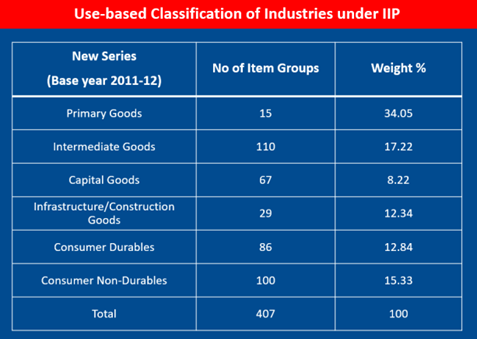
- Use-based sectors, namely Primary/Basic Goods, Capital Goods, Intermediate Goods, Consumer durables etc.
Core Industries in IIP
- The main or the key industriesconstitute the core sectors of an economy.
- In India, there are eight sectors that are considered the core sectors.
- The eight industries have a combined share of 40.27 per cent in the Index of Industrial Production (IIP),which gives the growth rates of different industry groups in a specified period.
- The eight-core sectors of the Indian economy are electricity, steel, refinery products, crude oil, coal, cement, natural gas and fertilizers.
- These sectors have a major impact on the Indian economy and significantly affect most other industriesas well.
- The Office of Economic Adviser, Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Tradereleases Index of Eight Core Industries (ICI).
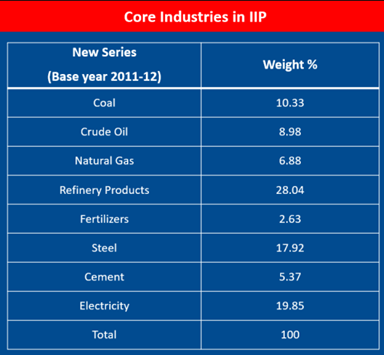
The Eight Core Industries in decreasing order of their Weightage:
Refinery Products> Electricity> Steel> Coal> Crude Oil> Natural Gas> Cement> Fertilizers
.jpg)
https://indianexpress.com/article/business/economy/industrial-output-hits-26-month-low-retail-inflation-silver-lining-8320928/#:~:text=The%20index%20was%20recorded%20at,growth%20in%20the%20previous%20year.






.jpg)











